
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Basic equations of stresses and deformations «perfect» bodies
Plan of the lecture:
1. Mechanical model of the «ideal» elastic body.
2. Mechanical model of the «ideal» viscous body.
3. Mechanical model of the «ideal» plastic body.
Purpose of the lecture: get acquainted with rheological models and the basic equations of stresses and deformations «perfect» bodies
In rheology there are two mutually exclusive concepts: «solid perfectly elastic body» and «non-viscous fluid. Under the first means the body equilibrium shape and voltage is achieved instantly. The liquid is called the residual, i.e. if the liquid is not able to create and sustain shear stress. Between the limiting States tel - perfectly elastic solids and inviscid fluids in nature, there is a huge variety of intermediate bodies nature.
Consider the basic model that can be encountered in the study of rheological properties of food masses. It is necessary to specify that the exact mathematical patterns obtained only for Newtonian fluids, for all non-Newtonian flows received only approximate formulas.
There are three intermediate models idealized materials (table 1.3): perfectly elastic body (Hooke); ideally-viscous liquid (Newton); perfectly plastic body (Saint-Venant).
1.-elastic body gook. In a perfectly elastic body (model - spring) energy spent on the deformation, builds and can be returned during unloading. Hooke's law describes the behavior of crystalline and amorphous solids under small deformations, and also liquids with isotropic enlargement - compression.
2.-viscous liquid Newton. Ideal-viscous liquid is characterized by the fact that the voltage is proportional to the speed of deformation. Viscous flow occurs under the action of all the forces, however small they were not; but the strain-rate decreases forces, and for the disappearance vanishes. For such liquids, viscosity, which is a constant proportional to the shear stress.
Newton's law describes the behavior of many low-molecular liquids shear and longitudinal current. The mechanical model of a Newtonian fluid is a damper consisting of a piston that moves in the cylinder of liquid. When moving the piston liquid through the clearance between the piston and the cylinder is leaking from one cylinder to another. This resistance movement of the piston is proportional to its velocity (see table 1.).
3 plastic body of Saint-Venant can be represented as element consisting of two pressed to each other plates. If the relative plate movement between them there is a constant friction force does not depend on the compressive their strength. The body of the Saint-Venant not start to deform up until shear stress will not exceed some critical value of the yield strength τÒ (maximum shear stress), then the element can move with any speed.
Table 1 Rheological models of simple idealized bodys
| The model | Type of model | graphics flow | the equation | legend |
  Guks’
Guks’
|

| 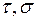 – tangent and normal stress, PA; – tangent and normal stress, PA;
 –angular and linear deformations;
G, E– E is the modulus of elasticity at the angular and linear deformations, PA –angular and linear deformations;
G, E– E is the modulus of elasticity at the angular and linear deformations, PA
| ||
  Newton
Newton
|

|  – the panning speed, c-1; – the panning speed, c-1;
 – the shear viscosity, c-1 – the shear viscosity, c-1
 – the speed of the longitudinal course c-1; – the speed of the longitudinal course c-1;
 – viscosity at longitudinal for (truth) PA•S – viscosity at longitudinal for (truth) PA•S
| ||
 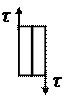 Saint-Venant
Saint-Venant
| When t < τÒ no deformation; t = τÒ. |  – over-limit of fluidity at shear, PA – over-limit of fluidity at shear, PA
|
In practice, a mechanical model of the «perfect» bodies and their basic equations used to describe the behavior, properties, real food materials, liquids, which are quite close in properties to them. However, most of this is impossible due to the fact that the food materials are quite complex compositions, which can simultaneously have two, three or more properties.
Checklist
1. Mechanical model of the «ideal» elastic body.
2. Mechanical model of the «ideal» viscous body.
3. Mechanical model of the «ideal» plastic body.
Date: 2015-12-24; view: 1481
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Basic terms and definitions rheology, axioms rheology | | | Basic equations of the complex rheological tel |