
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Define comparison logics LTL and CTL. Difference LTL and CTL. Verification problem of Model Checking
LTL


Language of formal logic has: syntax (the rule of creation of formulas) and semantics (the rule defining truthconditional value of formulas)

CTL Syntax
} Basic logic AND
} Temporal expressions:
◦ Temporal operators are defined in pairs
◦ Path part:
– A: means “all paths” (inevitably)
– E: means “on some path” (possibly)
◦ Property part:
– F : same as <> For some
– G : same as [ ] Globally holds
– X : same as X neXt
– U : same as U Until
} Sample expressions:
– AGp : On all paths, property p always holds
– EGp : On some paths, property p always holds
Temporal logicians of the branching time consider possible calculations (ways on a tree) - trajectories on development of structure of Kripke of CTL * – Computational Tree Logic * is one of possible the logician branching times

Comparison
1. Formulas these two logician characterize properties of different objects of
*-LTL – a formula of a way, CTL – formulas of conditions of
2. Express properties of calculations which are presented differently
*-LTL – a set of behavior, to CTL – trees of behavior
3. Interpreted differently
*formula LTL - on an infinite set of behavior
*formula CTL – on a final set of conditions
4. Methods of algorithms of model checking - absolutely different
5. Expressive power is incomparable: there are formulas CTL, inexpressible in LTL and vice versa
*for example, FGô can't be expressed in CTL (since some time in future ô there will be all the time true) AFAGp stronger, AFEGp – is weaker
*for example, AGEF in CTL can't be expressed in LTL
The algorithm of Model Checking is an algorithm of check of, whether any formula of temporal logic F on any structure of Kripke, model of technical system is carried out.
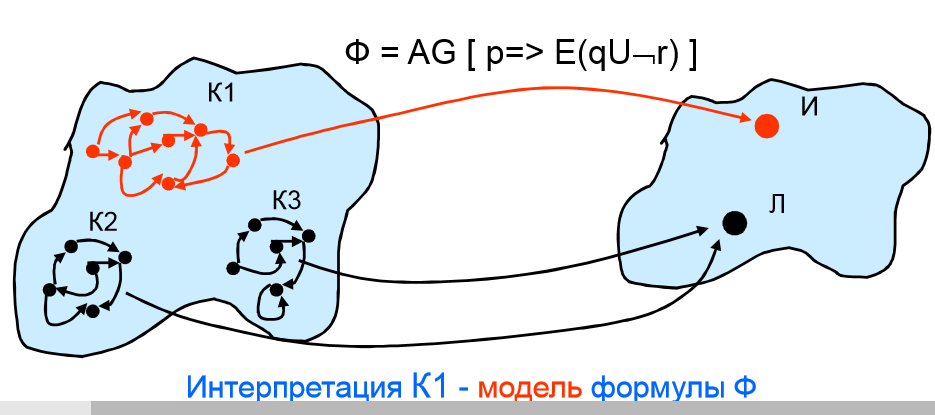
Interpretations F are structures of Kripke, in which each state the set of values of variables p, q, r
Date: 2016-01-03; view: 2231