
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Materials based on the ground wood
The ground wood appears both directly at sawmill and woodworking (sawdust, cutting waste) and after the special processing of raw waste lumber and non high quality wood (chips, shaving, fibred mass). It is possible to divide the construction materials from the ground wood into two groups:
- without application of the special binders or with their small addition;
- with the use of organic or mineral binders.
The wood particles are bound as a result of approaching and fiber splicing, their cohesiveness and action of physical and chemical bonds which arise up at piezo-thermal treatment in the materials of the first group.
Cane fiber boards are materials which are formed from wooden fibred mass with next thermal treatment. The boards can be also obtained from the fibers of bast plants or from the other fibred raw material which has sufficient durability and flexibility.
Depending on assignment the hard and soft boards are made.
Hard boards are intended for the facing of internal surfaces of buildings, the solid doors and other elements of house-building, soft - for heat-insulation of non-load-bearing structures and sound-proofing of partitions.
The cane fibers are tooling added, they can be endued with the texture of wood, skin and others like that.
Finishing boards are faced with the synthetic polymers with the gasket of texture paper. They are produced also with a matte surface or painted water-emulsion polyvinyl acetate paints. Boards, painted by enamels, have a glossy surface, enhanced water resistance.
The lignin carbohydrate and piezothermoplastics are the varieties of wood plastics, obtained from sawdust or raw waste lumber of agricultural production with the use of hot compaction. At the working of wood plastics there is a partial hydrolysis of polysaccharides of wood and formation of organic acids which are the catalysts of destruction of lignin carbohydrate complex under the action of temperature. Chemically active products (lignin and carbohydrates) interact between themselves at pressing. The stronger and dense material than initial wood appears in a result.
The substantial lacks of production of lignin carbohydrate plastics is a necessity of powerful press equipment and protracted cycle of pressing.
Piezothermoplastics can be made from sawdust by the two methods: without previous treatment of raw material and with its hydrothermal treatment.
According to the first method of piezothermoplastic production, the technology is similar to the method of obtaining of lignin carbohydrate plastics.
According to the second method, the standard sawdust less than 4 mm are processed in the autoclaves with vapor at a temperature 170-180°C and pressure 0.8-1 MPa. The hydrolyzed compacted mass is partly dried out and at certain humidity consistently exposed to the cold and hot pressing. Specific pressure of the cold and hot compaction is 15 MPa; temperature is 160°C.
Piezothermoplastics are divided into isolation, semisolid, hard and extra-hard.
At an average density 700-1,100 kg/m3 piezothermoplastics, made from birch sawdust, have the static bending strength 8-11 MPa. At an enhanced average density - to 1,350-1,330 the kg/m3 the ultimate strength arrives at 25-40 MPa.
The physical-mechanical properties of piezothermoplastics allow applying them for floors, doors, and also as finishing material.
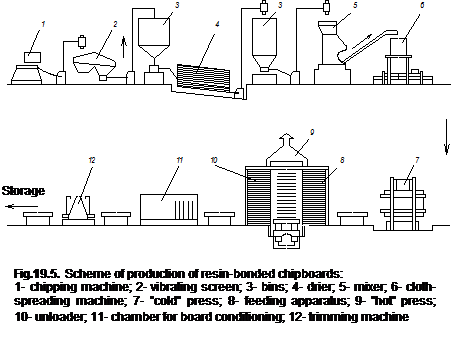
The resin-bonded chipboards are the most widespread among the materials with organic binder. This material is obtained by the hot compaction of the ground up wood, mixed with synthetic polymers (Fig. 19.5). Its advantages are homogeneity of physical-mechanical properties, possibility of high mechanization and automation of the manufacturing.
Industry produces flat and extrusion boards. At the first, the particles are placed parallel, in the second - athwart to the plane of board. It is arrived at the extrusion method of pressing.
Range of application of resin-bonded chipboards is various. As structurally finishing materials they are applied at arranging of floors, ceilings, walls, partitions, doors, built-in furniture and others like that. Easy boards are applied for heat-insulation.
The main representatives of group of materials on wood fillers and mineral binders are cement wood (sawdust concrete), woodwool and xylolite.
Cement wood is a light-weight concrete on the phytogenous aggregates, preliminary treated with the solution of mineralizer. It is used mainly as panels and blocks for the construction of walls and partitions, floor and roof slabs of buildings, heat-insulation and sound insulating slabs. Cement wood structures are exploited at relative humidity of premises not more than 60%, it is required to use the vapor sealing layer at greater humidity.
The systematic action of corrosive environments and temperatures on the cement wood more than 50°C and below zero of 40°C is shut out.
External surface of structure from to the cement wood which contacts with the precipitations, regardless of the humidity conditions of exploitation must have a texture (finishing) layer.
Depending on an average density in the dried up state a cement wood concrete is divided into heat-insulation (with density up to 500 kg/m3) and constructional (500-850 kg/m3).
The best type of aggregate for the cement wood is a wood mass (hogged chips) with attitude of the most size of particles toward the least 5-10, in thickness particles 3-5 mm and by the most length to 25 mm. Such form of particles allows approaching moisture deformations along and across the grains and reducing the negative influence on the structure formation and strength of this type of concrete.
Hogged chips from coniferous and deciduous wood are wet with the water or in solutions of mineral salts to decline the amount of harmful extract substances. Last, neutralizing the action of harmful substances in wood, simultaneously forces the cement hardening.
Technology of cement wood products includes the preparation of basic materials, obtaining of mixture and it’s placing in forms, hardening and drying, finishing and storage. Along with the non-reinforced products from the cement wood the products, reinforced by the steel reinforcement are manufactured.
At relative air humidity higher than 60% reinforcement is placed in a protective layer from a cement concrete which provides reliable bypassing of steel. It is recommended also to protect reinforcement by the special coatings.
A cement wood has the best heating engineering descriptions, than claydite concrete, that allows erecting the walls of the less thickness. The replacement of traditional materials with the cement wood allows reducing mass of buildings in 1.3-1.5 times. At the equivalent thickness of wall according to the conditions of heat-transfer, the mass of one square meter of cladding structure from the cement wood is in 7-8 times below, than from a brick and in 2-3 times below, than from claydite concrete.
Woodwool consists of the mineral binder and wood shaving as aggregate and simultaneously reinforcing component.
Woodwool with an average density 400 kg/m3 is applied for a thermal isolation. A heat-insulation woodwool has thermal conductivity 0.09-0.12W/(m·K).
At the average density not more 400 kg/m3 and more the woodwool as constructive-heat insulating material simultaneously can be utilized for the erecting of walls and ceilings.
Woodwool differs with the high acoustic absorption, the predefined connecting character of pores, and also good capacity for treatment, nailing, tripping with a bonding plaster and concrete. Negative properties of woodwool are considerable air permeability, big water absorption, low water resistance and ability to the fungi defeating in the moisture state.
Xylolite is an artificial construction material that is obtained as a result of hardening of mixture, which consists of magnesia cement, sawdust and solution of chloride or magnesium sulphate. This material is mainly used for arrangement of monolithic or precast floor coverages. Advantages of xylolite floors are their low coefficient of heat-absorption, hygienics, sufficient hardness, high abrasion resistance and possibility to the various coloring.
The recommended xylolite mixture consists of caustic magnesite and sawdust in ratio by a volume 1:1.5-1:1.4. The content of caustic magnesite at 100 m2 of coverage with the thickness at 10 mm is 410-620 kg and crystalline chloride of magnesium - 260-400 kg.
Date: 2015-12-18; view: 1572
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Wooden materials and products | | | ARTICLES WITH PROPER NAMES |