
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
English in the Germanic group of languages and in the Indo-European family. The English language in the world.
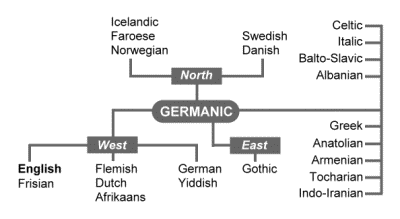
Languages can be classified according to different principles. The historical, or genealogical classification, groups languages in accordance with their origin from a common linguistic ancestor. Genetically, English belongs to the Germanic or Teutonic group of languages, which is one of the twelve groups of the IE linguistic family. 2 groups of 12 nowadays are dead. Indo-European family: 1,2,3,4 Hellic of Greek , 5 Albanian 6 Italic ( later Romance languages ) 7. Germanic, 8. Baltic, 9. Celtic, 10. Gallic, 11. Old Prusian 12. Slavonic. The migration of Germanic tribes to the British Isles and the resulting separation from the Germanic tribes from the mainland was a decisive event in their linguistic history. Being cut off from related OG tongues the closely related group of West Germanic dialect developed into a separate Germanic language, English. That is why The Germanic settlement of Britain can be regarded as the beginning of the independent history of the English language. Most of the area of Europe and large parts of other continents are occupied today by the IE languages, Germanic being one of their major groups. All the Germanic languages are related through their common origin and point development at the early stages of history. There are 250-300 million people who have English as their mother tongue. The total number of people speaking Germanic languages approaches 440 million. Over 50 countries use English as an official language.
Practical task
· Find the traces of strong and weak verbs in the text and explain their evolution from a historical point of view.
Card#29(1)
· Trace the history of the word “first” from a historical point of view. (vocalization of “R”first[first] i+r(ME)→[fә:st] ә: (NE))
Our knowledge of the Celts is slight. As with previous groups of settlers, we do not even know for certain whether the Celts invaded Britain or came peacefully as a result of the lively trade with Europe from about 750 BC onwards. At first most of Celtic Britain seems to have developed in a generally similar way. But from about 500 BC trade contact with Europe declined, and regional differences between northwest and southeast Britain increased. The Celts were organized into different tribes, and tribal chiefs were chosen from each family or tribe, sometimes as the result of fighting matches between individuals, and sometimes by election.
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 3342