
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Price of Good A Income of Good A Quantity demanded
Figure 2
4. Which of the graphs shown in Figure 2 correctly demonstrate the concept of increasing opportunity cost?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
5. If a legal price ceiling is established on a good above the existing equilibrium price, the effect would be to:
A. Raise the price of the good and lower the quantity purchased
B. Have no effect on the price or quantity of the good
C. Lower the price of the good and lower the quantity purchased
D. Raise the price of the good and raise the quantity purchased
E. Lower the price of the good and increase the quantity purchased
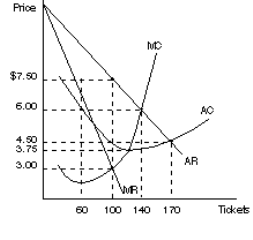
Figure 3
6. Chasey Company Inc. is the only producer in a small town. Cost and revenue information for the Chasey Company are shown in Figure 3. Chasey Company would set the price of its product at;
A. $7.50
B. $6.00
C. $4.50
D. $3.75
E. $3.00
7. In Figure 3 the Chasey Company would maximize profits by producing a quantity of;
A. 60
B. 100
C. 120
D. 140
E. 170
8. In Figure 3 the Chasey Company will make a profit of _______;
A. $750
B. $450
C. $300
D. $150
E. $150 loss
Figure 4
Number of workersOutput
0 0
1 5
2 11
3 19
4 25
5 29
6 31
7 31
8 30
9. Figure 4 represents production data for a perfectly competitive firm. Based on that data, the marginal physical product of the 4th worker is;
A. 4
B. 6
C. 8
D. 25
E. 60
10. In Figure 4 the ďlaw of diminishing returnsĒ sets in with the addition of the _____ worker.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 7
E. 8
11. Using the data in Figure 4, if workers are paid $35 and the product being produced sells for $10, how many workers would the Chasey Company hire?
A. 1
B. 4
C. 5
D. 7
E. 8

Figure 5
12. The profit-maximizing price for a perfectly competitive firm like the one shown in Figure 5 in the long run would be;
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
13. In Figure 5 at a market price of A, the profit-maximizing output for a perfectly competitive firm is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
14. Which of the following correctly describes the profit maximizing position for all firms regardless of the market structure under which they are operating?
A. P = MC
B. P = ATC
C. MR = MC
D. MR = P
E. MR = AR
|

15. Which of the graphs in Figure 6 indicate that a firm can sell any or all of its output at the prevailing market price?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. It is impossible to determine the correct answer to the question from the information given.
Figure 7
Assume that the following information is for Good A.
Price of Good A Income of Good A Quantity demanded
Consumersof Good A
$5.00 $200 20
$4.00 $175 40
$3.00 $150 60
$2.00 $125 90
$1.00 $100 100
16. What would be the effect on total revenue of changing the price from $5.00 to $4.00, based on the information in Figure 7?
A. Increase by $160
B. Increase by $100
C. Increase by $60
D. Decrease by $700
E. Decrease by $300
17. Based on the information in Figure 7 it can be correctly concluded that good A is
A. A normal good
B. An inferior good
C. A Giffen good
D. A good with a positive externality
E. A good with a negative externality
18. In order for resources to be efficiently allocated, what rule must be satisfied?
A. MR=MC
B. P=AC
C. P=MR
D. P=MC
E. P=AR
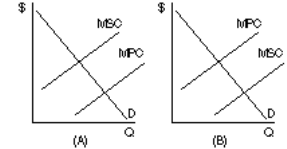
Figure 8
19. Given that MSC is marginal social cost and MPC is marginal private cost, based on the two graphs in Figure 8, it can be correctly concluded that
A. Both graphs demonstrate the existence of externalities
B. Both graphs demonstrate the existence of negative externalities
C. Both graphs demonstrate the existence of positive externalities
D. Graph A demonstrates inefficiency through underproduction
E. Graph B demonstrates inefficiency through overproduction
20. If a natural disaster occurs that adversely affects production and shipping,
A. the firmís supply curve will shift to the right
B. the firmís demand curve will shift to the right
C. the firmís demand curve will shift to the left
D. the firmís supply curve will shift to the left
E. Neither curve will shift, but instead movement will be along each curve
21. If supply and demand both increase, we can correctly conclude that
I. Equilibrium price will rise
II. Equilibrium price is indeterminate
III. Equilibrium quantity will rise
IV. Equilibrium quantity is indeterminate
A. I only
B. I and III only
C. II and IV only
D. II and III only
E. I and IV only
22. Market based economies allocate resources in which of the following ways?
I. Established customs and traditions decide which goods and services will be produced
II. Voluntary exchange determines which goods and services get produced
III. Government determined prices help producers allocate scarce resources
A. I only
B. II only
C. III only
D. I and II only
E. II and III only
23. If an increase in the price of one good increases the demand for another good, then these two goods are
A. regular goods
B. substitute goods
C. public goods
D. complementary goods
E. independent goods
24. Which of the following is true about the distances between average variable cost and average total cost when graphed?
A. As output increases the difference between them gets smaller
B. As output increases the difference between them gets larger
C. Is equal to average fixed cost at all levels of output
D. Is zero at all levels of output
E. A and C are both correct
25. Game theory, and price leadership are explanations for the profit-maximizing behavior of a firm under which of the following market structures?
A. Pure monopoly
B. Oligopoly
C. Monopolistic competition
D. Perfect competition
E. All of the above market structures
26. If your insurance company informed you that your insurance premium had been increased, what effect would this have on your business?
Average Variable CostAverage Fixed CostMarginal Cost
A. No Change No Change No Change
B. No Change Increase No Change
C. Increase Increase No Change
D. Increase Increase Increase
E. No Change Increase Increase

Figure 9
27. Which graph in Figure 9 shows the long-run profit maximizing position for a monopolistic competitor?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
28. Which graph in Figure 9 shows a profit maximizing natural monopoly?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
29. The scarce productive resources are _____, _____, _____, _____, and wants are _____.
A. Money, Savings, Production, GDP, unlimited
B. Money, Savings, Production, GDP, limited
C. Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship, unlimited
D. Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship, limited
E. Land, Labor, Capital, Money, unlimited
30. Which of the following embodies most of the principles of a pure public good?
A. Taking the Advanced Placement economics examination
B. Street lights
C. A new car
D. A new economics book
E. All of the above
31. Which of the following is a progressive tax?
A. Every taxpayer pays $10.00
B. Every taxpayer pays 10% of his/her income
C. Higher income taxpayers pay a higher percent of their income in tax
D. Higher income taxpayers pay a lower percent of their income in tax
E. None of the above correctly describes a progressive tax
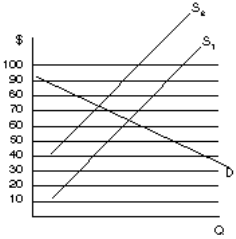
Figure 10
32. Based on Figure 10 if S1 represents supply before the imposition of an excise tax and S2 represents supply after the tax is imposed, how much is the tax?
A. 14
B. 30
C. 64
D. 78
E. None of the above
33. The burden (or incidence) of the tax in Figure 10 would be borne by
A. Producers entirely
B. Consumers entirely
C. Equally by producers and consumers
D. More by producers than consumers
E. More by consumers than producers
34. Models of consumer behavior explain the downward slope of a demand curve with each of the following EXCEPT:
A. Substitution effect
B. Complement effect
C. Income effect
D. Diminishing marginal utility
E. All of the above are used to explain consumer behavior
35. Each of the following would definitely raise the equilibrium price of a good with the single exception of:
A. Lowered cost of raw materials and increased popularity of the product
B. Increased cost of raw materials and increased popularity of the product
C. Decrease in the number of producers and increased numbers of consumers
D. Decrease in the number of producers and an increase in the price of a substitute good
E. An increase in the price of other goods that could be made by the producer and an increase in the incomes of the consumers of the good in question
36. If one firm in a perfectly competitive industry experiences a technological breakthrough that lowers only that firmís cost of production, which of the following correctly describes the effect on this firmís price, quantity, and profit?
PriceQuantityProfit
A. decrease decrease decrease
B. decrease increase increase
C. no change decrease increase
D. no change increase increase
E. increase increase increase
37. In which of the following combinations would a change in price result in the largest decrease in equilibrium quantity?
A. inelastic demand, inelastic supply
B. inelastic demand, elastic supply
C. elastic demand, elastic supply
D. elastic demand, inelastic supply
E. none of these choices would influence the equilibrium quantity
38. In the factor market, which of the following would happen if the workers became more productive and at the same time the price of the product fell?
A. The value of the marginal product of labor would increase
B. The value of the marginal product of labor would decrease
C. The value of the marginal product of labor would be indeterminate
D. The demand for labor would shift to the right
E. The demand for labor would shift to the left
39. Which of the following would shift the demand for a good to the right?
A. A decrease in the cost of production
B. A decrease in the price of the good
C. An increase in the price of the good
D. The introduction into the market of many similar products
E. The removal from the market of many similar products
40. Which of the following would shift the supply of a good to the left?
A. An increase in the cost of production
B. A decrease in the cost of production
C. An increase in the price
D. A decrease in the price
E. A decrease in demand
41. Which of the following would contribute to a reduction in consumer surplus?
A. imposition of an effective price floor
B. imposition of an effective price ceiling
C. an increase in supply
D. a decrease in equilibrium price
E. all of the above would contribute to a reduction in consumer surplus
42. Karenís Karmel Korn produces a type of caramel corn candy. Caramel, an ingredient in caramel corn, increases in price by 10%. Which of the following correctly describes the effect that this increase will have on the cost of production?
A. only marginal cost will increase
B. only marginal cost and average total cost will increase
C. marginal cost, average variable cost, average total cost will increase
D. marginal cost, average total cost, and average fixed cost will increase
E. marginal cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and average fixed cost will increase
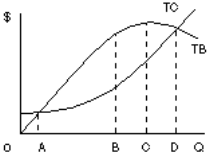
Figure 11
43. Government provides many goods and services to the public because free markets do not provide them. Some economists believe bureaucrats who manage the programs have no interest in maximizing net benefits, but instead maximize the size of a program constrained only by the need to have total benefit greater than or equal to total cost. Figure 11 shows total benefits and cost curves for a program. What point is the efficient point, and what point will the bureaucrat choose?
A. OA, OB
B. OA, OC
C. OB, OD
D. OD, OC
E. OD, OA
44. The following table indicates a production process characterized by
A. decreasing returns to scale
B. constant returns to scale
C. increasing returns to scale
D. increasing returns to labor
E. constant returns to labor
| OUTPUT | |||||||
| Units of CAPITAL | |||||||
Units of LABOR
45. A firm uses workers and seed to grow lettuce. Its output rises from 100 tons to 200 tons when the number of workers increases from 25 to 75. Its production process shows
A. decreasing returns to scale
B. diminishing returns to labor
C. increasing returns to scale
D. increasing returns to labor
E. increasing long-run average cost
46. Setting an effective price floor would:
A. increase consumer surplus and increase producer surplus
B. increase consumer surplus and decrease producer surplus
C. decrease consumer surplus and decrease producer surplus
D. decrease consumer surplus and increase producer surplus
E. leave both consumer and producer surplus unaffected
47. The ďinvisible handĒ
A. is the name of a Great Depression radio program
B. is a concept used by Adam Smith to describe the virtues of free markets
C. is a concept used by J.M. Keynes to describe the role of government in guiding the allocation of resources in the economy
D. is a concept used by John Gailbraith to describe market failure
E. always rewards individuals for using the well-being of society as the basis for economic decision-making
48. Economists tend to see ticket scalping as
A. a way for a few to profit while producing nothing of value
B. an inequitable interference in the orderly process of ticket distribution
C. a way of increasing the efficiency of ticket distribution
D. an unproductive activity which should be made illegal everywhere
E. a way of decreasing the efficiency of ticket distribution
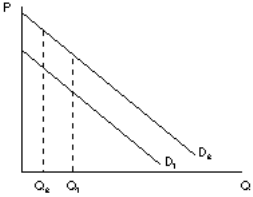
Figure 12
49. Refer to Figure 12. Given the information represented by the graph we can say that
A. demand curve one is more price sensitive over the given output range than demand curve two
B. both demand curves have the same price elasticities over the given output range
C. demand curve two is more price sensitive over the given output range than demand curve one
D. elasticities cannot be determined over the given output range without supply information
E. elasticities cannot be determined over the given output range without price information being given
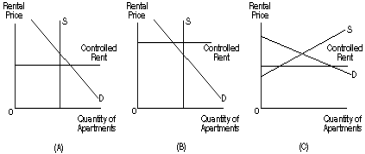
Figure 13
50. In Figure 13, which panel(s) best represent(s) a binding rent control in the short run?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. none of the panels
E. all of the panels
51. There are two generally recognized measures of economic efficiency; one measures efficiency from a production perspective and the other measures efficiency from an allocation perspective. Which of the following correctly states these two measures of efficiency, and in the order mentioned in the question?
A. P = minimum ATC, and P = AR
B. P = minimum ATC, and P = MC
C. P = MC, and MC = MR
D. P = MC, and P = AR
E. MC = MR, and MRP = VMP
52. The profit maximizing level of production in the product market, and the profit maximizing level of employing resources in the factor market are represented by which of the following combinations?
A. MC = MR, and VMP = MRC
B. VMP = MRC, and MC = MR
C. P = MC, and P = MR
D. P = MR, and P = MC
E. P = minimum ATC, and P = MC
Figure 14
Date: 2015-12-24; view: 995
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| The working language while studying in Romania is Romanian. | | | Quantity Average Average Marginal |