
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Improving Productivity
 New, more effective, technology makes it possible to extract more metal out of lower grade material, and at a lower cost than earlier generations of miners could achieve. External pressures have also had an impact on the operations of the mining industry, causing it to move in many ways.
New, more effective, technology makes it possible to extract more metal out of lower grade material, and at a lower cost than earlier generations of miners could achieve. External pressures have also had an impact on the operations of the mining industry, causing it to move in many ways.
Intensive cost-cutting is now standard in all companies, while, at the same time, they have been investing in new and more productive equipment. Non-core businesses have been sold off, in order to focus management attention, and many unprofitable mines have been closed down. Mergers and acquisitions have been made, in order to create larger, more cost-effective, and financially stronger entities.
During the first years of the new millennium, the international mining industry has been in the midst of an intensive period of change. Many long-established, well-respected mining companies have disappeared, and new giants are emerging.
Undergroun Mining
Table 1. Total world underground ore production.
| Region | Mt |
| North America 80 | Europe 160 |
| Latin America 105 | Asia 60 |
| Africa 160 | SUM 6 |
| Oceania 50 |
Mining is, to a large extent, about moving enormous amounts underground mining is by nature selective, always trying to take the meat out of the pie while leaving the crust. Open pit mining, on the other hand, takes the whole pie and then separates the meat from the crust.
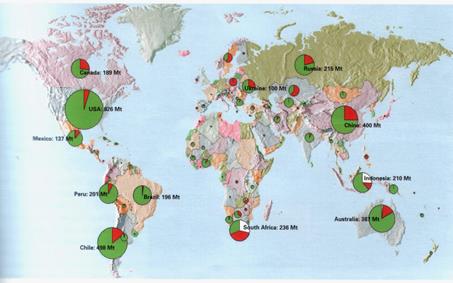
 Each year, around 4,100 Mt of ore containing the most important metals copper, gold, iron ore, lead/zinc, nickel, platinum group metals and diamonds is produced globally. Of this, some 615 Mt is mined underground, for which Table 1 gives the regional split. To support this level of activity, a considerable amount of development work has to be carried out.
Each year, around 4,100 Mt of ore containing the most important metals copper, gold, iron ore, lead/zinc, nickel, platinum group metals and diamonds is produced globally. Of this, some 615 Mt is mined underground, for which Table 1 gives the regional split. To support this level of activity, a considerable amount of development work has to be carried out.
The proportion mined underground equates with some 16% of the total volume of ores extracted. In the centrally planned economies of the eastern bloc, underground mining accounts for 32% of the total activity in the sector, while the figure is 15% in the Western world.
There are 365 underground mines in the Western world, many of which are fairly small, but efficient, operations, hoisting an average of 400,000 t annually. Notwithstanding, many underground mines are huge, with very sophisticated equipment and a high level of automation.
Date: 2015-12-24; view: 904
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Exploration Drilling | | | Volume proportion value developments entities cost-cutting |