
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
WHAT IS LAW?
Law is the whole set of rules that are supported by the power of government1 and that control the behavior of members of a society. The law itself provides the2 basic structure within which commerce and industry operate. It safeguards the rights3 of individuals, regulates their dealings with others and enforces the duties of4 government. 5
There are two main kinds of the law - public and private (civil). Private law6 concerns disputes among citizens within a country, and public law concerns disputes7 between citizens and the state, or between one state and another. The system of law8 consists of different categories of law. Constitutional law is a leading category of the9 whole system of law. Its principal source is the country's Constitution. It deals with10 social structure, state system, organization of state power and the legal status of11 citizens. Most countries have a formal written Constitution describing how laws are12 to be made and enforced. 13
Administrative law is closely connected with constitutional law but it deals14 with the legal forms of particular executive and administrative activity of a15 government and ministries. Criminal law defines the general principles of criminal16 responsibility, individual types of crimes and punishment applied to criminals.17 Crimes are wrongs which, even committed against an individual are considered to18 harm the well-being of society in general. Criminal law takes the form of a criminal18 code. 19
International law regulates relations between government and also between20 private citizens of one country and those of another. Financial law regulates the21 budget, taxation, credits and other spheres of financial activity. Civil law is connected with relations in the economic sphere of life, with relations involving property, its23 distribution and allocation. The right in property is the central institution of civil law. The rules of employment law include legislation on the employment of industrial and office workers and regulate matters arising from employment relations. 26
As well as defining the powers of government, most constitutions describe the fundamental rights of citizens. These usually include general declarations about28 freedom and equality, but, also some specific provisions. The European Convention29 on Human Rights (ECHR) was first adopted in 1950 and has now been signed by30 every country of Western Europe Individual citizens of these countries have the right to bring a complaint before the European Commission if they think their government has broken the Convention. But despite the development of legally binding national33 and international conventions, millions of people in the world still do not enjoy34 human rights. 35
Task 1. Practice to pronounce the words given below.
civil, human, commerce, fundamental, constitutional, provision, ideological, complain, equality, binding
Task 2. Match the English words and word-combinations given below with their
Russian equivalents.
| 1) civil law | |
| 2) European Convention on Human Rights | |
| 3) specific provisions | |
| 4) legally binding | |
| 5) behavior of members of a society | |
| 6) freedom and equality | |
| 7) to enable citizens | |
| 8) to regulate one’s dealings | |
| 9) despite | i) þðèäè÷åñêè îáÿçûâàþùèé |
| 10) commerce and industry_ | g) íåñìîòðÿ íà |
Task 3. Math the following words and phrases with their definitions below:
civil law, criminal law, international law, public law, constitutional law, law, financial law
1) ………. is a system of rules established by the state.
2) ……….. is a leading category of the whole system of law.
3) ………... concerns disputes among citizens within a country.
4) ………... concerns disputes between citizens and the state, or between one state and another.
5) ……….. regulates relations between governments and also between private citizens of one country and those of another.
6) ………... defines the general principles of criminal responsibility.
7) ……….. regulates budget, taxation and other spheres of financial activity.
Task 4. Read the text in detail to find the answers to the questions below:
1) What is law?
2) What is the main aim of law?
3) What categories of law does the system of law in Russia consist of?
4) What is the principle source of constitutional law?
5) What category of law is closely connected with constitutional law?
6) What is the central institution of civil (private) law?
7) What does criminal law define?
8) What does international law regulate?
9) What is civil law connected with?
10) What rules does employment law include?
11) When was ECHR adopted?
12) What does ECHR deal with?
Task 5. Fill in the following chart:
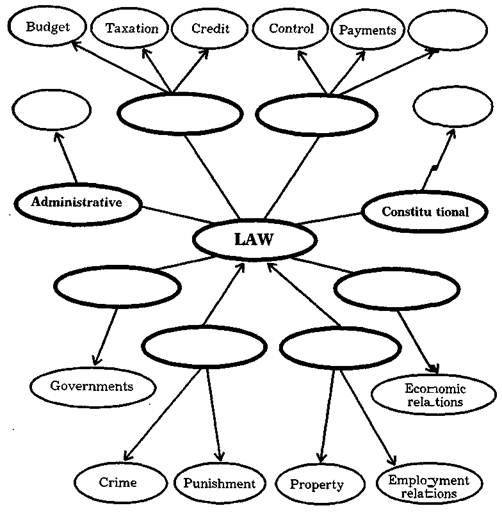
Task 6. Define:
1) which category of law deals with:
a) budget, taxation, state credits
b) relations in the economic sphere of life
c) matters arising from employment relations
d) individual types of crimes and punishment
e) legal forms of executive and administrative activity
2) which category of law would deal with the following crimes:
a) robbery
b) smuggling
c) violation of human rights
d) failure to pay customs duties
e) speed limit excess
Ex. 7. Comprehension check.
1. What does "it” in line 10 refer to?
a) Constitution
b) constitutional law
c) principal source
2. What does "its" in line 10 refer to?
a) constitutional law
b) leading category
c) system of law
3. What does "it” in line 14 refer to?
a) law
b) constitutional law
c) administrative law
4. What does "its" in line 23 refer to?
a) relations
b) property
c) sphere of life
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 6471
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| SOCIAL MORALITY, RULES AND LAW | | | Vocabulary Exercises |