
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Morphological composition of nouns.
The United States has a capitalist mixed economy, which is fueled by abundant natural resources, a well-developed infrastructure, and high productivity.
Mining. The United States is a major contributor to the global mining industry – petroleum, natural gas and coal.
Agriculture – is a major industry in the United States and the country is a net exporter of food. The country is a top producer of corn, soy beans, rice, and wheat. Beef cattle rank as most valuable product of American farms. Other leading farm products, in order of value, include milk, chickens and eggs, cotton. US farms also produce large amounts of hay, tobacco, turkeys, potatoes, tomatoes, apples and peanuts.
Fishing. The greatest quantities of fish are taken from the Gulf of Mexico (shrimp, oysters). The Pacific Ocean supplies Alaska Pollock, cod, crabs, herring, salmon, tuna. The Atlantic yields cod, flounder, herring and other fish.
Manufacturing. The value of American manufactured goods is greater than that of any other country. The leading categories of US products are, in order of importance, transportation equipment, food products, chemicals, nonelectrical machinery, electrical machinery and equipment, fabricated metal products, printed materials, primary metals, paper products, scientific and medical instruments.
Services: finance, insurance, real estate, commodity and security exchanges.
Creative industries: include more than 12,000 stations, about 1,550 television stations, and more than 1,400 cable TV systems. Hollywood film industry and popular music also make a great contribution to the country’s economy.
Transport. The backbone of the nation’s transportation infrastructure is a network of high-capacity highways. America created car culture, so don’t be surprised by the fact that nearly everyone of legal driving age has a car and uses it at every possible opportunity.
The rail network is among the world’s best, though the passenger rail network is underdeveloped by European and Japanese standards. For a country that owes so much to the penetration of railroads and that has such a potent railroad mythology, the US has a train system that can be surprisingly impractical and not always comfortable. Ticket prices vary in value, but the earlier you make a reservation, the cheaper the ticket.
Air travel is the preferred means of travel for long distances. Most visitors arrive by air, and heavy competition on popular routes means that inexpensive flights are often available. The main international airports are in Boston, New York, Washington, Miami, Chicago, Dallas-Fort Worth, Houston, Atlanta, Denver, Seattle, San Francisco and Los Angeles. There are connecting flights from these airports to hundreds of other US cities.
IT. The major centres for technology in the USA are the San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Northwest.
Silicon Valley is the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area in Northern California, United States. The term originally referred to the region’s large number of silicon chip innovators and manufacturers, but eventually came to refer to all the high-tech businesses in the area; it is now generally used as a metonym for the high-tech sector. Despite the development of other high-tech economic centers throughout the United States, Silicon Valley continues to be the leading high-tech hub because of its large number of engineers and venture capitalists. Geographically, Silicon Valley encompasses the northern part of Santa Clara Valley and adjacent communities.
5. Washington, D.C. – the capital city of the United States
Washington, D.C. is the capital of the United States, founded on July 16, 1790. The City of Washington was originally a separate municipality within the Territory of Columbia until an act of Congress in 1871 effectively merged the City and the Territory into a single entity called the District of Columbia. It is for this reason that the city, while legally named the District of Columbia, is known as Washington, D.C. The city is located on the north bank of the Potomac River and is bordered by the states of Virginia to the southwest and Maryland to the other sides. The District has a resident population of 591,833.
Washington replaced Philadelphia as the nation’s capital in 1800.
The District has a total area of 177 km2, of which 159 km2 is land and 18 km2 (10.16%) is water. The District is no longer 260 km2 due to the retrocession of the southern portion of the District back to the Commonwealth of Virginia in 1846. The District’s current area consists only of territory ceded by the state of Maryland. Washington is therefore surrounded by the states of Maryland to the southeast, northeast, and northwest and Virginia to the southwest.
Washington, D.C. is a planned city. The design for the City of Washington was largely the work of Pierre Charles L’Enfant, a French-born architect, engineer, and city planner who first arrived in the colonies as a military engineer with Major General Lafayette during the American Revolutionary War. In 1791, President Washington commissioned L’Enfant to plan the layout of the new capital city. L’Enfant’s plan was modeled in the Baroque style, which incorporated broad avenues radiating out from rectangles and circles, providing for open space and landscaping. In March 1792, President Washington dismissed L’Enfant due to his insistence on micromanaging the city’s planning, which had resulted in conflicts with the three commissioners appointed by Washington to supervise the capital’s construction. Andrew Ellicott, who had worked with L’Enfant surveying the city, was then commissioned to complete the plans. Though Ellicott made revisions to the original plans, including changes to some street patterns, L’Enfant is still credited with the overall design of the city. The City of Washington was bounded by what is now Florida Avenue to the north, Rock Creek to the west, and the Anacostia River to the east.
Major sights of Washington, D.C.
 The United States Capitol serves as the seat of government for the United States Congress, the legislative branch of the U.S. federal government. It is located in Washington, D.C., on top of Capitol Hill at the eastern end of the National Mall. Although not in the geographic center of the District of Columbia, the Capitol is the origin by which the quadrants of the district are divided. Officially, both the east and west sides of the Capitol are referred to as “fronts”. Historically, however, the east front was initially the side of the building intended for the arrival of visitors and dignitaries.
The United States Capitol serves as the seat of government for the United States Congress, the legislative branch of the U.S. federal government. It is located in Washington, D.C., on top of Capitol Hill at the eastern end of the National Mall. Although not in the geographic center of the District of Columbia, the Capitol is the origin by which the quadrants of the district are divided. Officially, both the east and west sides of the Capitol are referred to as “fronts”. Historically, however, the east front was initially the side of the building intended for the arrival of visitors and dignitaries.
The building is marked by its central dome above a rotunda and two wings, one for each chamber of Congress: the north wing is the Senate chamber and the south wing is the House of Representatives chamber. Above these chambers are galleries where visitors can watch the Senate and House of Representatives. It is an example of the neoclassical architecture style. The statue on top of the dome is the Statue of Freedom.
Underground tunnels (and even a private underground railway) connect the main Capitol building with each of the Congressional office buildings in the surrounding complex. All rooms in the Capitol (540) are designated as either S (for Senate) or H (for House), depending on whether they are north (Senate) or south (House) of the Rotunda.
 The White House is the official residence and principal workplace of the President of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., it was built between 1792 and 1800 of white-painted Aquia sandstone in the late Georgian style and has been the executive residence of every U.S. President since John Adams. When Thomas Jefferson moved into the home in 1801, he (with architect Benjamin Henry Latrobe) expanded the building outward, creating two colonnades which were meant to conceal stables and storage.
The White House is the official residence and principal workplace of the President of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., it was built between 1792 and 1800 of white-painted Aquia sandstone in the late Georgian style and has been the executive residence of every U.S. President since John Adams. When Thomas Jefferson moved into the home in 1801, he (with architect Benjamin Henry Latrobe) expanded the building outward, creating two colonnades which were meant to conceal stables and storage.
The White House is made up of six stories – the Ground Floor, State Floor, Second Floor, and Third Floor, as well as a two-story basement. The term White House is regularly used as a metonym for the Executive Office of the President of the United States and for the president’s administration and advisors in general. The property is owned by the National Park Service and is part of the President's Park.
The Washington Monument (also known as Pencil) is the most prominent structure in Washington, D.C. and one of the city’s early attractions. It was built in honor of George Washington, who led the country to independence and then became its first President. The Monument is shaped like an Egyptian obelisk and offers views in excess of thirty miles. It was finished on December 6, 1884.
 The Lincoln Memorial stands at the west end of the National Mall as a neoclassical monument to the 16th President. The memorial is designed by Henry Bacon, after ancient Greek temples. It is surrounded by a peristyle of 38 fluted Doric columns, one for each of the thirty six states in the Union at the time of Lincoln’s death, and two columns in-antis at the entrance behind the colonnade. The north and south side chambers contain carved inscriptions of Lincoln’s Second Inaugural Address and his Gettysburg Address. Lying between the north and south chambers is
The Lincoln Memorial stands at the west end of the National Mall as a neoclassical monument to the 16th President. The memorial is designed by Henry Bacon, after ancient Greek temples. It is surrounded by a peristyle of 38 fluted Doric columns, one for each of the thirty six states in the Union at the time of Lincoln’s death, and two columns in-antis at the entrance behind the colonnade. The north and south side chambers contain carved inscriptions of Lincoln’s Second Inaugural Address and his Gettysburg Address. Lying between the north and south chambers is  the central hall containing the solitary figure of Lincoln sitting in contemplation. The statue was carved in four years by the Piccirilli brothers under the supervision of the sculptor, Daniel Chester French. The statue of Lincoln weighs 175 tons. The original plan was for the statue to be only ten feet high, but this was changed so that the figure of Lincoln would not be dwarfed by the size of the chamber. A commission to plan a monument was first proposed in 1867, shortly after Lincoln’s death. The design for that plan called for six equestrian and 31 pedestrian statues of colossal size, with a huge statue of Lincoln in the center.
the central hall containing the solitary figure of Lincoln sitting in contemplation. The statue was carved in four years by the Piccirilli brothers under the supervision of the sculptor, Daniel Chester French. The statue of Lincoln weighs 175 tons. The original plan was for the statue to be only ten feet high, but this was changed so that the figure of Lincoln would not be dwarfed by the size of the chamber. A commission to plan a monument was first proposed in 1867, shortly after Lincoln’s death. The design for that plan called for six equestrian and 31 pedestrian statues of colossal size, with a huge statue of Lincoln in the center.
That project was never started for lack of funds. Congress approved the bill to construct this memorial in 1910. Construction began in 1914, and the memorial was opened to the public in 1922. The Memorial is visited by millions of visitors each year and is the site of many large public gatherings and protests. Martin Luther King, Jr. delivered his famous “I Have a Dream” speech to a crowd by the Lincoln Memorial in 1963. Damaged over the years by heavy visitation and environmental factors, the Lincoln Memorial is currently undergoing a major restoration.
 The Library of Congress is the de facto national library of the United States and the research arm of the United States Congress. Located in three buildings in Washington, D.C., it is the largest library in the world by shelf space and holds the largest number of books. The head of the Library is the Librarian of Congress, currently James H. Billington.
The Library of Congress is the de facto national library of the United States and the research arm of the United States Congress. Located in three buildings in Washington, D.C., it is the largest library in the world by shelf space and holds the largest number of books. The head of the Library is the Librarian of Congress, currently James H. Billington.
 Capitol Hill, aside from being a metonym for the United States Congress, is the largest historic residential neighborhood in Washington D.C., stretching easterly in front of the U.S. Capitol along wide avenues. It is one of the oldest residential communities in Washington, and with roughly 35 000 people in just under two square miles, it is also one of the most densely populated.
Capitol Hill, aside from being a metonym for the United States Congress, is the largest historic residential neighborhood in Washington D.C., stretching easterly in front of the U.S. Capitol along wide avenues. It is one of the oldest residential communities in Washington, and with roughly 35 000 people in just under two square miles, it is also one of the most densely populated.
As a geographic feature, Capitol Hill rises in the center of the District of Columbia and extends eastward. Pierre L’Enfant, as he began to develop his plan for the new Federal City in 1791, chose to locate the “Congress House” on the crest of the hill, facing the city, a site that L’Enfant characterized as a “pedestal waiting for a superstructure”.
The Capitol Hill neighborhood today straddles two quadrants of the city, Southeast and Northeast, and a large portion is now designated as the Capitol Hill historic district. The name Capitol Hill is often used to refer to both the historic district and to the larger neighborhood around it. To the east of Capitol Hill lies the Anacostia River, to the north is the H Street corridor, to the south are the Southeast/Southwest Freeway and the Washington Navy Yard, and to the west are the National Mall and the city's central business district.
The National Mall is an open-area national park in downtown Washington, D.C. Oficially termed by the National Park Service the National Mall and Memorial Parks, the term commonly includes the areas that are officially part of West Potomac Park and Constitution Gardens to the west, and often is taken to refer to the entire area between the Lincoln Memorial and the Capitol, with the Washington Monument providing a division slightly west of the center.
 Vietnam Veterans Memorial. Deliberately setting aside the controversies of the war, the Vietnam Veterans Memorial honors the men and women who served when their Nation called upon them. The designer, Maya Lin, felt that “the politics had eclipsed the veterans, their service and their lives.” She kept the design elegantly simple to “allow everyone to respond and remember”.
Vietnam Veterans Memorial. Deliberately setting aside the controversies of the war, the Vietnam Veterans Memorial honors the men and women who served when their Nation called upon them. The designer, Maya Lin, felt that “the politics had eclipsed the veterans, their service and their lives.” She kept the design elegantly simple to “allow everyone to respond and remember”.
The Memorial Wall, designed by Maya Ying Lin, is made up of two black granite walls 75 meters long. The walls are sunk into the ground, with the earth behind them.
Inscribed on the walls with the Optima typeface are the names of servicemen who were either confirmed to be KIA (Killed in Action) or remained classified as MIA (Missing in Action) when the walls were constructed in 1982.
 The Jefferson Memorial. Situated on the South side of the Tidal Basin, in West Potomac park, the Thomas Jefferson Memorial is one of the cities most picturesque landmarks. Dedicated in 1943, on the 200th anniversary of Jefferson’s birth, this simple circular classical white marble monument is in keeping with a style much favored by the third U.S. president, architect, scholar and political thinker. At its center, a towering bronze portrait statue (the plaster one, in position until after WWII, is in the basement, too large to be removed intact) stands on a pedestal. Panels are inscribed with excerpts of Jefferson’s writing, including one that best sums up the man: “I have sworn upon the alter of God eternal hostility against every form of tyranny over the mind of man”. The view from the steps is magnificent, especially at night when a halo of blue light crowns the structure.
The Jefferson Memorial. Situated on the South side of the Tidal Basin, in West Potomac park, the Thomas Jefferson Memorial is one of the cities most picturesque landmarks. Dedicated in 1943, on the 200th anniversary of Jefferson’s birth, this simple circular classical white marble monument is in keeping with a style much favored by the third U.S. president, architect, scholar and political thinker. At its center, a towering bronze portrait statue (the plaster one, in position until after WWII, is in the basement, too large to be removed intact) stands on a pedestal. Panels are inscribed with excerpts of Jefferson’s writing, including one that best sums up the man: “I have sworn upon the alter of God eternal hostility against every form of tyranny over the mind of man”. The view from the steps is magnificent, especially at night when a halo of blue light crowns the structure.
 The Franklin Delano Roosevelt Memorial in Washington DC is next to the Tidal Basin.
The Franklin Delano Roosevelt Memorial in Washington DC is next to the Tidal Basin.
The Roosevelt Memorial dedicated on May 2, 1997 traces twelve years of American history through a sequence of four outdoor rooms. Each is devoted to one of President Roosevelt’s terms of office.
The memorial has several statues with one showing Roosevelt in a wheeled chair and another depicting him riding in a car during his first inauguration.

Pennsylvania Avenue is a street in Washington, D.C. joining the White House and the United States Capitol. Called “America’s Main Street”, it is the location of official parades and processions, as well as protest marches and civilian protests. Moreover, Pennsylvania Avenue is an important commuter route and is part of the National Highway System.
Glossary
| arid | lacking sufficient water or rainfall |
| blazon | official symbols of a family, state, etc. |
| cede | relinquish possession or control over |
| chinook | warm dry wind blowing down the eastern slopes of the Rockies |
| conterminous/ contiguous | connecting without a break; within a common boundary |
| die (n) | mold into which molten metal or other material is forced |
| inuit | member of a people inhabiting the Arctic (northern Canada or Greenland or Alaska or eastern Siberia); the Algonquians called them Eskimo (“eaters of raw flesh”) but they call themselves the Inuit (“the people”) |
| median | value below which 50% of the cases fall |
| perseverance | persistent determination |
| talon | sharp hooked claw especially on a bird of prey |
| tincture | heraldic metal, color, or fur |
| valor | qualities of a hero or heroine; exceptional or heroic courage when facing danger (especially in battle) |
| vigilance | vigilant attentiveness |
Comprehension
Exercise 1. Fill in the gaps in the following text with proper names:
The United States of America (also known as the _________, the _______, the _______, and __________) is a country in ________ that shares land borders with _______ and _______, and a sea border with __________. Extending from the __________ Ocean to the __________ Ocean, the United States is a federal republic, with its capital in _____________.
Exercise 2. Answer the following questions bout the state symbols of the United States:
1. What is the flag of the US called? Describe it and the symbolic meaning of its parts.
2. What fulfills the functions of the coat of arms in the US? Describe it.
3. What is the bird symbol of the country?
4. What is the national anthem of the USA called?
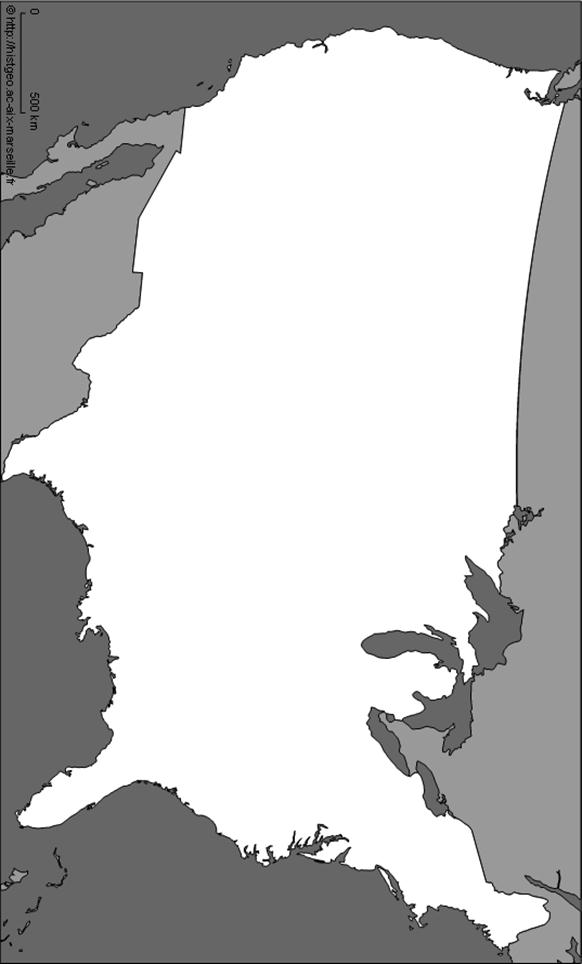
Exercise 3. Indicate the surrounding waters and major terrain features of the US mainland on the outline map (p. 104)
Exercise 4. Fill in the table about the USA:
| Total area | |
| Major rivers | |
| Major lakes | |
| The highest mountain | |
| Major cities |
Exercise 5. Fill in the gaps in the text with sentences below. There is one sentence you don’t need:
Due to its large size and wide range of geographic features, the United States contains examples of nearly every global climate. (1) Average annual temperatures range from -13 °C in Barrow, Alaska, to 25.7 °C in Death Valley, California. The highest temperature ever recorded in the country was 57 °C. (2) The lowest recorded temperature was -62 °C. It was registered at Prospect Creek, Alaska, near Barrow, on Jan. 23, 1971.
Precipitation varies from a yearly average of less than 5 centimeters at Death Valley to about 1,170 centimeters at Mount Waialeale in Hawaii. (3) The Midwest, the Middle Atlantic States, and New England experience warm summers and cold, snowy winters. In the South, summers are long and hot, and winters are mild. Along the Pacific Coast, and in some other areas near large bodies of water, the climate is relatively mild all year. (4) In the West, for example, the mountainous areas are cooler and wetter than the neighboring plains and plateaus. Parts of the West and Southwest have a desert climate.
The United States is affected by a large variety of natural disasters yearly. (5) Deadly and destructive hurricanes occur almost every year along the Atlantic seaboard and the Gulf of Mexico. The Appalachian region and the Midwest experience the worst floods, though virtually no area in the U.S. is immune to flooding. The Southwest has the worst droughts; the West is affected by large wildfires each year.
A In general, however, most parts of the United States have seasonal changes in temperature and moderate precipitation.
B The climate is temperate in most areas, tropical in Hawaii and southern Florida, polar in Alaska.
C In central portions of the U.S., tornadoes are more common than anywhere else on Earth.
D It was registered at Death Valley on July 10, 1913.
E The uninterrupted flat grasslands of the Great Plains also leads to some of the most extreme climate swings in the world.
F Mountains also affect the climate.
Exercise 6. Answer the following questions:
1. What mineral resources does the US have?
2. What other natural resources is the country rich in?
3. Where are the main deposits of these resources?
4. What are the main sources of energy for the country?
5. What is the population of the US?
6. What are the major ethnic and national groups living in the country?
7. What languages are spoken in the US? Is there a state language?
Exercise 7. Characterise the branches of the country's economy, say where the major centers are:
· mining
· agriculture
· fishing
· manufacturing
· services
· creative industries
· transport
· (IT) information technology
Exercise 8.
A. What is the history of Washington, D.C., how is it different from other American cities?
B. What do you know about the following places in Washington, D.C.?
l United States Capitol
l White House
l Washington Monument
l Lincoln Memorial
l Library of Congress
l Capitol Hill
l National Mall
l Vietnam Veterans Memorial
l Jefferson Memorial
l Roosevelt Memorial
 |
* Founding father Benjamin Franklin wanted the wild turkey to be adopted as the US bird symbol. He wrote in a letter to his daughter: “For my own part I wish the Bald Eagle had not been chosen the Representative of our Country. He is a Bird of bad moral Character. He does not get his Living honestly. You may have seen him perched on some dead Tree near the River, where, too lazy to fish for himself, he watches the Labour of the Fishing Hawk; and when that diligent Bird has at length taken a Fish, and is bearing it to his Nest for the Support of his Mate and young Ones, the Bald Eagle pursues him and takes it from him… “.
* The world’s longest river is the Nile, which is located in Egypt. It is almost 6 670 km long!`
Morphological composition of nouns.
According to their morphological composition we distinguish simple, derivative and compound nouns.
1. Simple nouns are nouns which have neither prefixes nor suffixes. They are indecomposable: chair, table, room, map, fish, work.
2. Derivative nouns are nouns which have derivative elements (prefixes or suffixes or both): reader, sailor, blackness, childhood, misconduct, inexperience.
Productive noun-forming suffixes are:
| -er: reader, teacher, worker | -ist: communist, telegraphist, dramatist |
| -ess: heiress, hostess, actress | -ism: socialism, nationalism, imperialism |
| -ness: carelessness, madness, blackness |
Unproductive suffixes are:
| -dom: freedom | -merit: development | -hood: childhood, manhood |
| -ty: cruelty | -ance: importance | -ship: friendship, relationship |
| -ity: generosity | -ence: dependence |
3. Compound nouns are nouns built from two or more stems. Compound nouns often have one stress. The meaning of a compound often differs from the meanings of its elements.
The main types of compound nouns are as follows:
(a) noun-stem + noun-stem: appletree, snowball;
(b) adjective-stem + noun-stem: blackbird, bluebell;
(c) verb-stem + noun-stem: pickpocket; the stem of a gerund or of a participle may be the first component of a compound noun: dining-room, reading-hall, dancing-girl.
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 4328
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| The USA economic geography | | | Classification of nouns. |