
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
III. ENVIRONMENTAL OBJECTIVES
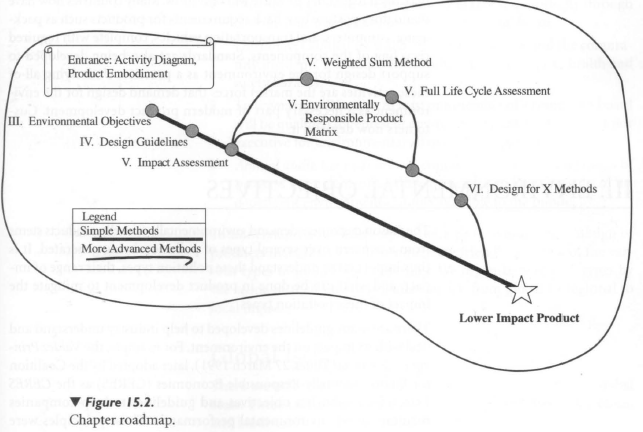
I. CHAPTER ROAD MAP
Figure 15.2 diagrams this chapter roadmap.
II. WHY DFE?
Design for the environment is an important activity for a design team because environmental damage is, as are most things, greatly influenced in the early design phases. Just as with production cost, a reasonable heuristic is that 80% of the environmental damage of a product is established after 20% of the design activity is complete. From a business case analysis viewpoint, the reasons a design team should choose to complete design for the environment studies is that modern customers are now demanding products with less environmental impact.
III. ENVIRONMENTAL OBJECTIVES
The reason customers demand environmentally friendly products stems from a concern over several types of pollution being generated. It is thus important to understand these pollution types, their range of impact, and what can be done in product development to mitigate the impact of these pollution types. There are many guidelines developed to help industry understand and deal with its impact on the environment. For example, the Valdez Principles (Financial Times, 27 March 1991)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I4YNelnCOZ4
later adopted by the Coalition for Environmentally Responsible Economies (CERES) as the CERES http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bOgLK1qCq5E
principles, establishes objectives and guidelines to help companies maintain good environmental
performance. These principles were adopted by the Exxon Corporation after the Exxon Valdez oil spill (March 24, 1989) and later adopted by hundreds of companies, including ITT Industries, Polaroid Corporation, General Motors Corporation, and many others. The content includes:
• Protect the biosphere: Companies will minimize the release of pollutants that endanger the earth.
• Sustainable use of resources: Companies will use raw materials at a level where they can be sustained.
• Reduction and disposal of waste: Companies will minimize waste wherever possible. When waste cannot be avoided, recycling will be adopted.
• Wise use of energy: Companies will use environmentally safe energy and invest in energy conservation.
• Risk reduction: Companies will minimize health risk to employees and the community.
• Marketing of safe products and services: Companies will sell products that minimize environmental impact and are safe for consumers to use.
• Damage compensation: Companies will take responsibility through
cleanup and compensation for environmental harm.
• Disclosure: Companies will disclose to employees and the community incidents that cause environmental harm or pose health and safety hazards.
• Environmental Directors: At least one member of a company's board will be qualified to represent environmental interests, and a senior executive for environmental affairs will be appointed.
• Annual audit: Companies will conduct annual self-evaluations of progress in implementing these principles and make results of independent environmental audits available to the public.
Global Issues
There are pollution problems whose manifestations exist on a global scale. These include concerns over climate change, ozone depletion, and biodiversity loss Climate change is a concern over the probable consequences of possible large changes in the Earth's climate due to increases in greenhouse gases.
Another global pollution concern is the depletion of the ozone layer.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XLY8m-dXOxo
Date: 2016-03-03; view: 1227
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Manufacturing Cost Analysis | | | Regional and Local Issues |