
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Algorithms and programming
Commercial advertising media can include wall paintings, billboards , street furniture components, printed flyers, radio, cinema and television ads, web banners, web pop-ups, skywriting, bus stop benches, magazines, newspapers, town criers, sides of buses, taxicab doors and roof mounts, musical stage shows, subway platforms and trains, elastic bands on disposable diapers, stickers on apples in supermarkets, the opening section of streaming audio and video, posters, and the backs of event tickets and supermarket receipts.
Television. The TV commercial is generally considered the most effective mass-market advertising format, as is reflected by the high prices TV networks charge for commercial airtime during popular TV events. The annual Super Bowl football game in the United States is known as the most prominent advertising event on television. The average cost of a single thirty-second TV spot during this game has reached US$3 million (as of 2009). The majority of television commercials feature a song or jingle that listeners soon relate to the product. Virtual advertisements may be inserted into regular television programming through computer graphics. It is typically inserted into otherwise blank backdrops. Virtual billboards may be inserted into the background where none exist in real-life. This technique is especially used in televised sporting events. Virtual product placement is also possible.
Infomercials. An infomercial is a long-format television commercial, typically five minutes or longer. The word "infomercial" is a portmanteau of the words "information" & "commercial". The main objective in an infomercial is to create an impulse purchase, so that the consumer sees the presentation and then immediately buys the product through the advertised toll-free telephone number or website. Infomercials describe, display, and often demonstrate products and their features, and commonly have testimonials from consumers and industry professionals.
Press advertising describes advertising in a printed medium such as a newspaper, magazine, or trade journal. This encompasses everything from media with a very broad readership base, such as a major national newspaper or magazine, to more narrowly targeted media such as local newspapers and trade journals on very specialized topics. A form of press advertising is classified advertising, which allows private individuals or companies to purchase a small, narrowly targeted ad for a low fee advertising a product or service.
Radio advertising. The radio might have lost its charm owing to the new age media however the radio remains to be the choice of small-scale advertisers. These ads have to be very simple and easy to be understood, since people are usually doing something, like driving, when listening to them. The radio jingles have been very popular advertising media and have a large impact on the audience, which is evident in the fact that many people still remember and enjoy the popular radio jingles.
Direct mail is another kind of advertising, sending the ads via mail system to the future customers. This system is also used through e-mails and offers graphics and links to more information. In order to do this kind of advertising, the advertisers have to buy so-called mailing lists, which contain the addresses of people with certain wanted characteristics.
The Yellow Pages are thick directories of telephone listings and displays of advertisements, mostly of local use, but nevertheless very effective.
Online advertising is a form of promotion that uses the Internet and World Wide Web for the expressed purpose of delivering marketing messages to attract customers. Examples of online advertising include contextual ads that appear on search engine results pages, banner ads, pop-ups, social network advertising, online classified advertising, advertising networks and e-mail marketing, including e-mail spam.
Billboard advertising. Billboards are large structures located in public places which display advertisements to passing pedestrians and motorists. Most often, they are located on main roads with a large amount of passing motor and pedestrian traffic; however, they can be placed in any location with large amounts of viewers, such as on mass transit vehicles and in stations, in shopping malls or office buildings, and in stadiums. Mobile billboards are generally vehicle mounted billboards or digital screens. The billboards are often lighted; some being backlit, and others employing spotlights. Some billboard displays are static, while others change; for example, continuously or periodically rotating among a set of advertisements.
In-store advertising is any advertisement placed in a retail store. It includes placement of a product in visible locations in a store, such as at eye level, at the ends of aisles and near checkout counters, eye-catching displays promoting a specific product, and advertisements in such places as shopping carts and in-store video displays.
Celebrity endorsement. This type of advertising focuses upon using celebrity power, fame, money, popularity to gain recognition for their products and promote specific stores or products. Advertisers often advertise their products, for example, when celebrities share their favorite products or wear clothes by specific brands or designers. Celebrities are often involved in advertising campaigns such as television or print adverts to advertise specific or general products. The use of celebrities to endorse a brand can have its downsides, however. One mistake by a celebrity can be detrimental to the public relations of a brand. For example, following his performance of eight gold medals at the 2008 Olympic Games in Beijing, China, swimmer Michael Phelps' contract with Kellogg's was terminated, as Kellogg's did not want to associate with him after he was photographed smoking marijuana.
Covert advertising embedded in other entertainment media is known as product placement. A more recent version of this is advertising in film, by having a main character use an item or other of a definite brand - an example is in the movie Minority Report, where Tom Cruise's character Tom Anderton owns a computer with the Nokia logo clearly written in the top corner, or his watch engraved with the Bulgrari logo. Another example of advertising in film is in I, Robtot, where main character played by Will Smith mentions his Converse shoes several times, calling them "classics," because the film is set far in the future. Cadillac chose to advertise in the movie The Matrix Reloaded, which as a result contained many scenes in which Cadillac cars were used. Similarly, product placement for Omega Watches and BMW cars featured in recent James Bond films.
Some companies have proposed to place messages or corporate logos on the side of booster rockets and the International Space Station.
Unpaid advertising (also called word of mouth advertising), can provide good exposure at minimal cost. Personal recommendations ("bring a friend", "sell it"), spreading buzz, or achieving the feat of equating a brand with a common noun ("Xerox" = "photocopier", "Kleenex" = tissue, and "Vaseline" = petroleum jelly) -- these are the pinnacles of any advertising campaign. However, some companies oppose the use of their brand name to label an object.
Subliminal advertising includes messages such as words, images, or sounds that might appear in television or radio commercials, TV shows or movies, print ads or recorded music. Usually when subliminal messages are seen or heard, they’re not recognized for what they are. In fact they may be ignored by the conscious brain and be beyond the level of conscious perception. So subliminal advertising is out of conscious perception. Visual messages may be quickly flashed before an individual may process them, or flashed and then masked. Audio messages may be played below audible volumes, similarly masked by other stimuli, or recorded backwards in a process called backmasking.
The theory holds that subliminal messages are perceived by the subconscious or unconscious mind. Since the conscious mind doesn’t have time to rationalize or analyze these messages, people might more easily accept them. For instance, the use of red in commercials for Target® is at least partly subliminal. The red itself really has nothing to do with the company, but persistence in using it for most commercials means advertisers hope that the color red, whenever seen, will remind people of Target and convince them to shop there.
Subconscious stimuli by single words are well known to be modestly effective in changing human behavior or emotions. This is evident by a pictorial advertisement that portrays four different types of rum. The phrase "U Buy" was embedded somewhere, backwards in the picture. A study was done to test the effectiveness of the alcohol ad. Before the study, participants were able to try to identify any hidden message in the ad, none found any. In the end, the study showed 80% of the subjects unconsciously perceived the backward message, meaning they showed a preference for that particular rum.
But still there’s disagreement on the degree to which subliminal messages can affect peoples’ mind. Till the mid 20th century, the use of subliminal messaging in advertising was considered standard fare, especially visual messages where something would flash for a split second on a screen that would subliminally convince the viewer to act in a certain way. But soon people became afraid that subliminal messages could be used to “brainwash” themselves or others. This fear became so great that by the 1970s, the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) banned the use of subliminal messages in advertisements.
Yet it’s never really been proven that subliminal messages work to any great degree. In 1957, market researcher James Vicary claimed that quickly flashing messages on a movie screen, in Fort Lee, New Jersey, had influenced people to purchase more food and drinks. Vicary also claimed that during the presentation of the movie Picnic he used a tachistoscope to project the words "Drink Coca-Cola" and "Hungry? Eat popcorn" for 1/3000 of a second at five-second intervals. Vicary asserted that during the test, sales of popcorn and Coke in that New Jersey theater increased 57.8% and 18.1% respectively. However, in 1962 Vicary admitted to lying about the experiment and falsifying the results, the story itself being a marketing ploy. An identical experiment conducted by Dr. Henry Link showed no increase in cola or popcorn sales.
Though today subliminal advertising--hidden messages embedded in ads--is considered a deceptive business practice and is banned a legal kind of "subliminal" persuasion happens every day. Shoppers are regularly encouraged to buy by appeals to their senses or unconscious assumptions.
Store owners know that playing music with a tempo faster than the human heartbeat causes shoppers to shop quickly--and therefore buy less. The slower the beat, the more time shoppers will take, and the greater the chances are that they'll buy something. Music also can direct us to certain products. For example, it can determine what kind of wine we pick up from the shelves. In one experiment over a two-week period, British researchers played either accordion-heavy French music or a German brass band over the speakers of the wine section inside a large supermarket. On French music days, 77% of consumers bought French wine, whereas on German music days, the vast majority of consumers picked up a German selection. Intriguingly, only one out of the 44 customers who agreed to answer a few questions at the checkout counter mentioned the music as among the reasons they bought the wine they did.
Shapes also have a Draw. A large food manufacturer once tested two different containers for a diet mayonnaise aimed at female shoppers. Both containers held the exact same mayo, and both bore the exact same label. The only difference? The shapes of the bottles. The first was narrow around the middle and thicker at the top and on the bottom. The second had a slender neck that tapered down into a fat bottom, like a genie bottle. When asked which product they preferred, every single subject--all diet-conscious women--selected the first bottle without even having tasted the stuff. Why? The researchers concluded that the subjects were associating the shape of the bottle with an image of their own bodies.
1. In the text find words and expressions that mean
1. to give, to allocate
2. the attributes of a brand as perceived by potential and actual customers
3. a group of related products marketed by the same company
4. talk, rumors, a kind of advertising
5. a small printed notice for distribution by hand
6. advertising goods by spreading information about them among other people
7. information about things that where lost and then found
8. location
9. to promote
10. to start, to release
11. to mean
12. ads in the press, usually divided into rubrics
13. ads which offer customers to order products by mail
14. a characteristic of a product that can be used in advertising to differentiate it from its competitors
15. to introduce
16. a company in the Internet
17. important, to the point
18. advertising gift
19. ad on TV
20. of, for, or appealing to a large number of people; popular
21. he time allocated to a particular programme, item, topic, or type of material on radio or television
22. a run of airtime
23. unplanned purchase
24. an intracity phone call
25. a recommendation of the character, ability, etc., of a person or of the quality of a consumer product or service, esp by a person whose opinion is valued
26. all the readers collectively of a particular publication or author
27. a song or a tune played in a commercial
28. by means of
29. a book, arranged alphabetically or classified by trade listing names, addresses, telephone numbers, etc., of individuals or firms
30. an advertisement, often animated, that extends across the width of a web page
31. something that appears over or above the open window on a computer screen
32. a characteristic of a product by a famous or reliable person
33. a famous person
34. tending to attract attention; striking
35. to include
36. the highest point or level, esp of fame, success, etc
37. the disadvantageous aspect of a situation
38. the act or the effect of perceiving
39. a trick or a tactic aimed at attracting public attention to the product
2. Say whether the following statements are true or false
1. Companies are trying not to spent too much of their budget on advertising
2. In ancient times the most common form of advertising was by town-criers.
3. Thomas Barratt is often referred to as the father of modern advertising as he was the first to use visual images to appeal to customers.
4. Lost-and-found advertising included simple descriptions, plus prices of products.
5. The TV commercial is generally considered the most effective mass-market advertising format.
6. The main objective in an infomercial is to create an impulse purchase.
7. Information in The Yellow Pages usually covers the whole country.
8. Usually one mistake by a celebrity advertising the product can be detrimental to the public relations of a brand.
9. Subliminal messages are perceived by conscious mind.
10. Most researchers agree on the degree to which subliminal messages can affect peoples’ mind
11. Today subliminal advertising is considered a deceptive business practice and is banned
Algorithms and programming
- What is the effect of executing the class Main above?
class Main
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
String mesg = "Answer is ";
int sum = 1 + 2;
System.out.println( mesg + sum );
}
}
· Prints mesg + sum
· Prints “mesg+sum”
· Prints 3
· Prints Answer is 3
· Prints Answer is 1 + 2
- Consider the following code snippet
String river = new String(“Columbia”);
System.out.println(river.length());
What is printed?
· 8
· Columbia
· 6
· 7
· river
- After the following code fragment, what is the value in a?
String s;
int a;
s = "Foolish boy.";
a = s.indexOf("fool");
· -1
· random value
· 0
· 4
· fool
- What is an infinite loop?
· A loop that functions infinitely well
· A loop that will never function
· An incorrect loop
· A loop that runs forever
· A loop that never starts
- The sequence \n does what?
· Makes a link
· Starts a new line
· Finishes text
· Prints a backslash followed by a n
· Adds 5 spaces
- Given the following code fragment:
int A[];
int i = 0;
A = new int A[4];
while (i < 4)
{
A[i] = 10;
i = i + 1;
}
What is the value of A[3]?
· 10 (if A = new int[4];)
· 4
· 0
· 3
· Integer.MAX_VALUE
- What is the value of the variable a3 after execution of the following code:
String a1, a2, a3;
a1 = “45”;
a2 = ”31”;
a3 = a2 + a1;
· “4531”
· “3145”
· 45
· 31
· 76
- Assume that x, y, and z are all ints equal to 50, 20, and 6 respectively. What is the result of x / y / z?
· 0
· A syntax error as this is syntactically invalid
· A run-time error because this is a division by 0
· 12
· 16
- Given that x is a double variable and num is an int variable containing the value 5, what will x contain after execution of the following statement:
x = num / 2;
· 2.5
· 5.0
· a compile-time error occurs
· 2
· 2.0
- After execution of the following code, what will be the value of item if its initial value is 10?
if (item > 5)
item = item + 5;
if (item < 10)
item = item + 10;
else if (item < 20)
item = item + 10;
· 15
· 25
· 0
· 5
· 10
- Consider the following switch statement where x is an int,
switch (x)
{
case 3 : y = x + 1;
case 4 : x = x + 2;
y = ++x;
case 5 : x = y + 3;
y = x++;
break;
case 6 : x++; y = x;
}
If x is currently equal to 4, what will the value of y be after the switch statement executes?
· 8
· 10
· 6
· 7
· 11
- If x is an int where x = 0, what will x be after the following loop terminates?
while (x < 100)
x = x*2;
· 100
· 128
· 2
· 64
· this is an infinite loop
- Given the following code, where x = 0, what is the resulting value of x after the for-loop terminates?
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
x = x + i;
· 3
· 5
· 0
· 1
· 10
- The do–while loop differs from the while loop in that
· the do–while loop will continue to loop while condition in the while statement is false and the while loop will continue to loop while the condition in the while statement is true
· the while loop will continue to loop while condition in the while statement is false and the do–while loop will continue to loop while the condition in the while statement is true
· the while loop will always execute the body of the loop at least once
· the do–while loop will always execute the body of the loop at least once
· none of the above, there is absolutely no difference between the two types of loops
- What is the value of someInt after control exits the following loop?
someInt = 3;
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++)
someInt = someInt * k;
· 5
· 6
· 0
· 2
· 7
- Using De Morgan’s law, how would you rewrite the following conditional statement
(i.e. is rewrite the statement using && instead of ||) ( c!='n' && z+2<=5 )
· !(c=='n' || z+2>5)
· !(c=='n' || z+2<5)
· !(c!='n' || z+2<=5)
· !(c=='n' || z+2>=5)
· !(c!='n' || z+2<=5)
- What will the following program fragment output?
Integer i = new Integer(5);
Integer j = new Integer(5);
if (i==j)
System.out.println(“Equal”);
else
System.out.println(“Not equal”);
· The program doesn't compile because == can't be used with references
· The program doesn’t execute because i and j are not correctly initialized
· Equal
· Not equal
· Equal Not equal
- Given the following method (you may assume it has all compiled correctly so there are no syntax errors), what will be output?
public void printloop()
{
int i;
for (i=1; i<9; i++)
if (i%2 == 0)
System.out.print(i + " ");
System.out.println();
}
· 2 4 6 8
· 9
· 2 4 6
· 8
· 1 3 5 7
- What will the method call mystery(1230) return, if the method is defined as follows:
public int mystery(int n) {
int m = 0;
while (n > 0) {
m = 10*m + n%10;
n = n/10;
}
return m;
}
· .123
· .0321
· 0321
· 321
· 0
- What will be printed by the code fragment below?
double height = 5.5;
if(height-- >= 5.0)
System.out.print("tall ");
if(--height >= 4.0)
System.out.print("average ");
if(height-- >= 3.0)
System.out.print("short ");
else
System.out.print("very short ");
· short
· tall
· very short
· average short
· tall short
- What is the output of loop(8), where loop is defined as follows?
public void loop(int n) {
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
System.out.print(i*(i-1)/2);
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
· 0 3 4 10 12 21 24 36
· 0 0 3 4 10 12 21 24
· 0 0 0 3 4 10 12 21
· 0 1 3 6 10 15 21 28
· 0 0 1 3 6 10 15 21
- An array with more than one index is called:
· partially filled array
· one dimensional array
· there are no such arrays
· multidimensional array
· bidirectional array
- Which of the following methods will correctly calculate the maximum value in an array? All of these methods compile correctly, so you are only looking for logic errors, not syntax errors. (The method Math.max() is a library method from the API and returns the maximum of its two arguments.)
public int max1(int[] a) {
int maxPos = 0;
for (int i=1; i<a.length; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[maxPos]) {
. maxPos = i;
}
}
return maxPos;
}
public int max2(int[] a) {
int max = a[0];
for (int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
if (a[i] > max) {
. max = a[i];
}
}
return max;
}
public int max3(int[] a) {
for (int i=1; i<a.length; i++) {
a[i] = Math.max(a[i],a[i-1]);
}
return a[a.length-1];
}
· max1 and max2 only
· max2 and max3 only
· max1 and max3 only
· None of them
· All of them
- Consider
public class MyClass{
public MyClass(){/*code*/}
// more code...
}
To instantiate MyClass, you would write?
· MyClass mc = new MyClass();
· MyClass mc = new MyClass;
· It can't be done. The constructor of MyClass should be defined as public void MyClass(){/*code*/}
· MyClass mc = MyClass();
· MyClass mc = MyClass;
- In the class Car, you want to create an instance method isSpeeding to check whether an object to type Car is speeding or not. One of the instance fields of the Car class is a double variable speed equal to the current speed of the Car object. The class also lists a constant static double field SPEED_LIMIT, equal to the legal speed limit for the driving conditions of the Car object. What method signature would be best for isSpeeding?
· public void isSpeeding(double speed)
· public isSpeeding()
· public boolean isSpeeding(speed,SPEED_LIMIT)
· public boolean isSpeeding()
· public boolean isSpeeding(double speed,double SPEED_LIMIT)
- Consider the two methods (within the same class)
public int foo(int a, String s)
{
s = "Yellow";
a=a+2;
return a;
}
public void bar()
{
int a=3;
String s = "Blue";
a = foo(a,s);
System.out.println("a="+a+" s="+s);
}
What is printed if method bar() is called?
· a=3 s=Yellow
· a=5 s=Blue
· a=3 s=Blue
· a=5 s=Yellow
· The code doesn't compile
- Consider the following class definition:
public class MyClass{
private int value;
public void setValue(int i){ /* code */ }
// Other methods...
}
The method setValue assigns the value of i to the instance field value. What could you write for the implementation of setValue?
· value == i;
· both “value = i;” and “this.value = i;” are correct
· value = i;
· this.value = i;
· All of the answers are correct
- The behavior of an object is defined by the object's
· visibility modifiers
· methods
· classes
· instance data
· constructor
- Which reserved word is used to create an instance of a class?
· public or private, either could be used
· import
· new
· class
· public
- What is GUI?
· uses buttons, menus, and icons
· uses buttons, menus, and icons for user and computer interaction
· for user and computer interaction
· stands for Graphic Use Interaction
· all of the above
- What does IDE stand for?
· Interior Development Environment
· Interior Design Environment
· Integrated Development Environment
· Integrated Design Environment
· Infrared Digital Environment
- Consider the following class with a single method
public class Doubler {
public void doubleIt(int n) {
n = 2*n;
}
public void doubleIt(int [] n) {
n[n.length-1] = 2*n[n.length-1];
}
}
What happens when the class is compiled, and the following sequence of statements (which is part of a method of another class) is compiled and executed?
int x = 20;
int [] y = {1, 5, 10};
Doubler d = new Doubler();
d.doubleIt(x);
d.doubleIt(y);
System.out.println(x + " " + y[y.length-1]);
· The values 40 20 will be printed to the terminal window.
· The values 20 10 will be printed to the terminal window.
· The values 20 2 10 20 will be printed to the terminal window.
· The values 40 10 will be printed to the terminal window.
· The values 20 20 will be printed to the terminal window.
- Consider the following code fragment
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle();
r1.setColor(Color.blue);
Rectangle r2 = r1;
r2.setColor(Color.red);
After the above piece of code is executed, what are the colors of r1and r2 (in this order)?
· Color.blue and Color.red
· Color.red and Color.blue
· Color.blue and Color.blue
· Color.red and Color.red
· Not enough information
- If result = 2 + 3 * 5, what is the value of result?
· 25
· 17
· 30
· 14
· 10
- What is data type of numbers such as 3.14159?
· long
· double
· int
· real
· string
- What is function?
· An entity that receives inputs and outputs
· An output
· A way of storing values
· A sequence of characters enclosed by quotes
· A kind of computer
- 5 bits can be used to represent ___ distinct items or values.
· 20
· 24
· 32
· 64
· 6
- If the int variables int1 and int2 contain the values 5 and 2, respectively, then the value of the expression (double)(int1) / int2 is:
· 2.0
· 2.5
· 0.25
· 0
· 2
- Mae's accounting service helps each customer figure their tax owed. The customer's first name, middle initial and last name go on the form. The number of dependents is needed, along with the total income for the year. Mae charges a fee of 1.5% of total income for the service. Which one of the following would be the best suitable type for a variable that stores the number of dependents of the customer?
· int
· char
· String
· boolean
· double
- What is the type and value of the following expression? (notice the integer division)
-4 + 1/2 + 2*-3 + 5.0
· int; -4
· double; -5.0
· int; -5
· double; -4.5
· not correct expression
- You are programming a game of dice. You need to generate a random integer that can be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. Which of the following expression would you select? Recall that Math.random() returns a random double >=0 and <1
· (int)(Math.random()*6)+1
· (int)(Math.random()+6)
· (int)(Math.random()*6)
· Math.random()*6
· ((int)Math.random())*6+1
- What will be the value of x after the following statement?
int x = 73/5%3;
· 2
· 36
· 0
· 1
· 35
- What does the method call fib(7) return if fib is defined as follows?
public int fib(int n) {
int[] a = new int[n];
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 1;
for (int i=2; i<n; i++) {
a[i] = a[i-1] + a[i-2];
}
return a[n-1];
}
· 13
· 21
· 6
· 8
· 55
- If a and b are variables of type boolean then select such an expression(by use of AND,OR, NOT), where it is true when exactly one of a and b is true, and false under all other circumstances?
· (a && !b) && (!a && b)
· (a || b) && (!a || !b)
· (a || b) || (!a || !b)
· a || b
· a && b
- What values do c and d respectively have after the following sequence of statements?
boolean a = true;
boolean b = false;
boolean c = (a || b) && !(a && b);
boolean d = c || (a && b || !(a && b || (a && !b)));
· false, true
· false, false
· true, 0
· true, true
· true, false
- What is the value of y when the code below is executed?
int x = 4;
int y = (int)Math.ceil(x % 5 + x / 5.0);
· 4
· 3
· 1
· 6
· 5
- What is the range of the random number r generated by the code below?
int r = (int)(Math.floor(Math.random() * 8)) + 2;
· 2 <= r <= 9
· 3 <= r <= 8
· 3 <= r <= 10
· 3 <= r <= 9
· 2 <= r <= 10
- What is Polymorphism?
· Ability to store objects of Subclass in references of Superclass.
· Technique to execute method with object’s implementation instead of reference’s.
· Ability to change form of appearance.
· The way to define relative and absolute position in object pool.
· Ability to change form of appearance and the way to define relative and absolute position in object pool.
- What is Multithreading?
· Ability to connect to multiple programs and download great amount of data at same time.
· Very powerful technology of programming to create programs that run fast.
· Very thick string with multiple tiny threads.
· Ability to execute multiple code segments simultaneously.
· None of above.
- What is Encapsulation?
· Ability to inherit multiple interfaces to provide powerful functionality of objects.
· Using GUI to interact with user when some input data is needed.
· Using private fields to protect data and supplying safe methods to manipulate them
· Creating capsules to store data.
· Separate data to small fragments, so that they easily accessed from memory.
- Consider the graph G where V(G)={A,B,C,D} and E(G)=[{A,B},{B,C},{B,D},{C,D}]. The degree of each vertices A,B,C,D respectively in G are…..
· 1,2,2,3
· 2,3,2,2
· 1,2,3,2
· 1,3,2,2
· 1,1,1,1
- The maximum number of edges in a n-node undirected graph without self loops is….......
· n2
· n * (n-1) / 2
· n * log(n)
· n * (n+1) / 2
· n - 1
- let G be a graph with 100 vertices numbered 1 to 100. Two vertices i and j are adjacent if |i-j|=8 or |i-j|=12. The number of connected components in G is…......
· 25
· 4
· 8
· 12
· 6
- A graph in which all nodes are of equal degree is known as…....
· non-regular graph
· regular graph
· single graph
· complete graph
· multi graph
- The minimum number of spanning trees in a connected graph with “n” nodes is…..
· 2
· 1
· log n
· n - 1
· n / 2
- The minimum number of edges in a connected cyclic graph on ‘n’ vertices is…....
· n2
· n-1
· n
· n+1
· none of these
- The minimum number of colours required to colour the vertices of a cycle with “n” nodes in such a way that no two adjacent nodes have the same colour is….......
· 3
· 2
· 1
· n – 2*[n/2] + 2
· n / 2
- A graph is planar if and only if it does not contain …..
· sub graphs isomorpic to k5 or k(3,3)
· sub graphs isomorpic to k3 or k(3,3)
· sub graphs homomorpic to k3 or k(3,3)
· a sub graph homomorpic to k3 or k(3,3)
· any of these
- Given a graph G=(V,E) and a vertex u∈V, the __________ of u is the number of vertices adjacent to u.
· degree
· path
· walk
· trial
· euler
- The graph given below is bipartite?
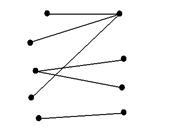
· false
· true
· false but not for all cases
· true but not for all cases
· true for some cases and false for the rest cases
- The number of spanning trees in the complete graph K8:
· 68
· 86
· 48
· 64
· none of the above
- If graph G is defined by an adjacency matrix below, what is the degree of G:

· (3, 2, 3, 2, 2)
· (1, 2, 3, 2, 3)
· (2, 2, 3, 3, 4)
· (0, 1, 1, 2, 0)
· (0, 0, 1, 1, 2)
- The first iteration of Bubble Sort over the sequence 7, 3, 4, 1, 5, 2, 6 would give the following result:
· 1, 7, 3, 4, 2, 5, 6
· 3, 7, 1, 4, 2, 5, 6
· 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
· 3, 7, 4, 1, 5, 2, 6
· 1, 7, 4, 3, 5, 2, 6
- A sorting algorithm is stable if elements with equal keys are left in the same order as they occur in the input. Which of the following sorting algorithms is NOT stable?
· Quick sort
· Bubble sort
· Merge sort
· Insertion sort
· All of the above
- When the input is already sorted, which of the following sorting algorithms has the Best running time?
· Merge sort
· Selection sort
· Insertion sort
· Quick sort
· All above have the same time
- An in-place algorithm is an algorithm that transforms input using a data structure with a small, constant amount of extra storage space. Which of the following sorting algorithms is NOT in-place?
· Quick sort
· Insertion sort
· Bubble sort
· Heap sort
· All of the above
- What is the Worst-case performance of Quick sort?
· O( N log N)
· O( N ^ 2 )
· O( 1 )
· O( log N )
· O( N )
- What is the Best-case performance of Selection sort?
· O( N )
· O( N log N)
· O( 1 )
· O( log N )
· O( N ^ 2 )
- Which of the following is NOT true about Heap sort?
· It is a comparison-based sorting algorithm
· Its average case performance is O( N log N )
· It has a better worst-case runtime than that of Quick sort
· It is a stable sort
· It is an in-place algorithm
- The second iteration of Radix Sort over the sequence 70, 3, 114, 10, 63, 2, 12 would give the following result:
· 2, 3, 10, 12, 63, 70, 114
· 2, 3, 114, 10, 63, 70, 12
· 10, 70, 2, 12, 3, 63, 114
· 2, 3, 10, 12, 114, 63, 70
· 3, 2, 70, 10, 63, 12, 114
- Which of the following would NOT be a good choice for a pivot of Quick sort?
· Middle element
· Median of the first, middle, and last elements
· Random element
· The minimum element in the partition (this causes worst-case behavior on already sorted arrays, which is a rather common use-case)
· All choices are good
- Which of the following sorting algorithms is the most efficient for large data sets?
· Bubble sort
· Selection sort
· Shell sort
· Merge sort
· Insertion sort
- Which of the following sorting algorithms is/are recursive?
I – Bubble sort II – Selection sort III – Quick sort IV – Merge sort V – Heap sort
· III and IV (merge sort can be either recursive or non-recursive)
· III, IV, V
· I and II
· III only
· All of the above
- What are disadvantages of using recursion?
· Recursion works very fast.
· Call to same function too many times, results to stack overflow.
· There are no disadvantages, it is cool feature.
· Recurrent functions such as Fibonacci are hardly implemented.
· Recursion is function that calls itself.
- What are advantages of using recursion?
· Recursion has cached variables for each call instance, so it can be used like stack.
· Recursion works very fast.
· Recurrent functions are easily implemented and have cached variables, so they can be used like stack
· Recursion is function that calls itself.
· Recurrent functions such as Fibonacci is easily implemented.
- What is recursion?
· Stack of variables are stored in recursion.
· Recursion is some type of cycle.
· Recursive function is something because of which computers works slowly.
· Recursion is solution of Fibonacci series.
· Recursion is function that calls itself.
- How many different passwords you can generate if you have alphabet of 5 symbols and maximum length is 3 symbols?
· 155
· 125
· 625
· 243
· None of above
- Define some simple process to generate all 6 digit telephone numbers.
· Create recursion with argument x that will output x, and call itself with x+1 argument, and stops when x reaches 6.
· In one cycle count from 1 till 6 and output 6 times counter value.
· Count till 6^10 and output each value.
· Create 6 nested cycles which counts from 0 to 9 inclusive, and output six counters in a row.
· None of these
- How many different binary strings of length 10 can be created?
· 1024
· 0
· 512
· 2048
· 10
- What is disadvantage of combinatorial (check all combinations) algorithms?
· They work too long.
· We can calculate number of operations needed to check all combinations.
· There are no disadvantages.
· They work very fast.
· None of these
- What is main principle of dynamic programming?
· To solve a given problem, we need to solve subproblems, then combine the solutions of the subproblems to reach an overall solution.
· To solve problem by using dynamic allocation data structures.
· Dynamic algorithms uses less memory that other algorithms.
· Using graphs in process of solution, presenting data as list of vertexes connected by edges, represented as relation of each data unit to each other.
· Creating two dimensional arrays to store data.
- What can be key logic for dynamic programming, in monkey and bananas problem? Where we have monkey at the top of tree and monkey wants to go down by tree (it cannot go up) and collect bananas as much as possible. Example of a tree is shown in following picture.
· Check all possible routes from top to bottom and select maximum result.
· Sum all numbers and divide by number of levels in tree.
· Take three maximum values and sum them.
· At each node store maximum possible amount of bananas collected by the route to reach this node
· Each step select largest amount and move there.
- Which algorithm divides greater problem into small subproblems, pre-calculates subproblem results, again by separating into even smaller subproblems and so on. Then combine that results and make decision for greater problem result.
· HeapSort algorithm
· Dejkstra’s algorithm
· Recursive algorithms
· Dynamic programming algorithms
· None of them.
- What is the difference between an array and a linked list?
· Linked lists allow insertion and removal of nodes at any point in the list and arrays don’t.
· Difference depends on the application.
· There is no difference.
· Arrays allow insertion and removal of nodes at any point in the list and linked list don’t.
· All of these are differences
- An ______________ is a list that contains no data records
· sentinel list
· null list
· zero list
· empty list
· a sentinel list
- Which data structure allocates all elements contiguously in memory, and keeps a count of the current number of elements?
· linked list
· string
· array
· dynamic array
· sentinel list
- In trees, which type of iterations behaviour is as follows: Visit the node closest to the root that it has not already visited
· depth-order
· depth-first order
· breadth-first order
· none of above
· all of the above
- Binary tree is a connected acyclic graph such that the degree of each vertex is no more than ______________
· three
· four
· five
· one
· two
- How can we determine the size of a graph?
· using the number of its vertices it has
· using the number of its edges it has
· using the number of its nodes it has
· none of above
· all of the above
- How much time will it take to modify the heap structure to allow extraction of both the smallest and largest element?
· (log n)
· (log 2n)
· O(n)
· O(log n)
· O(2 log n)
- Which is the fastest sorting algorithm to sort a list?
· binary sort
· linear sort
· quick sort
· bubble sort
· all of the above is correct
- ___________ is one of the fastest ways to store and retrieve data
· indexing
· none of these
· stacking
· sorting
· hashing
- ___________ method is used to remove elements from a stack
· pop( )
· lspop( )
· delete( )
· push( )
· remove( )
- On which principle does stack work?
· LILO
· FILO
· FIFO
· None of above
· All of the above
- On which principle does queue work?
· LILO
· FILO
· FIFO
· None of above
· All of the above
- The time required in best case for search operation in binary tree is
· O(2n)
· O(log 2n)
· (log 2n)
· O(n)
· O(log n)
- Breadth First search is used in__________.
· Graphs
· None of these
· Arrays
· Binary trees
· Stacks
- Key value pair is usually seen in
· Heaps
· Hash tables
· None of these
· Skip list
· All of the above is correct
- In a heap, element with the greatest key is always in the ___________ node
· Root
· Leaf
· First node of right sub tree
· Null
· First node of left sub tree
- If graph G is defined by an adjacency matrix below, what is the size of G:

· 10
· 2
· 7
· 3
· none of the above
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 2349
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| History | | | H I S T O R Y O F M E D I C I N E I N U K R A I N E . |