
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY
Actuality. The major focus of the clinical microbiology is to isolate and identify microorganism from clinical specimens rapidly. The purpose of the clinical microbiology laboratory is to provide the physician with information concerning the presents or absents of microorganisms that may be involved in the infectious disease process. These individuals and facilities also determine the susceptibility of microorganisms to antimicrobial agents. Clinical microbiology makes use of information obtained from research on such diverse topics as microbial biochemistry and physiology, immunology, molecular biology, genomics, and the host parasite relationships involved in the infectious disease process.
Primary objectives: be able to conduct and evaluate the microbiological diagnostics of the hospital infections.
QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSION
1. The determination, the aims and the tasks of the Clinical Microbiology.
2. Non-pathogenic microorganisms are the causative agents of the opportunistic infections.
3. The determination, conditions of arising of the opportunistic infections, mixinfections, dysbacteriosis and its features. Heterogeneity of the bacteria’s population is.
4. The determination of the hospital infections, its classification and conditions that are promoting its arising.
PROCEDURE OF PRACTICAL SESSION
Task 1. To study the smears from patients material.
Task 2. To study the growth of the Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Klebsiellla pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosae, Escherichia coli.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICAL WORK
Task 1.
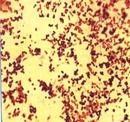 In the smear from the pus Staphylococcus are circum violet microorganisms that please in accumulation as bunch of the grapes.
In the smear from the pus Staphylococcus are circum violet microorganisms that please in accumulation as bunch of the grapes.
 Streptococcus pyogenes in the blood isspherical or ovoid violet cocci that are arranged in chains in the smear.
Streptococcus pyogenes in the blood isspherical or ovoid violet cocci that are arranged in chains in the smear.
 When we studyKlebsiella pneumonia staied by Burri-Ginse in the smear we see colorless capsule and pink cytoplasm on dark field.
When we studyKlebsiella pneumonia staied by Burri-Ginse in the smear we see colorless capsule and pink cytoplasm on dark field.

Pseudomonas aeruginosain the smear is Gram-negative rods that are one by one.
Task 2.
 Staphylococcus aureus on the EYA forms middle, convex, opaque, homogeneous, gold, white or yellow colony. On the EYA growth another bacteria is inhibiting. A ring of the dimness forms a round of the Staphylococcus colony because it is producing enzyme lecitinase.
Staphylococcus aureus on the EYA forms middle, convex, opaque, homogeneous, gold, white or yellow colony. On the EYA growth another bacteria is inhibiting. A ring of the dimness forms a round of the Staphylococcus colony because it is producing enzyme lecitinase.
 Streptococcus pyogeneson the blood agar forms the white or grey discoid colonies, usually 1-2 mm in diameter with hemolysis aroud.
Streptococcus pyogeneson the blood agar forms the white or grey discoid colonies, usually 1-2 mm in diameter with hemolysis aroud.
 Klebsiellla pneumoniae on the Ploskirev’s agar formsLac negative colonies.
Klebsiellla pneumoniae on the Ploskirev’s agar formsLac negative colonies.

Pseudomonas aeruginos on the ĚPŔ forms circum, dry or smooth (in capsulare strains) colony. The culture of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa has specific smell, like a jasmine or strawberry soap.
 Escherichia coli on the Endo forms Lac posetive colonies. It is red convex smooth with iridescent sheen.
Escherichia coli on the Endo forms Lac posetive colonies. It is red convex smooth with iridescent sheen.
Addition 1
Date: 2016-01-14; view: 1706
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Sanitary-microbiological research of water, air, soil, food products and objects of external environmental | | | Clinical microbiology |