
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
PARAMETERS OF LABOR PRODUCTIVITY
Labor productivity characterizes the efficiency of work in production of goods. It is not only one of the major parameters of the production efficiency, but also a parameter of a great economic and social value at the macrolevel. Citizens of that country where the best labor productivity is achieved will have the highest standard of living.
According to statistics, the USA is richer than European countries. Wall Street Journal informs that labor productivity in all sectors of economy in the countries of the European union is on the average by 20 % lower than in the USA, it especially concerns industrial production.
Labor productivity is the amount of production made for a certain period counting for one worker or expenditures of working time for a unit of production.
It is necessary to distinguish concepts of productivity and intensity of work. When increasing intensity of work the amount of physical and intellectual efforts during a unit of time raises and due to it the amount of production made during a unit of time increases. The increase of intensity of work demands increase of payment for it. Labor productivity rises as a result of changes in technology, application of more perfect equipment, application of new methods of work and not always demands increase of wages (fig. 1). The parameters determining labor productivity level take into account both changes in productivity proper and intensity of work.
The indicator determining the amount of production made during a unit of time is referred toas the manufacturing index. The manufacturing index characterizes the effectiveness of labor.
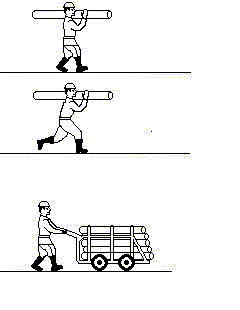
Fig. 1. Productivity and intensity of work
The labour inputis the amount of work necessary for manufacturing a unit of production. Labor input is a characteristic of cost-based labor (consumption of labor force).
Natural (t, m, m3, pieces, etc.) and cost parameters are used as measuring instruments of the amount of production manufactured.
The manufacturing index is defined for one basic worker, for one worker and for one working person.
When defining the manufacturing indexfor one basic worker the amount of production manufactured is divided by the number of basic workers.
When defining the manufacturing indexfor one worker the amount of production manufactured is divided by the total number of basic and auxiliary workers.
When defining the manufacturing indexfor one working person the amount of production manufactured by the total number of the industrial and production personnel:
MI = P m / N w , (1)
where MI is the manufacturing indexof production; Pm is the amount of production manufactured for the period in natural or cost measuring instruments; N w is the number of workers (basic workers, basic and auxiliary workers, the industrial and production personnel).
The labour input of production, as well as the manufacturing index, can be calculated in different ways. Technological, industrial and full labor inputs are distinguished.
Technological labor input of production is found with the help of the division of labor expenditure of basic workers by the amount of the production manufactured by them.
Industrial labor input of production is calculated with the help of the division of labor expenditure of basic and auxiliary workers by the amount of production manufactured.
Full labor input is defined with the help of the division of labor expenditure of the industrial and production personnel by the amount of production manufactured:
LI = L exp / V m , (2) where LI is the labor input of production; L exp represent labor expenditure of various categories of working people for production manufacturing; V m is the volume of production manufactured.
Date: 2015-12-18; view: 1131
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF PERSONNEL | | | BASIC FORMS OF PAYMENT AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON RESULTS OF ENTERPRISE ACTIVITY |