
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Uczelnia Łazarskiego Fall 2011
Economic integration and globalisation as natural phenomenon of development?
Globalisation – Definition
Globalisation – the increased global sourcing of goods and services, global flow of capital and importantly labour /Gordon Brown/
Globalisation describes the parallel emergence of three new forces:
The first is the information and communication revolution
The second is the world wide movement from the planned economies to market economies and from self-reliance to integration within the global economy
The third is the entry to the world economy of vast new sources of hard working and highly motivated but cheap labour
/Martin Wolf, Financial Times/
• Determinants of globalisation:
• Technological revolution
• Easing of barriers to international trade
• Freedom of labour movement
• Gold standard system
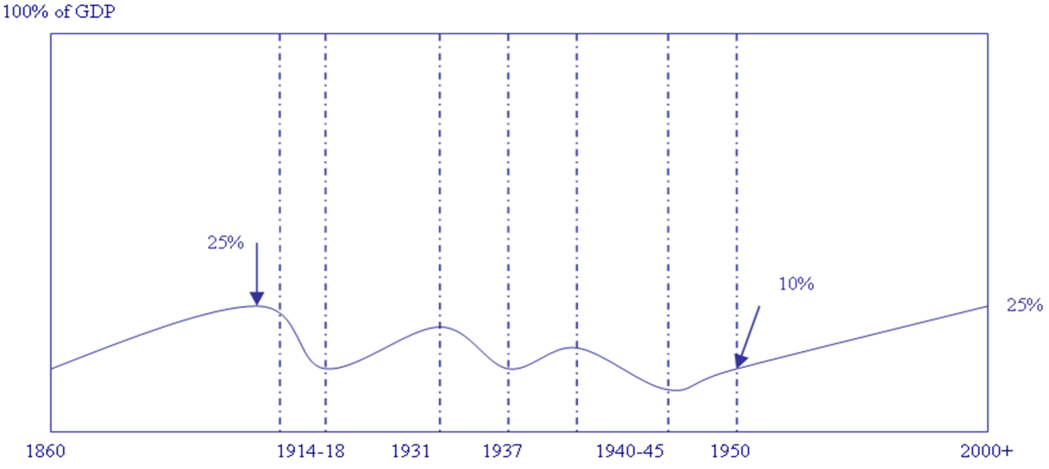
Rapid economic growth
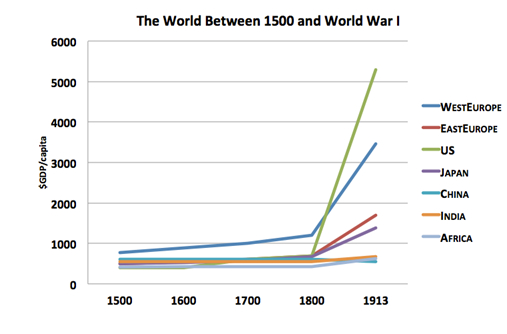

Technological revolution
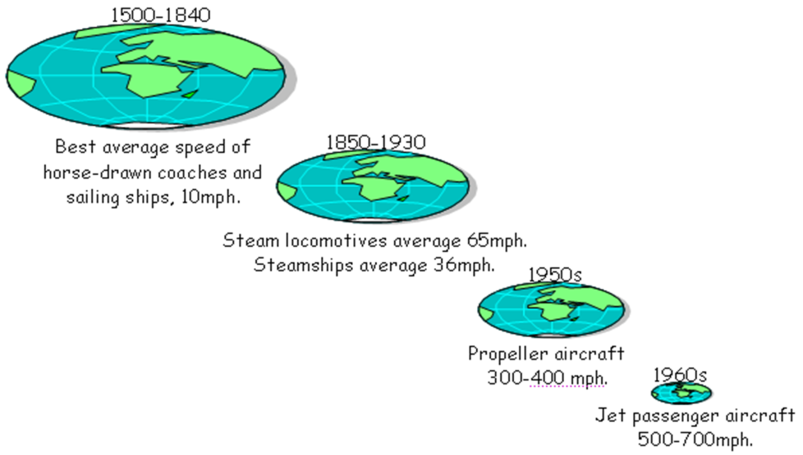
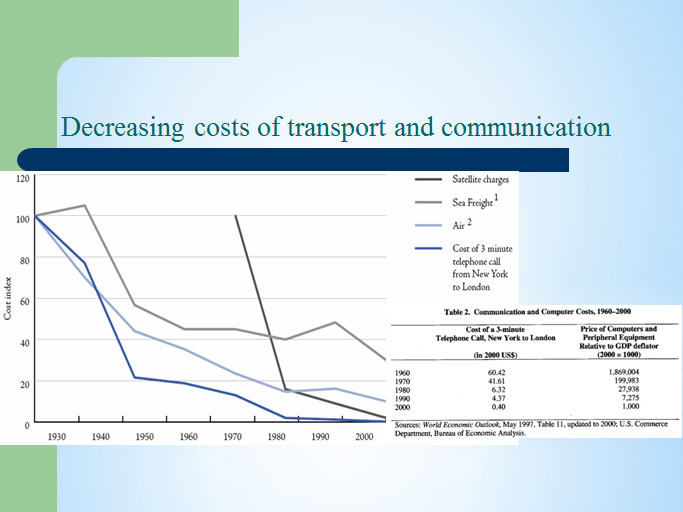
* Decreasing costs of transportation and communication due to technological developments
* Steamships became more and more important compared to sailing ships, hence decreased time of delivery
* Emergence of railroads networks
* Faster transmission of information due appearance of telegraphs as opposed to regular mail
“Shrinking globe” phenomenon
* “Most favoured nation treatment” introduced by the UK. It established the sovereign equality of states with respect to trading policy.
* Gradual reduction of barriers to trade as well as better protection of property rights
* Decline in barriers to trade of manufacturing products at first
* There was a free labour movement among the countries since people had no passports, except for Russia and Turkey
* Shift from agricultural to industrialised manufacturing sector that was in need of more people
* In 1891 Publication of Pope Leo XIII's foundational document, Rerum Novarum, also known as "On the Condition of the Working Classes“ that advocated workers’ rights, minimum wage, length of work day
* The idea behind that system was to convert paper currency into gold on demand of fixed exchange rate
* Exchange rate was based on parity and the currency costed more if had more gold in its reserves
* It brought balance-off-trade equilibrium for all countries and reduced uncertainty in trade, hence accelerating it
Stages of economic integration
• Free trade area
• Customs union
• Common market
• Currency area
• Political union
Date: 2015-01-11; view: 1146
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Adding the biomedical model to indigenous beliefs. | | | Gold standard |