
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Output: Summary
The results of processing are output as hard copy (printed) or soft copy (displayed on a screen or played as sounds).
Printers have different features to consider such as the kind of paper used, color printing or not, the speed of printing, the quality of print, the kind of cable needed to connect to the computer, the number of ink or toner cartridges, and the physical size compared to where you want to put it. Color printers use CMYK colors: cyan, magenta, yellow, and black.
Impact printers are still used for multi-copy forms but sheet printers (laser or ink jet) have taken over most of the market otherwise.
LCD monitors are standard now with thin screens that take much less space than CRT monitors. Colors are created using just 3 colors in subcells, red, green, and blue. The eye blends these together to make millions of colors.
Other output devices include projectors for presentations, 3D printing of objects, microfilm, speakers, medical devices like EEG and EKG recordings, and scientific devices like seismographs.
Output: Quiz
For each question, click on  the radio button beside your answer. You will be notified immediately whether your choice is correct or not. Double clicking may work better.
the radio button beside your answer. You will be notified immediately whether your choice is correct or not. Double clicking may work better.
Top of Form
1. When a computer prints a report, this output is called_____.
 hard copy
hard copy
 soft copy
soft copy
 COM
COM
 none of the above
none of the above
2. Output which is made up of pictures, sounds, and video is called_____.
 COM
COM
 hard copy
hard copy
 graphics
graphics
 multimedia
multimedia
3. An impact printer _____.
 is loud
is loud
 has a mechanism somewhat similar to a typewriter
has a mechanism somewhat similar to a typewriter
 can use multipart paper
can use multipart paper
 all of the above
all of the above
4. A dot-matrix printer uses ____ to form the letters.
 bars
bars
 codes
codes
 pins
pins
 laser
laser
5. For a test print of a newly created document, you should use____ quality print.
 letter
letter
 near letter
near letter
 draft
draft
 outline
outline
6. A laser printer is an example of a _____ printer.
 dot-matrix
dot-matrix
 continuous-form
continuous-form
 chain
chain
 nonimpact
nonimpact
7. An individual dot on a computer screen is called a(n)_____.
 character
character
 screen point
screen point
 font
font
 pixel
pixel
8. A screen which can only display white letters on a blue background is a _____ monitor.
 monochrome
monochrome
 CGA
CGA
 EGA
EGA
 VGA
VGA
9. Which of the following is not an output device?
 pen plotter
pen plotter
 data projector
data projector
 dot-matrix printer
dot-matrix printer
 keyboard
keyboard
10. The speed of a printer can be measured in_____.
 ppm
ppm
 lps
lps
 pps
pps
 none of the above
none of the above
Storage: Intro
What is Storage?
| Input Processing Output Storage | 
|
Storage refers to the media and methods used to keep information available for later use. Some things will be needed right away while other won't be needed for extended periods of time. So different methods are appropriate for different uses.
Earlier when learning about processing, we saw all the kinds of things that are stored in Main Memory.
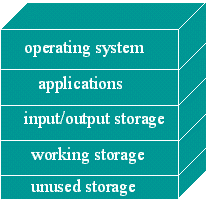
Main Memory = Primary Storage
Main memory keeps track of what is currently being processed. It's volatile, meaning that turning the power off erases all of the data.
For Main Memory, computers use RAM, or Random Access Memory. These memory chips are the fastest, but most expensive, type of storage.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
 Auxiliary Storage = Secondary Storage
Auxiliary Storage = Secondary Storage
Auxiliary storage holds what is not currently being processed. This is the stuff that is "filed away", but is ready to be pulled out when needed.
It is nonvolatile, meaning that turning the power off does not erase it.
Auxiliary Storage is used for:
- Input - data and programs
- Output - saving the results of processing
So, Auxiliary Storage is where you put last year's tax info, addresses for old customers, programs you may or may not ever use, data you entered yesterday - everything that is not being used right now.
Storage: Magnetic Disks
Of the various types of Auxiliary Storage, the types used most often involve some type of magnetic disk. These come in various sizes and materials, as we shall see. This method uses magnetism to store the data on a magnetic surface.
| Advantages: |
|
A drive spins the disk very quickly underneath a read/write head, which does what its name says. It reads data from a disk and writes data to a disk. (A name that actually makes sense!)
Types of Magnetic Disks
Hard Disks

Credit: Western Digital
A hard disk consists of 1 or more metal platters which are sealed inside a case. The metal is one which is magnetic. The hard disk is usually installed inside the computer's case, though there are removable and cartridge types, also.
Technically the hard drive is what controls the motion of the hard disks which contain the data. But most people use "hard disk" and "hard drive" interchangeably. They don't make that mistake for floppy disks and floppy drives, described below. It is clearer with floppies that the drive and the disk are separate things.
Diskette / Floppy Disk (extinct?)
Both sizes are seem to be extinct in work places. The only remaining flocks of such disks are hiding among the dust balls in back storage closets, waiting for someone to decide what to do with them.
Sizes:
5¼" (really ancient stuff) 
| 3½" (just horribly old) 
|
Both sizes are made of mylar with an oxide coating. The oxide provides the magnetic quality for the disk. The "floppy" part is what is inside the diskette covers - a very floppy piece of plastic (i.e. the mylar).
 Other Removable Magnetic Media
Other Removable Magnetic Media
Several other kinds of removable magnetic media are in use, such as the Zip disk. All of these have a much higher capacity than floppy disks.
Each type of media requires its own drive. The drives and disks are much more expensive than floppy drives and disks, but then, you are getting much larger capacities.
There are other kinds of storage devices that are not magnetic, such as flash drives and optical discs (CD and DVD) or that are not disks, such as magnetic tape. These will be discussed later.
Care of Hard Disks
To keep your hard disk happy and healthy you must observe a few precautions. Each medium has its own particular weaknesses and hazards to avoid. Be careful or suffer the consequences - lost data, which means, at best, lots of lost time and effort!
| Don't |  Jar the computer while the disk is spinning. Jar the computer while the disk is spinning.
|  Turn the computer off and quickly back on before spinning has stopped. Turn the computer off and quickly back on before spinning has stopped.
|  Drop it - ever. Drop it - ever.
|
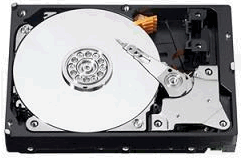
Credit: Western Digital
Hard disks are protected by being sealed in air-tight cases. But when damage does occur, it is a more serious matter that with removable media. Larger amounts of data can be lost and hard disks are much, much more expensive that removable disks.
Hard disks can have problems from magnetic fields and heat, but these are rare.
Most problems occur when the read/write head (looks like a pointer in the photo) damages the metal disk by hitting or even just touching it. This is called a head crash.
 When the computer is on, the hard disk is spinning extremely fast. Any contact at all can cause pits or scratches. Every scratch or pit is lost data. Damage in the root directory turns the whole hard disk into a lovely doorstop! It's completely dead.
When the computer is on, the hard disk is spinning extremely fast. Any contact at all can cause pits or scratches. Every scratch or pit is lost data. Damage in the root directory turns the whole hard disk into a lovely doorstop! It's completely dead.
So the goal here is to keep that read/write head where it belongs, just barely above the hard disk, but never, ever touching it.
Storage: Disk Format
All magnetic disks are similarly formatted, or divided into areas, called
tracks
sectors
cylinders
The formatting process sets up a method of assigning addresses to the different areas. It also sets up an area for keeping the list of addresses. Without formatting there would be no way to know what data went with what. It would be like a library where the pages were not in books, but were scattered around on the shelves and tables and floors. You'd have a hard time getting a book together. A formatting method allows you to efficiently use the space while still being able to find things.
Tracks
| A track is a circular ring on one side of the disk. Each track has a number. The diagram shows 3 tracks. | 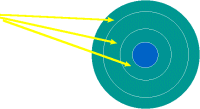
|
Sectors
| A disk sector is a wedge-shape piece of the disk, shown in yellow. Each sector is numbered. On a 5¼" disk there are 40 tracks with 9 sectors each. On a 3½" disk there are 80 tracks with 9 sectors each. So a 3½" disk has twice as many named places on it as a 5¼" disk. | 
|
| A track sector is the area of intersection of a track and a sector, shown in yellow. | 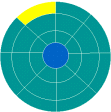
|
Clusters
| A cluster is a set of track sectors, ranging from 2 to 32 or more, depending on the formatting scheme in use. The most common formatting scheme for PCs sets the number of track sectors in a cluster based on the capacity of the disk. A 1.2 gig hard drive will have clusters twice as large as a 500 MB hard drive. 1 cluster is the minimum space used by any read or write. So there is often a lot of slack space, unused space, in the cluster beyond the data stored there. There are some new schemes out that reduce this problem, but it will never go away entirely. The only way to reduce the amount of slack space is to reduce the size of a cluster by changing the method of formatting. You could have more tracks on the disk, or else more sectors on a track, or you could reduce the number of track sectors in a cluster. | 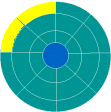
|
Cylinders
| A cylinder is a set of matched tracks. | |
| On a double-sided floppy, a track from the top surface and the same # track from the bottom surface of the disk make up a cylinder. The concept is not particularly useful for floppies. | 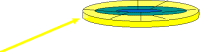
|
| On a hard disk, a cylinder is made of all the tracks of the same # from all the metal disks that make up the "hard disk". If you put these all together on top of each other, you'd have something that looks like a tin can with no top or bottom - a cylinder. | 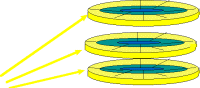
|
| The computer keeps track of what it has put where on a disk by remembering the addresses of all the sectors used, which would mean remembering some combination of the cylinder, track, and sector. Thank goodness we don't have to remember all these numbers! Where the difference between addressing methods shows up is in the time it takes for the read/write head to get into the right position. The cylinder method writes data down the disks on the same cylinder. This works faster because each metal platter has a read/write head for each side and they all move together. So for one position of the read/write heads, the computer can put some data on all the platters before having to move the heads to a new position. |
What happens when a disk is formatted?
| 1. | All data is erased. Don't forget this!! | 
|
| 2. | Surfaces are checked for physical and magnetic defects. | 
|
| 3. | A root directory is created to list where things are on the disk. | 
|
Storage: Disk Capacity
The capacity of a magnetic disk depends on several factors.
We always want the highest amount of data stored in the least possible space. (People are so greedy this way!) So the capacities of storage media keep increasing while cost keeps decreasing. It's a lovely situation for the user!
Capacity of a Disk depends on:
| 1. # of sides used: | |
single-sided

| double-sided

|
2. Recording density -
how close together the bits can be on a track sector of the innermost track

| |
3. # of tracks on the disk

|
Capacity of Disks

| 5¼" floppy | - 360 KB or 1.2 MB | |||||

| 3½" floppy | - 720 KB or 1.44 MB | |||||

|
|
The future???
Advances in technology for the read/write head and for the densities on the disks are bringing larger and larger disk capacities for about the same price. In fact, you cannot find a small capacity drive to buy, even if you wanted one! 2 TB drives are plentiful (July 2010) and for the same price that we used to buy 1 Gig drives (under $200). It's enough to make you cry to think of what we paid over the years and what we could get for those dollars today. Ah, well. That's the way the computer world works!
Date: 2015-01-11; view: 1564
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Types of Non-Impact Printers | | | Storage: Accessing Data |