
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Lipolysis of triglycerides in adipose tissue
The triglycerides deposited in adipose tissue are hydrolyzed by tissue lipases (triglyceride lipase, diglyceride lipase, monoglyceride lipase) into glycerine and free fatty acids.
The velocity of lipolysis of triglycerides changes under the influence of hormones, in stress, physical exercise, starvation, cooling. Under the influence of hormones (adrenaline, noradrenaline, glucagon) with participation of adenylate cyclase messenger system triglyceride lipase is activated by phosphorylation.
Fatty acids formed during lipolysis can pass from fat depots into blood plasma and be used by tissues and organs as an energy material. Fatty acids are transported as a complex with blood serum albumines. In tissues the complex breaks down, and fatty acids are exposed to β-oxidation. Partially they can be used for synthesis of lipids and cholesterol ethers.
Fatty acids oxidation
It occurs basically in the liver, kidneys, skeletal and heart muscles, in adipose tissues.
1. Fatty acid (FA) activation. It occurs in cytisole.
 R–COOH + HS-CoA + ATP R–CO–S-CoA+AMP+PP1
R–COOH + HS-CoA + ATP R–CO–S-CoA+AMP+PP1
fatty acid Acyl-CoA-synthetase
Transport of FA inside mitochondrion.
|
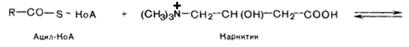

Acylcarnitine
Acylcarnitine from cytoplasm diffuses through mitochondrion membrane. Enzyme iscytoplasm carnitine-acyl transferase. Then the reverse reaction starts - splitting of acylcarnitine with the assistance of HS-CoA and mitochondrion carnitine-acyl transferase:
acylcarnitine + ÍSCîÀ® acyl-CîÀ + carnitine
It is believed to be the rate-limiting step in fatty acid oxidation.
3. Inside the mitochondrial matrix, fatty acids undergo β-oxidation.
A) dehydrogenation
|
|
|

There are three FAD-depending acyl-CoA-dehydrogenases, preferring short, medium and long-chain acyl radical.
B) hydration
|
|


|
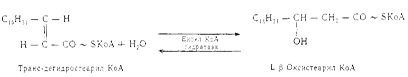
Hydration is stereospecific. L-isomer is formed.
Date: 2016-04-22; view: 1147
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Digestion and absorption of fats | | | Acetyl-CoA metabolism |