
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Describe the Incomplete Information Factors
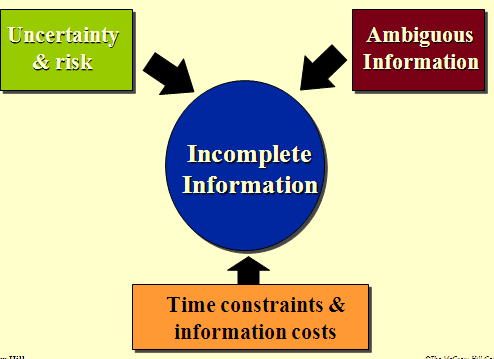
∑ Incomplete information exists due to many issues:
∑ Risk: managers know a given outcome can fail or succeed and probabilities can be assigned.
∑ Uncertainty: probabilities cannot be given for outcomes and the future is unknown.
∑ Many decision outcomes are not known such as a new product introduction.
∑ Ambiguous information: information whose meaning is not clear.
∑ Information can be interpreted in different ways.
∑ Time constraints and Information costs: Managers do not have the time or money to search for all alternatives.
∑ This leads the manager to again decide based on incomplete information.
∑ Satisficing: Managers explore a limited number of options and choose an acceptable decision rather than the optimum decision.
∑ This is the response of managers when dealing with incomplete information.
∑ Managers assume that the limited options they examine represent all options.
Describe the The Planning Process
Planning is the process used by managers to identify and select goals and courses of action for the organization.
l The organizational plan that results from the planning process details the goals to be attained.
l The pattern of decisions managers take to reach these goals is the organizationís strategy.
Planning - is the process of developing a plan that defines the who, what, with what resources and when to perform. To plan the necessary development goal (the desired result) organization. Planning is correlated with the success of the organization. The greatest success of the plans - in terms of ratio of profit to sales volume and return on capital.
Key components of organizational planning:
- Definition of the mission and goal-setting (the main general goal of the organization - is a clear cause or mission)
- making decisions.
Planning principles: timeliness, comprehensiveness, rationality.
The planning process (stages):
- Forecasting;
- Identification and selection of development options;
- Formulation of objectives;
- Development of action programs and scheduling of work;
- Budgeting (budgeting).
Planning Methods:
- Matrix (based on standardized units)
- Optimal (based on defined criteria)
- Adaptive (note change)
- The balance (a balance of income and expenditure)
- Planning from the achieved level (based on data for the period)
- Planning with a focus on competition
Date: 2015-12-18; view: 805
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Describe the Industry Life Cycle | | | Characteristics of Plans |