
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Products of autoclave hardening
Products of autoclave hardening are one of the most widespread wall construction materials aside from the ceramic bricks and precast concrete. The silica bricks and wall products from cellular concrete are the most used autoclave products. The abundance of autoclave products is explained by the prevalence of raw materials, simplicity of technology, high quality and low cost.
The main raw materials for manufacture of autoclave products are the binders used for autoclave hardening and aggregates. Binders of autoclave hardening at normal temperature and moisture conditions and steaming are characterized by relatively low strength. However, their strength increases significantly as the temperature and pressure in the autoclave increase. This results in obtaining an artificial stone of high strength.
Binders of autoclave hardening are divided into clinker-free, lime-based withsilica and aluminosilicate components (lime-silica, lime-ash, etc.) and composite, based on Portland cement or Portland cement with lime and aluminosilicate components (sand, pozzolanic and slag cements). The strength of these binders depends on the ratio between components, their chemical and mineralogical composition and fineness of grinding. Components of binders should be characterized by a reduced water demand for production of durable and frost-resistant products.
Lime – silica binders are the most widespread of the production of autoclave products. Their main components are air-hardening lime and powdered quartz sand. Fly ash and others industrial wastes can also be used as the silica component of these binders along with fine-grained sand.
Autoclave hardening occurs as the result of chemical reactions between components of the binder in the presence of water under high pressure and temperature. The main chemical process during autoclaving is the interaction between calcium hydroxide, silica and water. As a result of this chemical process calcium hydrosilicates, are formed. Thus an artificial conglomerate can be obtained. The speed of chemical reactions and strength of the conglomerate are increased if the initial materials have the higher dispersibility.
Lime-sand bricks are non-fired wall material made from a mixture of quartz sand and lime-silica binder, by pressing and subsequent autoclaving under the action of steam of high pressure.
Manufacture of lime-sand bricks involves making lime-silica binder by screening of sand, lime burning and grinding in ball mills along with the sand. This is then followed by mixing of sand with lime-silica binder and slaking of the mixture produced, pressing the bricks and steaming it in the autoclave.
Lime content in the raw material mixture is in the range of 7-10% (by the CaO content). Quartz sand with grains in the range of 2-0.2 mm can be used; content of clay impurities in sand should not be more than 10%.Duration of full cycle of autoclave processing is 8-12 hours under the pressure of 0.8-1.6 MPa.
Solid or hollow lime-sand bricks based on heavy-weight or light-weight aggregates can be manufactured. Average density of light-weight bricks is not more 1400 kg/m3, and ordinary solid bricks – not more 1650 kg/m3. Products may be manufactured as white or colored.
Effective lime-sand products have thermal conductivity of not more than 0.486 W/(m·K), they can reduce the thickness of structures on comparison with the ordinary ceramic bricks.
Ultimate compressive strength of lime-sand bricks and blocks is in the range of 7.5-30 MPa and freeze-resistance range between 15-50 cycles of freezing and thawing.
Water absorption of lime-sand products should not be less than 6%.
Along with ordinary bricks, face lime-sand bricks and blocks are produced.
The lime-sand bricks are used along with ceramic brick for masonry work of overground structures. As the result of insufficient waterproofing, lime-sand brickscannot be used for foundations of buildings. Application of these bricks at high moisture and also in conditions of high temperatures without special protection is not permitted.
The technical economic indexes of lime-sand brick are higher than those of ceramic bricks due to the lower fuel and energy consumptions, and lower labour-intensiveness.
Lime-slag and lime-ash bricks are the varieties of lime-sand bricks.
Also, cellular concrete blocks can be manufactured by autoclaving. Such blocks can have different dimensions. Ultimate strength of blocks is in the range of 2.5-10 MPa. The average density of blocks varies depending on the strength. For example, density of blocks having a strength of 2.5 MPa equals 500 -700 kg/m3; for a strength of 10 MPa, density ranges between 900 -1100 kg/m3.
Blocks from cellular concrete are used for masonry work of structures involving dry operating conditions. Vapor sealing is needed if there are moist operating conditions.
Exterior walls of cellular concrete blocks are covered with cement plaster. Application of cellular concrete blocks, reduces the weight of walls by up to 4-5 times, compared with the lime-sand brick.
Gypsum products
 Gypsum binder is used for the production of gypsum sheathing, slabs and panels, wall stones, facing, architectural and ornamental products, air channels, etc. Gypsum products are light-weight, have a low density, and are non-combustible. However, they have reduced strength when moistened and are characterized by plastic deformation under the influence of loads. Their water-resistance increases when 5-25% of lime, granulated blast furnace slag, at impregnation with the carbamide resins, organic-silicon fluids, etc are added. In many cases, water-resistance of gypsum products is increased when produced in composite forms useing gypsum-cement-pozzolanic binders andgypsum-cement-slag binders.
Gypsum binder is used for the production of gypsum sheathing, slabs and panels, wall stones, facing, architectural and ornamental products, air channels, etc. Gypsum products are light-weight, have a low density, and are non-combustible. However, they have reduced strength when moistened and are characterized by plastic deformation under the influence of loads. Their water-resistance increases when 5-25% of lime, granulated blast furnace slag, at impregnation with the carbamide resins, organic-silicon fluids, etc are added. In many cases, water-resistance of gypsum products is increased when produced in composite forms useing gypsum-cement-pozzolanic binders andgypsum-cement-slag binders.
Gypsum products are used for facing bricks, reinforced concrete, wood surfaces of dwelling houses, public and industrial buildings with dry and normal moisture operating conditions. Increasing the strength of gypsum products with reduced average density is achieved by their reinforcement with fibrous materials. One of the most effective ways to reduce the weight of gypsum products is through creating a porous or cellular structure by introduction of foam into the gypsum mixture.
High aesthetic properties and simplicity of technology give gypsum products a very good visual effect when used as facing for structures of different types.
The most widespread are gypsum paper boards, the decorative appearance and sound-absorbing properties of which are provided through perforations, facing with film materials and application of drawings on the board. Gypsum paper boards consist of a hardened gypsum core, firmly connected to the carton envelope (Fig. 13.3). The process of gypsum paper boards manufacturing includes making of the molding mass, carton preparation, forming of the continuous sheet, cutting it into separate boards after curing and drying in the tunnel dryers. The humidity of the boards should not be more than 1%.
 |
The density is about 950 kg/m3, and thefailure load is in the range of 250-520 N, depending on the thickness. The boards usually have a rectangular shape and come in different dimensions.
Gypsum fibre boards, unlike the gypsum paper boards, are reinforced not by carton, but with uniformly positioned fibers. Loosened waste-paper is used mainly as a fibrous initial material. The main advantageof gypsum fibre boards, as compared with gypsum, is higher strength. They keep the shape during drying and wetting, provided a good microclimate exists in hot and cold weather. They also have high sound insulating ability, are noncombustible, have good processability,are easily glued by paper and colored plastics. Veneered. Gypsum fibre boards are applied in the same ways as gypsum paper boards. Along with gypsum fibre boards, gypsum fibre slabs can be manufactured, whichareused as window stools, elements of built-in furniture, etc.
Gypsum decorative boards are produced usually as cast, smooth or corrugated, with different patterns on the surface, reinforced and non- reinforced, with fillers or without them. Gypsum decorative boards are produced, usually square with different dimensions.
Glass cloth, galvanized iron, aluminum and other materials are used for reinforcement of boards.
Front-face area of boards can be covered with water-repellent compounds to reduce the water absorption.
 Pressed gypsum boards (artificial marble) can also be manufactured. They are obtained from water-gypsum mixture at specific pressure 7-10 MPa with removing of water surplus and curing under the pressure till the beginning of gypsum hardening. Products obtained after 1.5 hours of the formation have compressive strength values ranging from 25-28 MPa and 10% humidity. They are characterized by glossy a surface that imitates the color and texture of natural marble. The products can also be polished to get a smooth surface.
Pressed gypsum boards (artificial marble) can also be manufactured. They are obtained from water-gypsum mixture at specific pressure 7-10 MPa with removing of water surplus and curing under the pressure till the beginning of gypsum hardening. Products obtained after 1.5 hours of the formation have compressive strength values ranging from 25-28 MPa and 10% humidity. They are characterized by glossy a surface that imitates the color and texture of natural marble. The products can also be polished to get a smooth surface.
Artificial marble can be used for internal facing of shops, markets, bus terminals, halls, etc.
Considerable amount of gypsum products are used as acoustic materials to build acoustical ceilings and walls ashlaring.
Sound-absorbing boards consist of gypsum perforated screen and absorbent materials, which are heat-insulating plates based on glass fiber, mineral wool, pearlite sand, etc.
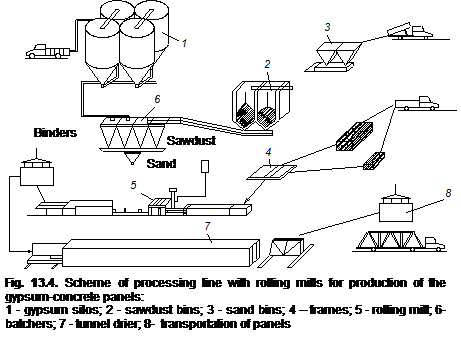
Basic typesof gypsum-concrete products are: blocks and panels for walls, ventilation panels and sanitary cabins. Gypsum concrete are reinforced with different fibrous materials, metallic and wooden elements. Their density range between 800 -1900 kg/m3, but the ultimate strength depends on the type of mineral aggregates used. For heavy-weight mineral aggregates, the ultimate strength is between 8-12 MPa; light-weight porous aggregates – 3.5 to 7 MPa, organic – 1 to 3 MPa.
 Processing lines with rolling mills are widely used for mass production of the gypsum-concrete panels (Fig. 13.4, 13.5).
Processing lines with rolling mills are widely used for mass production of the gypsum-concrete panels (Fig. 13.4, 13.5).
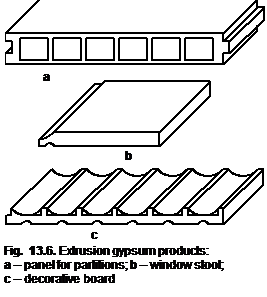
Extrusion is an advanced method of gypsum products manufacture. Extrusion allows forming of products (Fig. 13.6) from the plastic gypsum mixtures with low water contentofany cross-section with the high voidage, low weight, and compressive strength up to 30 MPa.
Wall gypsum blocks are produced by casting or other methods and can be used for frame fillings of structures. Blocks are manufactured on conveyor lines. Gypsum blocks are of 100% fire safe. Once installed, they can be quickly finished. Paintwork, wallpaper, tiles and sprayed finishes can be applied. These products have high mechanical resistance.
Date: 2015-12-18; view: 1010
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Asbestos - cement products | | | REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIALS |