
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Costs in the Short Run and in the Long Run
THE DEADWEIGHT LOSS OF TAXATION
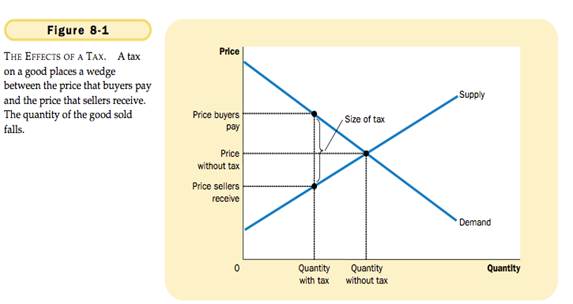
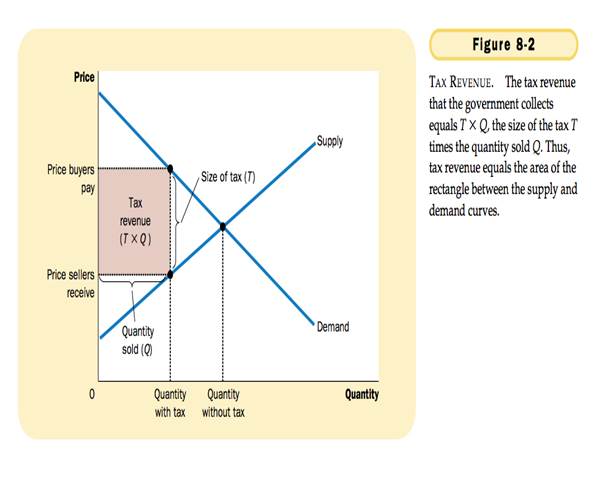
HOW TAX AFFECT WELFARE
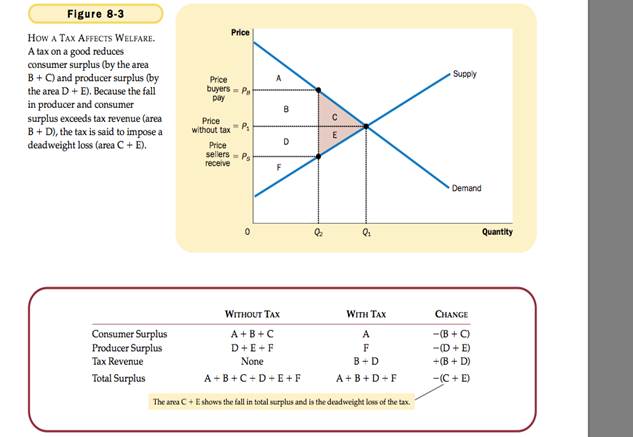
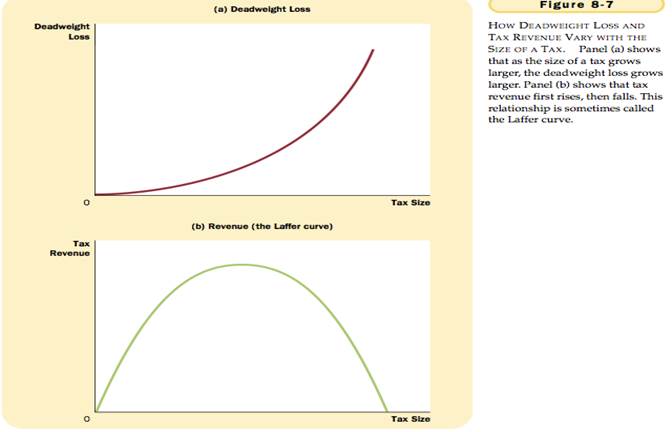
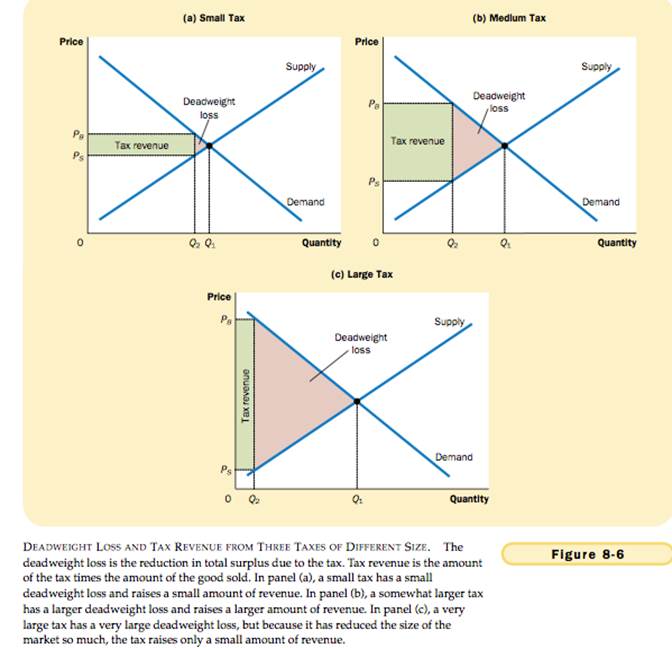
Deadweight Loss - the fall in total surplus that results from a market distortion, such as a tax
DEADWEIGHT LOSSES AND GAINS FROM TRADE

THE DETERMINANTS OF THE DEADWEIGHT LOSS
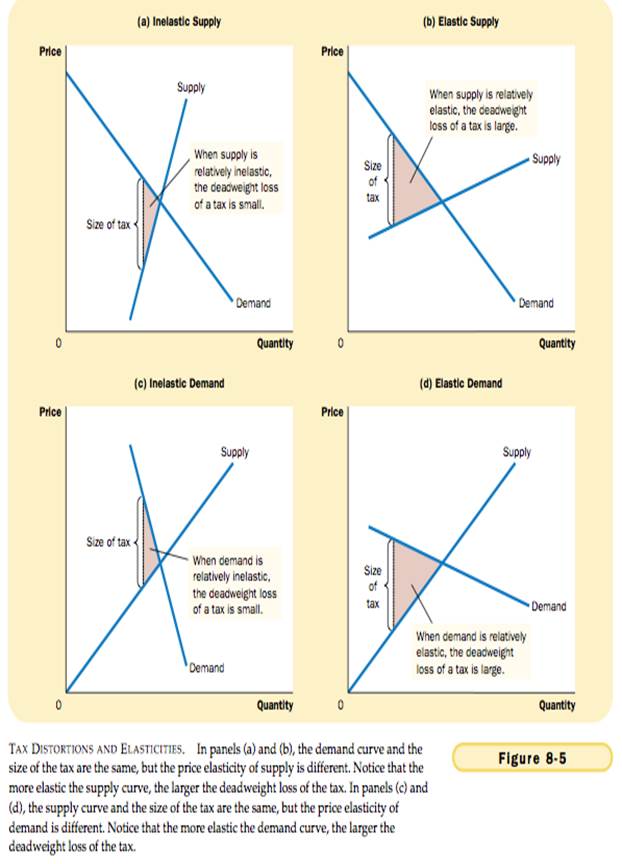
DEADWEIGHT LOSS AND TAX REVENUE AS TAXES VARY
CHAPTER 13
Total Revenue – the amount a firm receives for the sale of its output.
Total Cost – the market value of the inputs a firm uses in production.
Profit – total revenue – total cost.
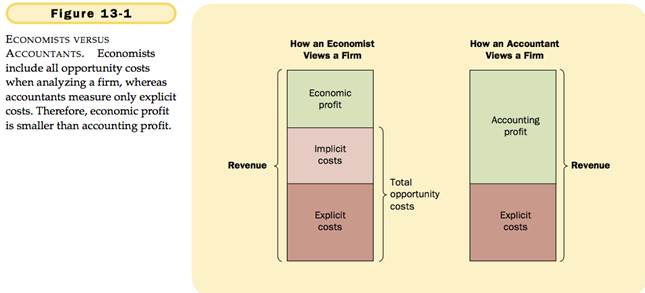
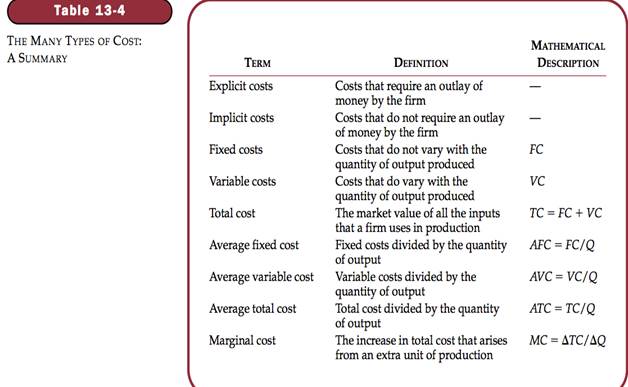
Explicit costs – Input costs that require an outlay of money by the firm.
Implicit costs – input costs that do not require an outlay of money by the firm.
Economic Profit – total revenue minus total cost, including both ixplicit and implicit costs.
Accounting profit – total revenue minus toal explicit cost.
ECONOMIC PROFIT VS ACCOUNTING PROFIT
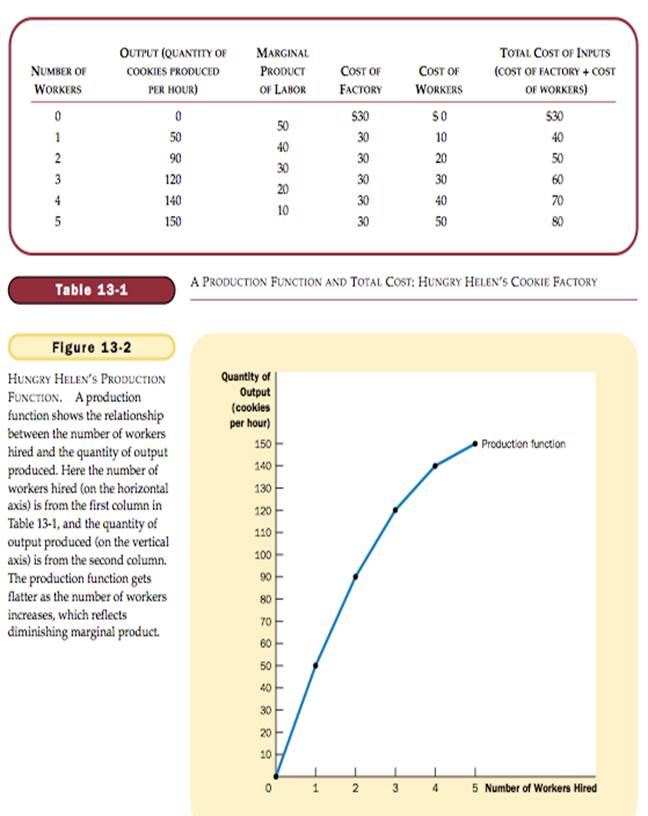
Production Function – the relationship between quantity of inputs used to make a good and the quantity of output of that good.
Margianal Product – the increase in output that arises from an additional unit of input.
Diminishing Marginal Product – the property whereby the marginal product of an input declines as the quantity of the input increases.
THE PRODUCTION FUNCTION
TOTAL COST CURVE
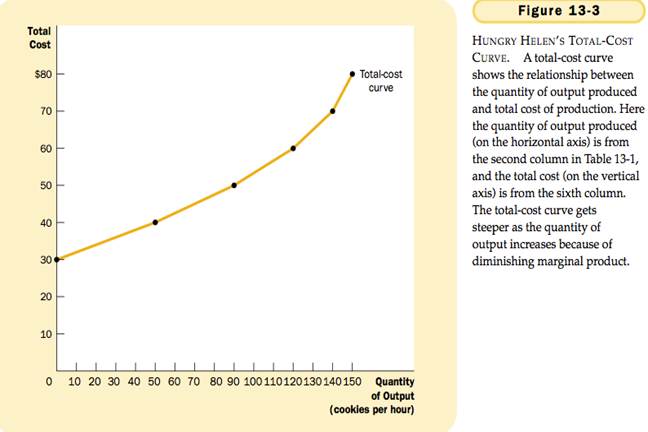
Fixed Costs – costs that do not vary with the quantity of output produces.
Variable Costs – costs that vary with the quantity of output produced.
Average Total Cost – total cost divided by the quantity of output.
Average fixed Cost – fixed costs divided by the quantity of output.
Average Variable Cost – variable cost divided by the quantity of output.
Marginal Cost – the increase in total cost that arises from an extra unit of production. Change(delta) in TC divided by the delta in quantity.
TYPICAL COST CURVES


Costs in the Short Run and in the Long Run
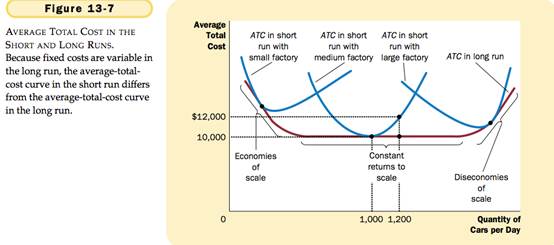
Economies of Scale – the property whereby long-run average total cost falls as the quantity of output increases.
Diseconomies of Scale– the property whereby long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output increases.
Constant Return to Scale – the property whereby long-run average total cost stays the same as the quantity of output changes.
CHAPTER 14
Date: 2015-12-24; view: 2066
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Answer Key – Unit 5 | | | True or false: A firm should always produce at an output at which long-run average cost is minimized. Explain. |