
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Classification of Elements and the long periodic table
- The atomic number:
It is the number of protons or electrons in the atom.
Isotops
They are different forms of the same element, which have the same atomic number but different mass number as the number of neturons differs in the nuclei.
- The long periodic table
It is a system in which elements are arranged in an ascending order according to their atomic numbers. It depends on the building up principle (Auf-bau) which state that sublevels of low energy are filled at first.
- The periodic table is divided into four main blocks:
1) S-block elements
2) P- block elements
3) d- block elements
4) f- block elements
- Elements of S- block are located at the left of the table, it contains two groups (1A) and (2A).
The sublevel - S contains one orbital which is saturated with two electrons.
- Elements of P- block are found at the right of the table including (6) groups. This groups are 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, and zeroth group.
- orbitals of d- block are filled with electrons frequantly through d- block elements. It includes ten vertical rows and eight groups of (B) groups . D- block is found in the middle of the table
- Element of d- block are called the main transition elements. They are divided into three horizontal chains which are 3d, 4d and 5d.
- The first transition series:
(3d) sublevel is frequantly filled with electrons. It is located in the long fourth period. It starts with scandium  and ends with Zinc
and ends with Zinc  . The electronic configuration of this seris is:
. The electronic configuration of this seris is: 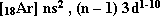 . where n = 4.
. where n = 4.
- The second main transition series:
(4d) sublevel is frequently filled with electrons. It is located in the long fifth period. It starts with
 . The electronic configuration of this series is period.
. The electronic configuration of this series is period.  . The electronic , where n = 5 .
. The electronic , where n = 5 .
- The thrid main transition series:
(5d) sublevel is frequntly filled with electrons. It is located in the long sixth period. It starts with Lanthanum  . The electronic configuration of this series is
. The electronic configuration of this series is 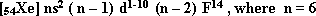 where n = 6.
where n = 6.
- Elements of f- block:
- The orbitals of f- sublevel are filled freqauntly, it carries 14 electrons, and consists of two serieses (Lanthanides) in the sixth period after Lanthaum (57La), and (Actinides) in the seventh period after Actinium (89AC).
Mostly, f- block elements are separated under the periodic table to keep the general shape of it. F-block elements are called The inner transition elements.
- The lanthanides series elements (4F elements) have the electronic configuration 
- The Actinides series elements ( 5 f elements) have the electronic structure 
- Nobel gases
- They are the zeroth group, the electronic structure is (np6) except Helium (1s2) .
All energy levels of nobel gases are completely filled with electrons, so they are stable. Each element of this group is the end of a period in the periodic table.

- The Representative elements:
The are elements of S-block and P-block, except the elements of zeroth group. All the energy levels are completely filled with electrons except the outer most energy level.

So, the main energy level (M) is not completely filled with electrons.
- The main transition elements:
They are elements of d-block, All energy levels are filled with electrons except the last two main energy levels.
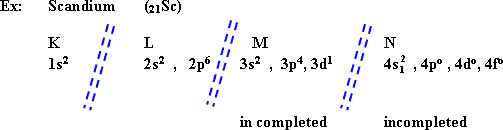
From the electronic structure of Scandium (a transition element), M, and N levels are not completely filled with electrons.
- The inner transition elements:
(F-block elements)
- All the energy levels are filled with electrons except the last three levels.

From this electronic structure of cerium (an inner transition element)
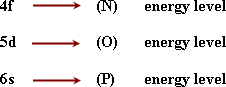
are not completely filled.
Description of the long form periodic table:
1- Contain 18 columns and 7 periods (horizontal).
2- Elements are arranged ascendingly of their atomic numbers.
3- The elements in the same group are indentical in the electron composition of the highest energy level.
4- Every new period begins by filling a new energy level of larger prinicpal quantum number with one.
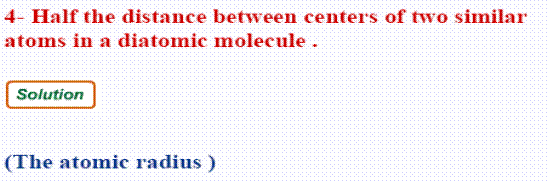
- The atomic radius:
It is half the distance between centres of two similar atoms in a diatomic molecule.
The bond length = the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms.
- In the horizontal periods:
The atomic radius decreases gradually upon increasing in the atomic number. Because the (+ve) charges in the nucleus increases, and the attraction force of the nucleus for electrons increases, so the atomic radius decrease. i.e in the horizotnal periods, the biggest atoms in size are found in the first group (the period start), then it decreases gradually unitl it reaches the smallest size in the seventh group (the period end).
- In the vertical groups:
The atomic radius increases as the atomic no. increases due to the following reasons.
1- The no. of energy levels increases as the period no. increases
2- The repulsive forces between elelctrons increases which leads to increasing in distances between the levels.
3- The completely filled energy levels prevent the attraction force of the nucleus on electrons.
- The radius of the +ve ion (the metal ion) is less than the radius of its atom, due to the increase of the +ve charges. The metal atom tends to lose the electrons of the outer most energy level.
ex: Sodium 11Na
The radius of (Na+) is smaller than that of (Nao) . The no. of +ve protons is bigger than no. of electrons as a result of the sodium atom ionization (lose one -ve electron).
- The radius of a negative ion is bigger than that of its atom, because of the increase of -ve charges, since the non-metals atom tends to gain some electrons in the outer most level.

The anionic radius is larger than the atom radius. The no. of electrons is bigger the no. of +ve charges.
- Ionization potential:
The amount of energy required to remove the smallest bounded electron completely from an isolated gaseous atom.
- In the horizontal periods:
The ionization potential values increase as the atomic no. increases, since the atomic radius decreases and the attraction force of the nucleus on electrons increases, ie. The ionization enegry is inversely proportional to the atomic radius.
- In the vertical groups:
The ionization energy decreases as the atomic no. increases , since the atomic radius increases and the no. of shells surrounding the nucleus increase, separating the nucleus charge from valence electrons, and so the binding between the electron and the atom becomes very weak and easy to separate the electron with low energy.
- Ionization energy increases in the case of (Be) and (Mg) elements, and other elements of (2A) group have big increase since the outer most sub-level (ns) is completely filled with 2 electrons making the atom stable.

- The atom which has one electron in the outer most level, has first ionization potential when it loses this electron, and has second ionization potential upon breaking up a completely filled level such as sodium.
- The atom that has two electrons in the outermost energy level has first ionization enegy when it loses an electron and a second ionization energy when it loses the second electron and has third ionization energy when a completely filled level is breaked up such as in Magnessium.
- The ionization energy is very great in the case of breaking up a completely filled level, so the first ionization energy of inert gases is very high, the same with the second ionization energy of sodium and potassium.
- The electron affinity:
It is the amount of energy released when an extra electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to form an anion (-ve ion).
- In the horizontal periods:
The electron affinity increases as the atomic no. increases. The atomic size decreases and the ability of the atom to attract a new electron increases.
- In the vertical groups:
The electron affinity decreases as the atomic no. increases, since the atomic size increases, the no. of energy levels increases and screen the attraction force of the nucleus on the valence electrons, so it is difficult to add an extra electron to them.
- The electron affinity of the atom increases if the added electron makes stability for the atom, and this occurs if the gained electron fill the energy sub-level.
- Fluorine has electron affinity less than that of chlorine, although the atomic radius of fluorine atom is smaller than that of chlorine because the gained electron is affected by a great repulsion force with nine electrons already existed around the nucleus.
- Electron affinity in noble gases = zero becaue the outer most energy level is completely filled, and this make the atom high stable.
- The electronegativity:
It is the tendency of an atom to attract the electrons of the chemical bond to itself.
- In the horizontal periods:
Electronegativity increases as the atomic no. increases due to the gradual decrease in the atomic radius and the increase in the attractive force of the nucleus to the electrons of the bond.
- In the vertical groups:
The electronegativity decreases as the atomic no increases, because the increase in the number of energy levels which increase the atomic size and decrease the attractive force of the nucleus to the electrons of the bond.
- The difference in the electronegativity between elements plays a very important role in determining the nature of the bond formed between them.
ex: If the difference in the electronegativity is more than 1.7 the compound is ionic compound and equal to zero in case of pure covalent bond, and less than 1.7 the compound is polar covalent.
- Fluorine is the highest electronegativity in the periodic table, due to its small atomic radius, while cesium has the smallest electronegativity, due to its big atomic radius.
- Characteristics of metals:
- The valence shell contains less than four (1, 2, or 3 electrons)
- electropositive elements
- big radii
- small ionization potentials
- easy motion of their electrons.
- Characteristics of non-metals:
- The valency shell contains more than four electrons (5, 6, or 7)
- electronegative elements.
- Small radii
- high vlaues of ionization energy and electron affinity
- bad conductivity of electricity.
- Metalloids:
They have metallic appearance, but non-metallic propeties
- valency shell contains 4 electrons (nearly half filled) ex: silicon (Si)14
- Germanium (Ge)32.
- In the horizontal periods:
Peiords start with the strongest metals, metallic properties decrease gradually as the atomic no. increases until the metalloids appear, then the non-metallic properties start to appear, it increases gradually until the period ends by the strongest non-metals.
- In the vertical groups:
The metallic properties increase and the non-metallic properties decrease gradually as the atomic no. increases. The strongest metals are located at bottom left of the table, so cesium is the strongest metal, while the strongest non-metal at top right of the table. So fluorine is the strongest non-metal.
- In horizontal period the basic character decreases, then the amphoteric character appears , then the acidic character appears with the end of the period.
- Acids and bases are considered as hydroxy compounds, with general formula (MOH)

- when the two attractions are equal so, the substance is called amphoteric.
- The formula of oxygenated acid [MOn(OH)n]
- The strong acid is that which has more number of non bonded oxygen atoms.
- orthosiliconic acid H4SiO4 (Si(OH)4 has no nonbinded oxygen with hydrogen so, it is weak acid.
- Perochloric acid HClO4 [Cl O3 (OH)] has three unbinded oxygen atoms with hydrogen, so, it is very strong acid.
- Oxidation number:
It is a number that referes to the electric charge (+ve or -ve) of the atom in the compound.
- The oxidation no. of Hydrogen in all compounds (+1) except in its hydrides like (NaH) = (-1).
- The oxidation no. of oxygen = (-2), but in 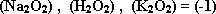
- The oxidation no. of oxygen in  because the electronegativity of fluorine is greater than that of oxygen.
because the electronegativity of fluorine is greater than that of oxygen.
- The oxidation no. in the element molecule = zero whatever the no. of atoms in its molecule.
- The oxidation no. in the atomic group = the no. of charge on the group (ion)

- Remarks on the periodic table:
- First period: contains S- block elements (hydrogon and Helium)
- The second and the third periods: involve S-block and P-block elements. S-block (two elements), while P-block contains six elements, so the two periods contain 8 elements.
- The fourth and the fifth periods they include S- block elements (two elements), P- block (six elements), and d- block (ten elements), so each period contains 18 elements.
- The sixth period include: S-block elements, P- block elements, d- block and f- block elements. So it contains 32 element
QUESTIONS and ANSWERS 1:
I. Choose the correct answer from those between brackets:
1- The first period in the periodic table contains ........... elements. (a-2, b-8, c-18, d-32)
1- a- 2
2- The second period in the periodic table contains .............. elements
(a-2, b-8, c-18, d-32)
2- b- 32
3- The third period in the periodic table contains .............. elements (a-2, b-8, c-18, d-32)
3-b- 8
4- The fourth period in the periodic table contains .............. elements (a-2, b-8, c-18, d-32)
4-c- 18
5- The fifth period in the periodic table contains .............. elements (a-2, b-8, c-18, d-32)
5-c- 18
6- The sixth period in the periodic table contains .............. elements
(a-2, b-8, c-18, d-32)
6-d- 32
7- The s-block elements consists of .. Groups of elments (a-2, b-6, c-10, d-14)
7-a - 2
8- The p-block consists of . groups of elements. (a-2, b-6, c-8, d-5)
8-b- 6
9- The d-block conistis of . groups of elements (a-6, b-8, c-10, d-14)
9-b- 14
10- The f-block conistis of . groups of elements (a-6, b-8, c-10, d-14)
10-d- 14
11- The f- block includes . Series. (a-noble gases, b-lanthanide, c- lanthanide and actinde, d-actininde)
11- c- lanthanide and actinde
12- The oxidation number of hydrogen in 
(a: 1+, b: 1-, c: 2-, d: 2+)
12 -b) (1-)
13- The oxidation number of Nitrogen in  is ................. (a: 1-, b: 1+, c: 0, d: 2-)
is ................. (a: 1-, b: 1+, c: 0, d: 2-)
13-a) (1-)
14- The oxidation number of sulpher in 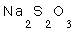 is
.. (a: 2+, b: 4-, c: 5+, d: 6-)
is
.. (a: 2+, b: 4-, c: 5+, d: 6-)
14-a) (2+)
15- The oxidation number of chlorine in 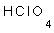 is
. (a: 1-, b- 1+, c: 0, d: 7+)
is
. (a: 1-, b- 1+, c: 0, d: 7+)
15-d) (7+)
16- The oxidation number of calcium in  is
.. (a: 1+, b: 1-, c: 2+, d: 2-)
is
.. (a: 1+, b: 1-, c: 2+, d: 2-)
16-c) (2+)
17- The oxidation number of Hydrogen in LiH is .. (a: 1+, b: 1-, c: 2+, d: 2-)
17-b) (1-)
18- Titanium  element lies under the
. Block (a: s, b: p, c: d, d:f)
element lies under the
. Block (a: s, b: p, c: d, d:f)
18- c: d
19- The d-block elements are the elements. ( a- representive, b- main transition, c- actinides, d- lanthanides)
19- b- main transition
20- In group IA, the largest atom lies at the .. Of the group. (a-top , b- middle, c- bottom, d- upper)
20- c- bottom
21- In group 7A, the smallest atom lies at the .. Of the group. (a-top, b- middle, c-bottom- d- right side)
21- a-top
22- The atom with atomic number (17) has similar properties as that of atomic number .. (a-11, b-13, c-35, d- 36)
22- c- 35
23- Calcium oxide is .. Oxide. (a-acidic, b-basic, c-neutral, d- a mphoteric)
23- b- basic
24- The 2nd ionization energy is then the 1st ionization energy. (a- greater, b-smaller, c- equal, d- nearly equal)
24- a- greater
25- Elements whose valence shell has less than half its capacity of electrons are (a-metalloids, b-metals, c-nonmetals, d- amphoteric)
25- b- metals
26- Elments whose valence shell has more than half its capacity of electrons are . (a-metalloids, b-nonmetals, c- metals, d- amphoteric)
26- b- nonmetals
27- Sulpher dioxide is oxide (a-basic, b-acidic, c-neutral, d- amphoteric)
27- b- acidic
28- Sodium hydroxide ionzed in water and release OH- because
.
a) Attraction between Na+ and O- is weak.
b) attraction between O- and H+ is weak.
c) Attraction between O- and H+ is strong.
d) a and b are correct answer.
c) attraction between O- and H+ is strong.
29- The strong oxygenated acid contain
a) more number of hydrogen atom.
b) more number of oxygen atom.
c) more number of non bonded oxygen atoms with hydrogen.
d) a and b correct answer
c) more number of non bonded oxygen atoms with hydrogen.
II. Mark the sign (  ) in front of the correct statements and the sign (
) in front of the correct statements and the sign (  ) in front of the woring ones:
) in front of the woring ones:
1- The elements of group IA have the electronic configuration 
1- 
2- The elements of group IIA have the electronic configuration 
2- 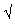
3- The elements of group IIIA have the electronic configuration 
3- 
4- The elements of IVA have the electronic configuration 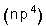
4- 
5- The elements of group VA have the electronic configuration 
5- 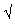
6- The elements of group VIA have the electronic configuration 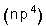
6- 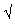
7- The elements of group VIIA have the electronic configuration 
7- 
8- The elements of zero group (VIII) have the electronic configuration 
8- 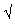
9- The element has the electronic configuration  lies under group
lies under group  in period 6.
in period 6.
9- 
10- In the same group, the atomic radius increases with the increase of ionization energy.
10- 
11- In the same group, the atomic radius decrease with the increase of electron affinity.
11- 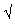
12- In the same group, the electronegativity increases with the increase of the atomic radius.
12- 
13-The atomic radius increase across a period with the increase in atomic number.
13- 
14- The electronegativity increases across a period with the decrease in atomic radius.
14- 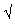
15- The element which its atomic no. 37 is a transition element.
15- 
16- The element which its atomic no. 27 is a transition element.
16- 
17- Fluorine ion has the same configuration of sodium ion.
17- 
18- The acidic properites of the elements across group 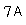 decrease with the increase of its atomic numbers.
decrease with the increase of its atomic numbers.
18- 
19- The oxidation no. of  equals (-2).
equals (-2).
19- 
20- The atomic raduis increases down a group with the increase in atomic number.
20- 
21- The raduis of a cation is less than that of its atom.
21- 
22- The raduis of the anion is less than that of its atom.
22- 
23- Perchloric acid  is the strongest acid.
is the strongest acid.
23- 
24- The oxidation No. of a noble gas = 0
24- 
25- Orthosiliconic acid H4SiO4 is stronger than sulphuric acid H2SO4
26- Perechloric acid HClO4 is the strognest acid in the 3rd peroid in the perodic table
26- 
27- Orthophoric acid H3PO4 contain four nonbinded oxygen atoms with hydrogen.
27- 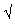
28- In sodium hydroxide NaOH the attraction between Na+ and O- is weaker than that between O- and H+
28- 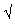
29- In perochoric acid HClO4 the attraction between Cl- and O- is weaker than that between O- and H+
29- 
III. Write down the scientific concept for each.
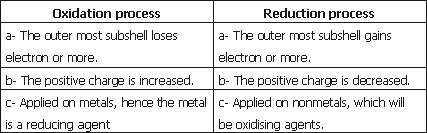
1- The process of losing electrons resulting in an increase in the positive charge.
1- Oxidation process.
2- The process of gaining electrons resulting in an increase in the positive charge.
2- Reduction process.
3- The No. of (+ve) or (-ve) electric charge that the atom would have in the compound, be it ionic or covalent.
3- Oxidation No.
4- All their energy levels are completely filled except for the external level.
4- Representative elements.
5- All their energy levels are completely filled except for the two external levels.
5- Transition elements (d-block).
6- All their energy levels are completely filled except for the three external levels.
6- Inner transition elements (f-block).
7- All their energy levels are completely filled with electrons.
7- Noble gases.
8- Half the distance between the centres of two similar atoms in a diatomic molecule.
8- Raduis of an atom.
9- The distance between the nuclei of two covalency bonded atoms.
9- The length of a covalent bond.
10- The amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from an atom in its gaseous state.
10- Ionization energy.
11- The amount of energy relased when an extra electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom.
11- Electron affinity.
12- The tendency of an atom to attract the electrons of the chemical bond to itself.
12- Electronegativity.
13- The energy required to convert an atom to an ion with one positive charge.
- 1st ionization energy
14- It is the energy required to convert M+ to M2+.
- 2nd ionization energy.
15- Group of elements whose vallence shell generally has less than half its capcity of electrons.
- Metals.
16- Group of elements form ionic compounds by gaining electrons.
-Nonmetals.
17- Group of elements that has a metallic appearance and has most of the properties of nonmetals at the same time.
- Metalliods.
18- Oxides react with alkalies forming salt and water.
- acidic oxide (non metallic oxide)
19- Oxides react with acids forming salt and water.
- Basic oxide (metal oxide)
20- Oxides react either as basic oxides or as acidic oxides.
- amphoteric oxides.
21- The formula that represents the acid or base as hydroxy compounds.
- MOH
IV. Differentiate between:
1- Metals and nonmetals.

2- Oxidation process and reduction process.
3- atomic raduis and ionic radius.

4- Electronegativity and electron affinity.

5- 1st. ionization energy of (Mg) and the 2nd one.
5-1st. ionization energy of Mg: 
2nd. ionization energy of Mg: 
The 2nd. ionization energy is nearly equals twice the 1st. ionization energy due to the increased nuclear charge
6- Basic, acidic and amphoteric oxides.

V. Calculate the oxidation No. of the element mentioned in each of the following:
1- Iron in ferricyanide ion  .
.
1-  X+(6X-1)=-3
X+(6X-1)=-3  X-6=-3 (X=3)
X-6=-3 (X=3)
2- Manganese in 
2-  X+ (2X-2)=0
X+ (2X-2)=0  X-4=0 (X=4) Manganese
X-4=0 (X=4) Manganese
 1+X+(4X-2)=0
1+X+(4X-2)=0  X-7=0 (X=7) Manganese
X-7=0 (X=7) Manganese
 X+(2X-1)=0
X+(2X-1)=0  X-2=0 (X=2) Manganese
X-2=0 (X=2) Manganese
3- Sulpher in  .
.
3- 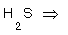 (2x1)+X=0
(2x1)+X=0  2+X=0 (X=2-) Sulpher
2+X=0 (X=2-) Sulpher
 (2x1)+X+(4X-2)=0
(2x1)+X+(4X-2)=0  2+X-8=0 (X=6) Sulpher
2+X-8=0 (X=6) Sulpher
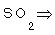 X+(2X-2)=0
X+(2X-2)=0  X-4=0 (X=4) Sulpher
X-4=0 (X=4) Sulpher
 X+(3X-2)=0
X+(3X-2)=0  X-6=0 (X= 6) Sulpher
X-6=0 (X= 6) Sulpher
4- Nitrogen in  .
.
4-  X+(3x1)=0
X+(3x1)=0  X+3=0 (X=3-) Nitrogen
X+3=0 (X=3-) Nitrogen
 X+(4x1)=1
X+(4x1)=1  X+4=1 (X=3-) Nitrogen
X+4=1 (X=3-) Nitrogen
 2X=0 (X=0) Nitrogen
2X=0 (X=0) Nitrogen
 X+(2X-2)=0
X+(2X-2)=0  X - 4 = 0 (X=4) Nitrogen
X - 4 = 0 (X=4) Nitrogen
5- Oxygen in  .
.
5-  (2x1)+X =0
(2x1)+X =0  2+X=0 (X=2-) Oxygen
2+X=0 (X=2-) Oxygen
 (2x1)+ (2X)=0
(2x1)+ (2X)=0  2+2X=0 (X=1-) Oxygen
2+2X=0 (X=1-) Oxygen
 1+2X=0
1+2X=0  2X=-1 (X=-1/2) Oxygen
2X=-1 (X=-1/2) Oxygen
6- Hydrogen in 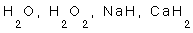 .
.
6-  2X-2=0
2X-2=0  2X=2 (X=1) Hydrogen
2X=2 (X=1) Hydrogen
 2X + (2X - 1)
2X + (2X - 1)  2x-2=0 (X=1) Hydrogen
2x-2=0 (X=1) Hydrogen
 1+X=0 (X=-1) Hydrogen
1+X=0 (X=-1) Hydrogen
 2+2X=0 (X=-1) Hydrogen
2+2X=0 (X=-1) Hydrogen
VI. Problem:
1- Knowing that the lenght of (Cl-Cl) equals 1.98  , and that between carbon and chlorine (C-Cl) equals 1.76
, and that between carbon and chlorine (C-Cl) equals 1.76  . Calcualte the raduis of carbon atom.
. Calcualte the raduis of carbon atom.
1- raduis of Chorine = (1.98/2) = 0.99 
raduis of carbon = 1.76-0.99 = 0.77 
2- Calculate:
a- the raduis of nitrogen atom.
b- the raduis of Hydrogen atom.
c- the lenght of the bond in ammonia molecule.
knowing that (N-N) equals 1.4  , and (H-H) equals 0.74
, and (H-H) equals 0.74  .
.
a- raduis of Nitrogen atom = 1.4/2 = 0.7 
b- raduis of Hydrogen atom = 0.74/2 = 0.37 
c- bond lenght in  = 0.7 + 0.37 = 1.07
= 0.7 + 0.37 = 1.07 
3- Calculate the bond length of (N-O) bond; knowing that the length of the bond in  equals 1
equals 1  , and (H-H) equals 0.74
, and (H-H) equals 0.74  , and that in water molecule equals 0.96
, and that in water molecule equals 0.96  .
.
3- raduis of Hydrogen = 0.74/2 = 0.37 
raduis of Nitrogen = (N-H) - raduis of 
= 1-0.377 = 0.63 

raduis of Oxygen ( O-H) - raduis of 
= 0.96 - 0.37 = 0.59 

Bond length (N-O) = 1 + 2 = 0.63 + 0.59 = 1.22 
 4- What's the bond length in (H-Cl), if you know that (H-H) = 0.74
4- What's the bond length in (H-Cl), if you know that (H-H) = 0.74  and that of (Cl-Cl) = 2 .
and that of (Cl-Cl) = 2 .
4- bond length (H-Cl) = raduis of  + raduis of
+ raduis of 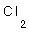 = 0.74/2 + 2/2 = 0.37 + 1 =
= 0.74/2 + 2/2 = 0.37 + 1 =
1.37 
VII. Complete:
1-  is ............ oxide, while
is ............ oxide, while  is ........... oxide.
is ........... oxide.
1- an amphteric, acidic.
2- Metals are characterised by the ............. raduis, and the ........... value of its electron affinity.
2- relative great, small.
3- The oxidation no. of oxygen in  equals ............, and that of phosphorus in
equals ............, and that of phosphorus in 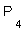 molecule equals ..............
molecule equals ..............
3- +1, 0
4- In actinide series the sublevel ........... is successively filled, and they are included in the ........... period.
4- 5f, seventh.
5- Lanthanides are ............ elements, where the sublevel .......... is successively filled.
5- 14, 4f
6- The first tranisition series includes ............... elements, the sublevel ........... is not filled.
6- 10, 3d
7- The maximum oxidation no. of an element never exceeds the No. of its ..............
7- group
8- There are groups A & B except group ............ and group ..........
8- eight, zero
9- Carbon dioxide is .......... odxide , cupper oxide is .......... oxide, and Zinc oxide is ............. oxide.
9- an acidic , basic, an amphoteric.
10- Orthosiliconic acid is . Than orthophosporic acid.
- weaker
11- Lithium hydroxide is . Than sodium hydroxide.
- weaker
12- The algebraic sum of the oxidation number of all atoms in a neutral compound is .
- zero
13- The oxidation number of group IA elements is always . While Group IIA elements is .
- (+1) , (+2)
14- Oxidiation no. of hydrogen in NH3 equal while with NaH equal
- (+1) , (-1)
15- When MOH ฎ M+ + OH- so MOH is considered as ..
- Base
16- The metallic character increase with the increase in the and . In groups.
- atomic No. , atomic radius
17- The fluorine is considered as the higest . Character, while Caesium is considered ast the highest ..
- non metallic - metallic
18- In peroids , the atomic raidus . but ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity .
- decrease, increase
VIII. Give reasons for:
1- Although the oxidation No. of oxygen is always = -2, we observe some exceptions.
1- The well known oxidation no. of Oxygen is (-2) in its normal oxides, but there are 3 exceptions:
a- its oxidation No. = (-1) in 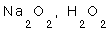
b- its oxidation No. = (-1/2) in 
c- its oxidation No. = (+2) in 
2- There are not redox changes in the following reactions:
- 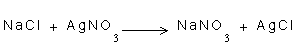
- 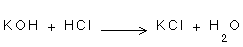
- 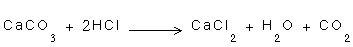
2- In the three mentioned equations, there is no loss or gain of electron, there is no decrease or increase of the positive charge.
3-  is used in dryign the acidic gas, and it is not used in drying basic gas.
is used in dryign the acidic gas, and it is not used in drying basic gas.
3-  is not used in drying the basic gases, becuause it is acidic and will react with such gases in there aqueous states.
is not used in drying the basic gases, becuause it is acidic and will react with such gases in there aqueous states.
4- Metals are electrapositive elements, while nonmetals are electronegative ones.
4- Becuase metals atom tend to lose electrons and converted to (+ve) ion while non metals tend to gain electrons and converted to (-ve) ions
5- The large value of ionization energy of the noble gases.
5- Because, thier energy levels are completely filled by electrons and they are very stable elements, so there is no loosely bound electron.
6- The electron affinity in the same group decreases as the atomic no. increases.
6- As the atomic No. increases, the outer most sublevel will be far from the nucleus and the attractive force for an extra electrons will decrease.
QUESTIONS and ANSWERS 2:





























SOLVE BY YOURSELF:
















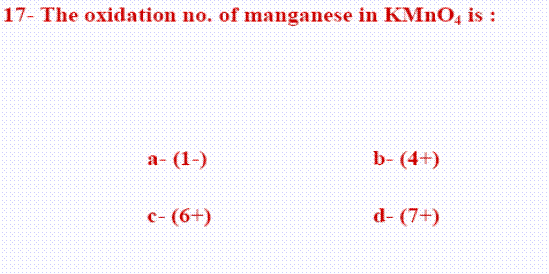


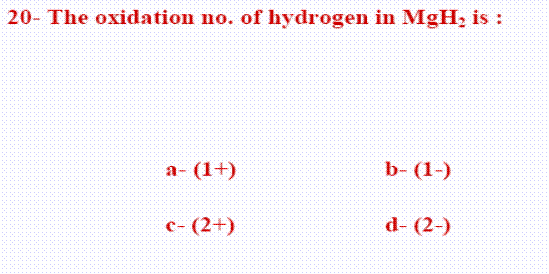
TEST 1 ON CH.2:
1 - The 2nd ionization energy is then the 1st ion
greater
smaller
equal
2 - The fourth period in the periodic table contains .
18
2
8
32
3 - In the same group, the electronegativity increase
True
False
4 - The s-block elements consists of .. Groups of e
2
6
8
5
5 - The element which its atomic no. 37 is a transitio
True
False
6 - The d-block elements are the elements
main transition
representive
actinides
lanthanides
7 - In the same group, the atomic radius decrease with
True
False
8 - The fifth period in the periodic table contains ..
18
2
32
8
9 - The atom with atomic number (17) has similar prope
35
11
13
10 - The acidic properites of the elments across group
True
False
11 - Fluoride ion has the same configuration of sodium
True
False
12 - The element which its atomic no. 27 is a transitio
True
False
13 - The first period in the periodic table contains ..
2
8
18
32
14 - Sulpher dioxide is oxide
acidic
acidic
neutral
15 - The atomic radius increase across a period with th
True
False
16 - In the same group, the atomic radius increases wit
True
False
17 - Calcium oxide is .. Oxide
basic
acidic
neutral
18 - The p-block consists of . groups of elements
6
8
10
14
19 - In group 7A, the smallest atom lies at the .. O
top
middle
bottom
20 - The electronegativity increases across a period wi
True
False
TEST 2 ON CH.2:






Date: 2015-12-18; view: 1713
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Chapter III. Tom's meeting with the Prince. | | | Read the text and fill in the missing words. Compare with a partner. |