
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Index of Greek Terms
A few Greek words appear in the original in the text, because they are technical terms or otherwise resist satisfactory translation. Equivalents are offered here for the more important of these.
 118 , 119 , 125 n122, 128 , 151 , 156
118 , 119 , 125 n122, 128 , 151 , 156
 41 , 48 , 51 , 65 n68, 125 n122, 151 , 202
41 , 48 , 51 , 65 n68, 125 n122, 151 , 202
 36 , 39 , 40 , 45 -46
36 , 39 , 40 , 45 -46
 48 , 125 , 187
48 , 125 , 187
 52 , 53 , 65 , 71 , 72 , 77 , 116 -19, 143 , 231 , 252
52 , 53 , 65 , 71 , 72 , 77 , 116 -19, 143 , 231 , 252
 viii , 72 , 79 , 89 , 98 , 113 , 116 , 133 , 138 , 163 , 169 , 220 , 250 , 257 -59
viii , 72 , 79 , 89 , 98 , 113 , 116 , 133 , 138 , 163 , 169 , 220 , 250 , 257 -59
 20 , 64 , 151 , 225
20 , 64 , 151 , 225
 101 -2
101 -2
 22 -43, 85 , 129 , 136 , 160 , 181 , 183 , 195 , 297
22 -43, 85 , 129 , 136 , 160 , 181 , 183 , 195 , 297
 39 , 42 , 53 , 82 n113, 87 -90, 117 , 142 , 165 -69, 196 , 225 , 228 , 230 , 312 -14
39 , 42 , 53 , 82 n113, 87 -90, 117 , 142 , 165 -69, 196 , 225 , 228 , 230 , 312 -14
 28
28
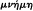 115
115
 vii , 87 , 95 -99, 104 -6, 127 , 141 , 143 , 154 -55, 162 , 166 , 167 -69, 189 , 191 , 203 , 207 , 210 , 211 , 221 , 225 -26, 230 , 245
vii , 87 , 95 -99, 104 -6, 127 , 141 , 143 , 154 -55, 162 , 166 , 167 -69, 189 , 191 , 203 , 207 , 210 , 211 , 221 , 225 -26, 230 , 245
 76 -77, 87 , 93 -94, 106 , 162 -64, 189 , 206 , 217 , 231
76 -77, 87 , 93 -94, 106 , 162 -64, 189 , 206 , 217 , 231
 80 , 141 n162, 185 , 186 , 188 , 190 , 196 , 240 , 246
80 , 141 n162, 185 , 186 , 188 , 190 , 196 , 240 , 246
 76 -77
76 -77
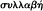 76 -77
76 -77
 17 , 23
17 , 23
 115 , 225
115 , 225
 123 , 129 , 207
123 , 129 , 207
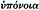 48 , 136 -37
48 , 136 -37
 87 , 92 , 105 -6, 143 , 162 , 166
87 , 92 , 105 -6, 143 , 162 , 166
― 355 ―
General Index
A
Abelard, 287
Academy, 56 -57, 75 , 83 n1
Achilles, 3 , 6 , 18 , 41 , 179 n57, 215 , 220 , 265 , 274 ;
and Athena, 93 -95, 203 , 260 -61, 276 ;
and Thetis, 250 n63, 265 , 277
Adam, 46 , 53
Adrastus, 84
Aeneid. See Allegory; Augustine of Hippo; Virgil
Aeolus, 274
Aeschylus, 77
Agamemnon, 17 , 18 , 179 n57, 206 -7, 274
Agenor, 220
Ajax, 274
Alain de Lille, 284 , 286
Albertus Magnus, 270
Albinus, Caecina, 263
al-Biruni, 238
Albricus, 282
Alcaeus, 145 n3
Alexander, 84
Alexandria, 26 , 44 , 45 , 48 , 53 , 75 , 80 , 85 , 109 . See also Clement of Alexandria; Origen the Christian; Philo
al-Farabi, 237 , 239
Allegory
—defensive, 124 , 183 -84, 261 n109
—deliberate, x , 142 , 145 -50
—interpretation of: Aeneid , 146 -47, 257 -60, 270 , 282 n184, 284 -88, 292 , 294 ;
in Arabic commentators, 239 -41;
in Christianity, 144 -61;
in later Latin authors, 286 -92;
in Medieval period, 282 -97;
in modem period, 298 -305;
in Neoplatonism, 21 -22, 47 -49
—levels of: in Christian Neoplatonism, 158 -61;
as distinguished by Dante, 291 -94;
in Medieval exegesis, 283 -84;
multiplicity of, 20 -21, 43 ;
in Philo, 47 -53;
in Porphyry, 115 , 120 -21, 127 ;
in Proclus's defense of Homer, 185 -88, 196 -97, 216 -21
—literal meaning and: in Dante, 291 -93;
in Homeric interpretation, 224 ;
in Julian, 139 ;
in Philo, 47 -53;
in Porphyry, 124
—moral: Aeneid as, 270 ;
in Dante, 291 , 293 ;
in Fulgentius, 281 -82;
in Macrobius on Scipio's dream, 271 ;
in Neopythagoreanism, 115 ;
Odyssey as, 130 , 224 ;
in Pythagoreanism, 32 -35, 43 , 270
—mystical: in Christian authors, 78 -81, 241 -49;
and early interpretations of Homer, 12 ;
in Heliodorus, 149 -61;
Iliad as, ix , 1 , 43 , 223 -33;
in Macrobius on Scipio's dream, 271 ;
in Neoplatonism, 139 , 288 , 293 , 318 -24;
Odyssey as, ix , 1 , 43 , 132 -33, 222 -33, 318 -24;
in Porphyry, 108 -10, 115 ;
in Proclus, 219 -21;
in Pythagoreanism, 31 -43, 320 ;
role of Philo in development of, 44 -51;
and use of term theologos , 27 -31
—personification, 146 , 273 , 275 -79, 284 , 288 -91
—physical: Iliad as, 32 , 223 -24;
in Julian, 137 -38;
in Macrobius on Scipio's
― 356 ―
Allegory, physical (continued )
dream, 271 ;
in Philo, 47 ;
in Porphyry, 129 ;
in Proclus, 219 -21;
Pythagorean, 32 -33, 43 ;
in Stoicism, 143 , 164 n5
Ambrose, Saint, 263
Amelius, 84 , 132
Ammonius Saccas, 45 , 78 , 84
Anacreon, 145 n3
Anaxagoras, 97 n48
Antenor, 5
Antiochus of Ascalon, 45 , 46
Aphrodite, 202 , 250 . See also Homer, Odyssey
Apollo, 218 , 219 , 220
Apuleius, 98 , 233 , 260 -61
Arabic interpretive tradition. See Allegory; Homer
Arcesilaus, 56 , 58
Archilochus, 145 n3
Ares. See Homer, Odyssey
"Ares" (the philosopher), 248
Argonauts, 180
Aristarchus, 26 , 109 , 113 -14, 202
Ariston of Chios, 58
Aristotle: in Dante, 289 , 294 -95;
in list of seven philosophers, 248 ;
and Plato, 183 -85, 188 , 252 ;
praise of Homer by, 237 ;
as source for later commentators, 112 , 120 , 202 , 240 -41, 252 , 295 ;
testimony on Pythagoreanism, 36 , 39 , 43 ;
translations of by later authors, 262 , 274 , 275 n171;
and theologoi , 23 -24, 27 , 28
Aristoxenus, 274
Arnobius, 250
Artemidorus of Ephesus, 125
Artemis, 219 n230
Aspasius, 84
Astrology, 69 , 71 , 73 , 163 , 253 -54, 318 -19
Athena: allegorical use of, 65 , 202 , 276 ;
and Achilles, 93 -95, 203 , 260 -61, 276 ;
and Diomedes, 178 , 276 ;
and Pandarus, 19 , 20 ;
and Odysseus, 8 , 175 -76, 233 n1;
and Pandarus, 19 , 20 , 207 -8
Atlantis, myth of, 65
Atticus, 84
Attis, 143 , 261
Auerbach, E., 187
Augustine of Hippo, Saint: critique of Aeneid by, 227 , 257 -60;
language theories in, 257 -60;
and Platonism, 16 , 81 , 91 n33, 249 -51, 256 -61, 267 ;
treatment of Homer by, 227 , 233 n1, 259 -61
Averroes, 240
Avicenna, 237
B
Bachelard, G., 73
Basil of Caesarea, Saint, 139 , 242 , 243 -44
Battle of the gods. See Homer, Iliad
Bernard Silvestris, 272 , 284 -85, 287 , 289 , 292 n212, 294
Beutler, R., 54 , 64 n66, 176
Bidez, J., 108 , 110 , 111
Blake, W., x , 234 , 235
Bloom, H., 145 , 298
Boethius, 249 , 256 , 274 -79, 283 , 286 , 290
Boyancé, P., 33 n110, 35 -36, 39 , 46 , 178
Bréhier, E., 103
Buffière, F., 1 n1, 32 , 33 , 44 , 64 n66, 66 , 319 -24
Burkert, W., 34 , 42 , 324
Byzantine interpretive tradition. See Homer
C
Calchas, 2 , 4
Calcidius, 221 n240, 236 , 249 , 250 -56, 282
Callimachus, 176 , 181
Calypso, 206 -7, 225
Carcopino, J., 33 n110, 74
Carneades, 56
Cassiodorus, 256
Celsus, 81 , 82 n113
Chaldaean Oracles , 30 , 169 , 175 , 180 , 213 , 228 n264
Chapman, G., 8 , 9 , 22 , 223 , 234 , 235
Chariclea. See Heliodorus; "Philip the Philosopher"
Chartres, School of, 240 , 247 , 286 -88
Chrétien de Troyes, 287
Christianity: allegorical tradition in, 16 , 78 -82, 144 -61, 233 -34, 241 -49;
etymological speculations in, 46 -47;
Julian's attitudes toward, 136 -39;
and Neoplatonism, 30 , 144 -49, 156 -61;
and Numenius, 60 -61, 75 -76;
Philo's influence on, 53 -54, 75 -76;
and Porphyry, 53 , 61 . See also Exegesis
Chrysippus, 21 n54, 25 -26, 210 n191
Cicero, 13 , 24 , 45 , 66 , 260 n105, 264 , 267 , 273 . See also Scipio, dream of
Cilento, V., 101
― 357 ―
Circe, 8 , 41 -42, 106 -7, 115 -19, 153 , 274 , 279 , 295 . See also Odysseus
Cleanthes, 265
Clement of Alexandria, 27 , 45 , 53 , 55 , 65 n68, 78 -80, 146 , 242 -43, 284
"Cleomedes", 248
Constantius, 135 -36
Copulation, myth of divine, 209 -14. See also Homer, Iliad : deception of Zeus
Cornificius, 265
Cornutus, 187
Cosmology, 24 , 30 , 47 , 77 , 230 -32, 252 -54, 264 , 270
Coulter, J., 185 n77, 215 n211
Crates of Mallos, 26 , 109
Critic (  11 -12, 120 , 179
11 -12, 120 , 179
Cronius, 44 , 54 , 55 , 84 , 85 , 111 , 113 , 121 -23, 125 , 128 , 132 , 197 , 250 , 318 -20
Cumont, F., 1 n1
Cyclopes, 51
Cynics, 58 , 137 , 138
D
Dante: allegorical modes in, 86 n15, 290 -94;
influences on, 8 -9, 240 -41, 272 , 289 -90, 291 -94;
interpretation of Homer by, 282 -83, 294 -97;
and interpretive tradition, x , 234 -35, 282 -83, 298 -99;
language in, 89 , 171 ;
letter to Can Grande of, 142 , 186 n82, 289 , 292 -94;
Platonism in, 289 -90;
Pythagorean elements surviving in, 274 ;
use of Virgil by, 288 -94, 292 -97
Dares Phrygius, 285 , 287 , 295
DeLacey, P., 25
Delatte, A., 32 , 34 -35, 43 , 74 , 319 , 322 , 324
De Lubac, Henri, 283 -84
Demetrius of Phaleron, 187 n86
Demodocus. See Homer , bards in
Derveni papyrus, ix , 12 n28, 36 n123, 299
Des Places, E., 57 , 59 , 77
Detienne, M., 32 , 33 n110, 35 , 39
Dictys Cretensis, 295
Dillon, J., 54 , 56 , 64 n66
Dilthey, W., 302 , 303
Diogenes Laertius, 16 n43, 36 n123, 60 n53
Diomedes, 178 , 276
Dionysius the Areopagite, 232 , 244 . See also Platonism, Dionysian; Ps.-Dionysius
Diotima, myth of, 98
Dodds, E. R., 54 , 180
DöRrie, H., 15 , 180
Dreams, interpretation of, 150 -51
Dronke, P., 287
E
Egypt, 23 , 60 , 62 , 69 , 71 , 72 , 110 , 142 , 155 , 253 -54, 257
Eidothea, viii , 227
Empedocles, 116 , 228
Epicureanism, 81 , 84 , 222
Epimetheus, 103
Er, myth of, 7 -8, 200 , 270 n149, 323 ;
Numenius' commentary on, 37 , 63 -64, 69 -73, 102 -3;
Porphyry and, 115 , 118 -19;
Proclus' commentary on, 66 -73 (text: 66-68), 102 -3, 202 , 221 , 230 , 232 ;
Pythagoreanism in, 42 , 102 -3, 118
Erbse, H., 248
Erennius, 84
Eriugena, John Scotus, 232 , 247 , 287
Esthetics, 19 , 185 -88
Etymology: examples of, 28 , 241 , 212 , 231 n269, 252 , 264 , 266 , 281 ;
in Lydus, 250 ;
in Philo, 45 -49;
in Plotinus, 86 -87;
in Proclus, 39 -40, 166 , 200 , 214 -15, 221 ;
origin of interpretation by, 38 -41, 280 -82
Euclid. See Proclus
Euhemerists, 24
Euripides, 251 n71, 266
Eusebius, 55 , 60 , 63
Eustathius, 95 , 198 , 233
Exegesis: in Alexandria, 44 ;
in Christianity, 82 , 160 -61, 251 , 283 -84, 291 -92;
in Dante, 282 -97;
Neoplatonic, 197 , 201 , 261 , 282 -83, 318 -24;
in Plotinus, 275 ;
in Porphyry, 113 , 120 -24;
Pythagorean, 35 -43, 74 -75, 320 ;
role of in ancient education, 13 -14;
Stoic, 45 -48
F
Favonius Eulogius, 249 , 272 -73
Festugière, A. J., 66
Finsler, G., 234
Flamant, J., 266 , 319
Flavianus, Nichomachus, 263
Fortin, E., 243 -44
Friedl, A. J., 198
Fulgentius, 279 -82, 285 , 292 , 294
― 358 ―
G
Gadamer, H.-G., 302 , 303
Gaius, 84
Ganymede, 53
Gelzer, T., 149 , 157 -61
Gnostics, xi , 42 , 95 , 106 , 145
Gorgias, 207
Grammarians, 24 , 26 , 32
Gregory of Nyssa, 160
Grube, G. M. A., viii -ix, 20 , 299
Guillaume de Conches, 287 -88
H
Hades, 73 -74, 100 , 114 -15, 208 , 215 n212, 231
Hadot, P., 106
Hazlitt, W., 301 -2
Hebrew scriptures, 44 , 47 , 99 , 244 -47, 250 ;
in Dante, 291 -94;
in Prudentius, 146 -49;
as read by Philo, 75 -76, 82 , 211 -12;
as source for Numenius, 60 , 69 , 75 -76, 80 -81;
use of by Augustine, 257 -59
Hector, 18 , 215 , 220
Hegel, G. W. E, 301
Heidegger, M., 302 -3
Helen, 5 -6, 19 , 196 , 199 -200, 207
Heliodorus, 149 -61
Helios, 137
Hephaestus, 51 , 168 , 204 -6, 210 , 212 , 219 , 228 -29
Hera, 202 ;
as 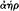 20 , 51 , 137 , 219 n230, 259 .
20 , 51 , 137 , 219 n230, 259 .
See also Homer, Iliad ; Juno
Heracles, 100 -102, 104 , 191
Heraclitus (author of Homeric Allegories ), ix n7, 16 , 26 , 47 , 52 , 62 , 145 n3, 183 -84, 199 n142, 224 -25, 226 n256, 253 , 254 , 320
Heraclitus of Ephesus, 254 -55
Hermeneutics, 47 , 49 , 54 , 78 , 109 , 244 -45, 282 -83, 301 -5
Hermes, 42 , 117 , 225
Hermes Trismegistus, 30 -31, 200 , 257
Hermias, 30 , 158 , 200 , 226
Herodotus, 11 , 22 -23, 25 , 79
Hesiod, 29 , 30 , 156 , 231 n269, 237 , 250 ;
and Homer, 11 , 35 , 80 , 86 , 140 ;
in Julian, 137 ;
myths in, 16 -17, 103 -6, 124 ;
in Philo, 49 , 87 ;
in Proclus, 176 -77;
as theologos , 27 , 28 , 31 .
See also Kronos
Hierocles of Alexandria, 177 n49
Hollander, R., 294 n218
Homer: anthropomorphism in, 97 -100, 260 n105;
Augustine's treatment of, 227 , 233 n1, 259 -61;
as authority on literature and philosophy, 12 -14, 40 , 242 -43, 253 , 275 -79, 294 -97;
bards in, 3 -4, 6 -7, 22 , 65 , 189 , 191 , 201 , 226 n257, 227 ;
blindness of, 8 -10, 177 n51, 196 , 199 -200, 211 ;
Boethius's use of, 275 -79;
Byzantine interpreters of, 241 -49;
Christian interpreters of, 78 -82, 145 -48, 241 -49 (see also Clement of Alexandria; Origen the Christian);
defenses of, 18 -20 (see also Plato; Proclus);
and Demodocus, identification with, 9 , 22 ;
as divine, 1 -10, 136 , 181 , 236 , 239 , 243 -47, 254 -55, 281 -82;
as educator, 16 -20, 275 -79;
as an Egyptian, 79 , 151 n23, 254 ;
as etymological authority, 38 -39, 280 -83;
and Hesiod, 7 , 11 , 35 -36;
Hymn to Aphrodite , 100 ;
Hymn to Apollo , 9 ;
later Latin interpreters of, 249 -82;
narrative voice in, 5 -6, 9 ;
as philosopher, 113 , 248 , 253 ;
and Philosophy, 274 -79, 294 -97;
as the Poet, 22 , 51 , 83 , 181 , 202 , 264 , 294 ;
treatment of by Pythagoreans, 15 , 19 , 31 -43, 73 -75;
as sage, 1 , 10 , 236 , 237 -39, 282 ;
as seer, 9 , 133 , 253 , 274 , 282 ;
seers in, 2 , 4 (see also Tiresias);
doctrine of souls in, 64 -73, 100 -103, 114 -19, 121 , 251 -52, 271 -72, 282 (see also Odysseus);
as theologian, 1 -10, 15 , 22 -43, 51 , 129 , 181 , 260 n105;
and Tiresias, identification with, frontispiece, 8 , 9 , 10 , 22 ;
and Virgil, 284 -88, 294 -97.
See also Scholia on Homer
Homer, Iliad (episodes in): battle of the gods, 32 , 201 , 210 n189, 216 -21, 226 -27;
deception of Zeus, 11 , 18 -19, 172 -73, 190 , 208 -17, 246 , 273 ;
dream sent by Zeus to Agamemnon, 179 n57, 206 , 271 ;
fall of Hephaestus, 204 -6;
Judgement of Paris, 202 ;
pithoi on the doorstep of Zeus, 17 , 220 -21, 226 -27, 275 ;
Zeus's visit to the Ethiopians, 203 -4, 271 .
See also Achilles; Athena; Trojan War
Homer, Odyssey (episodes in): cattle of the sun, 137 ;
cave of the nymphs, history of allegorical interpretation of, 256 , 318 -24;
cave of the nymphs,
― 359 ―
Numenius's commentary on, 44 , 55 , 64 -65, 66 , 70 -74, 109 -10, 126 , 128 , 130 , 143 , 270 , 318 -24;
cave of the nymphs, Porphyry's essay on, 29 , 33 n109, 44 , 55 , 64 n66, 66 , 70 -73, 108 -11, 114 -32, 143 , 151 n23, 178 , 200 -1, 226 , 234 -35, 265 , 269 , 288 , 290 , 318 -24;
cave of the nymphs, Proclus's summary of, 70 -71, 73 ;
cave of the nymphs, text of, 119 -20;
Polyphemus, 130 -31;
Proteus, viii , 172 , 226 -27;
song of Ares and Aphrodite, 11 , 18 , 19 , 189 , 201 , 208 , 226 -30.
See also Calypso; Circe; Nekyia; Odysseus; Sirens
Homeridae of Samos, 35
Horace, 120 , 277 n176
I
Iamblichus, 35 , 39 , 72 n83, 134 -35, 138 , 262
Iliad. See Homer, Iliad
Isidore of Seville, 38 , 46 , 256 , 280
J
Jesus, 60 , 81 , 147 , 260
John the Evangelist, logos doctrine of, 88
Jones, J. W., 269 -70
Judaism, 61 , 69 , 75 , 78 , 80 , 82 . See also Hebrew scriptures
Julian the Apostate, 134 -39, 152 , 241 , 249 , 262 , 264 , 265
Juno, 259 , 273 . See also Hera
Jupiter, 273 . See also Zeus
K
Kindstrand, J. F., 201 -2
Klibansky, R., 236 , 239
Kraemer, J., 238
Kronos, 17 , 87 , 104 -6, 141 -42, 204 , 213 n203, 264 . See also Hesiod
L
Labeo, Cornelius, 249 -50
Leonas, 174
LéVi-Strauss, C., 201
Linus, 80 , 260 n105, 274
Lloyd-Jones, H., 299
Longinus, 84 , 86 , 110 -11, 188
Lucian, 9 , 54 , 56
Luscinius, Gaius Fabricius, 273
Lydus, Ioannes, 55 , 250 , 262
M
Macrobius: commentary on Cicero's Scipio's Dream , 66 , 71 , 249 , 269 -73, 289 , 318 -19;
role of in transmission of Homer and Plato, 71 , 226 , 236 , 256 , 270 -72, 282 , 283 , 288 -90;
Saturnalia of, 193 -94, 263 -71, 289 , 319 ;
sources for, 68 -69, 71 -74, 231 n269, 250 , 263 , 266 , 271 -73, 279 , 288 , 318 -19
Marcellinus, Ammianus, 262
Margolin, J.-C., 186
Marie de France, 287
Marinus, 174 -76, 180
Mars, 264 -65
Martianus Capella, 249 , 273 -74, 282 , 283 , 286 , 290
Maximus of Tyre, 57
Menelaus, 207 , 227 . See also Helen
Mentor, 56
Mercury, 273 -74
Metalanguage, 168 -73, 207 , 229 -30
Metempsychosis (metensomatosis), 37 , 41 , 116
Methodius of Olympus, 242 -43
Milky Way, 67 , 70 , 73 -74, 115 , 128
Milton, 86 n15
Mimesis, 18 , 65 , 87 , 188 -97, 215 , 288
Minos, 99 -100
Moderatus, 84
Moses, 16 n45, 29 , 30 , 60 , 242
Mras, K., 77
Musaeus, x , 29 , 35 , 60 , 80 , 149 , 157 -61, 260 n105
Muses, 4 -6, 7 , 10 , 36 , 196 , 230 , 231 , 274 , 275
Music of the spheres, 7 -8, 37 -38, 52 , 230 -32
Mythographers, 279 -82, 285
Myths: in education, 16 -17, 197 , 241 -43;
in Julian, 137 , 152 ;
in Plato, 16 -17, 29 n86, 31 , 37 -38, 41 -42, 98 , 100 , 118 -19, 140 , 170 , 197 , 202 , 215 -16, 220 -21;
in Sallustius, 139 -43;
Stoics' treatment of, 13 -14, 260 ;
as source material, 24 -25;
use of by Neoplatonists, 13 -14, 83 -84, 170 -71, 185 -97, 203 -5, 230 -32.
See also Er, myth of; Hesiod; Mythographers; Plato; Socrates
N
Negative theology, 90 , 244 , 278
Nekyia (journey to the dead), 42 -43, 70 , 100 , 115 , 119 , 191 , 277 n176
Neoplatonism, x , 2 , 10 , 19 , 127 ;
and Christianity, 30 , 138 -39, 149 , 156 -
― 360 ―
Neoplatonism (continued )
61;
and Julian, 134 -39;
doctrine of souls in, 159 , 251 -52, 271 -72;
influence of in later interpretations, 43 , 234 -36, 271 -72, 284 -88;
and Numenius, 63 -65;
and Pythagoras, 39 ;
and Sallustius, 139 -43;
use of term theologos , 22 .
See also Plato; Plotinus; Porphyry; Proclus
Neopythagoreanism. See Pythagoreanism
New Testament, 60 , 62 , 81 , 124 , 156 , 158 , 294
Nicoll, A., 8
Nikolaos Mesarites, vii
Nonnus, 158
Numbers, ideal, 40
Numenius, 16 , 19 , 33 , 45 , 51 , 53 , 140 , 143 , 197 , 211 -12, 221 n240, 250 ;
attitudes toward earlier literature of, 14 , 55 -58;
doctrine of souls in, 65 -74, 103 -4 (see also Er, myth of);
explication of Plato by, 55 -69;
and Judaism, 60 -62, 75 -76;
language theories of, 76 -77;
life of, 54 -57;
Origen's attitudes toward, 61 -62, 80 -81;
and Plotinus, 61 , 83 -85, 93 , 99 , 102 , 104 ;
and Porphyry, 55 , 61 , 66 , 109 -11, 128 -30, 256 , 319 ;
and Proclus, 66 -71, 73 -74;
as a Pythagorean, 54 , 68 -69, 73 -75;
as source for later authors, 84 , 253 -56, 279 , 318 -24;
use of Homeric language by, 54 -59, 69 , 71 -73, 90 , 93 , 110 , 318 -20.
See also Homer, Odyssey : cave of the nymphs
O
Oceanus, 252
Odysseus: allegorical interpretations of, 41 -43, 53 , 71 , 102 , 106 -7, 119 -20, 129 -33, 153 , 175 -76, 221 -32, 251 -52, 279 , 307 ;
and Athena, 8 , 175 -76, 233 n1;
in Dante, 295 -97;
wanderings of, 121 -22, 125 -27, 274
Odyssey . See Homer, Odyssey
Old Testament. See Hebrew scriptures
Olympiodorus, 30 , 198
Oracles, 7 , 12 , 29 , 30 , 132 -33, 134 , 140 -41, 153 , 169 , 177 , 178 n52, 213 , 245 , 248 , 266
Origen the Christian, 45 , 53 , 60 n51, 61 -62, 75 -76, 78 , 80 -82, 84 , 142 , 145 n3, 146 , 210 n191, 242 , 260 , 283 -84
Orion, 174
Orpheus, 22 , 29 -31, 35 , 80 , 177 , 180 , 228 n264, 260 n105, 274
Orphic poetry, ix , 27 , 28 , 213 , 299 . See also Orpheus
Osiris, 144 n1
Ouranos, 17 , 105 , 124 , 204
Ovid, 146
P
Pandarus. See Athena
Pandora, 103 -4
Paris, 35 , 202
Parmenides, 176
Patroclus, 6 , 18 , 215 n212
Penelope, 7 n13, 179 n57
PéPin, J., 1 n1, 48 -49, 106 , 120 -21, 124 , 288
Peripatetics, ix , 84
Petrarch, 282
Pézard, A., 289 -90
Pfeiffer, R., 13
Phemius. See Homer, bards in
"Philip the Philosopher," 148 -50, 152 -56;
text of An Interpretation of the Modest Chariclea by, 306 -11
Philo of Alexandria, 16 n43, 29 , 30 , 44 -54, 75 -76, 78 , 146 , 211 -12, 284
Philolaus, 27 , 28 , 322
Philologia, personification of, 273 -74
Philoponus, John, 65 n68
Philosophy, personification of, 275 -79
Photius, 177 -78
Pisander, 30
Plato: critique of mimetic art, 188 -97, 215 -16 (see also Mimesis);
discussion of love in the dialogues, 155 ;
doctrine of souls in, 64 -73, 100 -3, 118 -19, 202 (see also Er, myth of);
and Homeric anthropomorphism, 97 -100;
language of, 45 -48, 85 -90, 165 -73, 205 -7;
in list of seven philosophers, 248 ;
methodology of, 38 -39, 230 ;
Neoplatonic reconciliation of Homer and Plato, 66 , 97 -100, 112 , 118 -19, 134 , 169 -70, 182 -85, 194 -97, 205 -7, 219 -21, 228 -29, 232 , 242 , 266 , 275 , 279 , 282 ;
and poetry, 16 , 25 , 28 -29, 80 , 280 -85;
Porphyry and tradition of commentary on, 63 ,
― 361 ―
255 -56;
role of dialogues in transmission of Homer, 37 -43, 99 -100, 180 -81, 205 -6, 235 -37, 250 -53, 261 , 285 -86;
as source for Latin authors, 289 -90;
treatment of by Numenius, 55 -73;
treatment of by Plotinus, 86 ;
treatment of Homer as divine by, 2 -3, 136 , 181 -85, 195 , 282 ;
use of dialogues in interpretation, 300 -1.
See also Myths; Neoplatonism; Platonism; Socrates
Platonism, ix , 13 -14, 16 , 128 , 133 n140;
Dionysian, 283 -84, 287 -88 (see also Dionysius the Areopagite);
Middle, 46 , 49 , 53 -54, 82 n1, 250 ;
and Pythagoreanism, 34 -43, 128 , 177 , 210 , 270 -72;
and Pythagoreanism in Numenius, 60 -61, 75 ;
and Pythagoreanism in Porphyry, 30 , 84 -85, 115 -18.
See also Neoplatonism
Plotinus, 15 , 43 , 44 , 91 ;
allegorical interpretation of Heracles by, 100 -3;
allegorical interpretations of Odysseus by, 102 , 106 -7;
and Cronius, 85 ;
doctrine of souls in, 86 n15, 100 -7, 156 ;
Hesiodic myths in, 86 , 87 , 103 -6;
Homeric language in, 90 -103, 202 , 277 -79;
reconciliation of Homer and Plato by, 97 -100;
logos doctrine of, 87 -90, 165 -66;
negative theology of, 90 ;
Neoplatonism of, 83 -85, 162 -64;
and Numenius, 61 , 83 -85, 93 , 99 , 102 , 104 ;
oracle on fate of soul of, 153 ;
and Philo, 85 ;
Platonic language in, 40 , 85 -90, 164 -73;
and Porphyry, 83 -84, 111 -12, 131 , 132 , 256 ;
Pythagorean elements in, 82 , 101 -3;
as source for later authors, 289
Plutarch, ix , 21 n54, 23 , 38 , 40 -41, 185 , 231 n269, 248 , 320 , 322
Polemon, 56
Polyphemus, 130 -31
Porphyry, 35 , 42 , 53 , 143 , 197 , 212 , 250 , 304 ;
allegory in, 115 , 120 -21, 127 , 129 ;
association with Longinus, 110 -12;
attitudes toward earlier literature, 14 ;
and Christianity, 30 , 82 , 160 -61;
commentary on Plato's Republic , 319 (see also Er, myth of);
defense of Homer by, 19 , 121 -24;
doctrine of souls in, 73 -74, 113 -19, 121 , 132 , 200 -1 (see also Homer, Odyssey : cave of the nymphs);
Homeric interpretations by, 64 , 108 -33 (see also Homer, Odyssey : cave of the nymphs);
Homeric Questions of, 108 -14, 198 ;
and Numenius, 55 , 61 , 66 , 109 -11, 128 -30, 256 , 319 ;
and Platonism, 30 , 65 n68;
and Plotinus, 83 -84, 111 -12, 131 , 132 , 256 ;
and Proclus, 174 -75, 178 -79;
and Pythagoreanism, 30 , 112 , 115 , 118 -19;
as source for later authors, 255 -56, 265 -66, 279 , 289 ;
The Styx , 113 -19, 121 ;
use of theologos , 24 , 27 , 29 , 30 -31
Poseidon, 65 , 219 n230, 227 , 228 , 231
Posidonius, 251 , 265
Praechter, K., 120 -21, 272 -73
Praetextatus, Vettius Agorius, 249 , 262 -67
Priam, 5 , 18 , 215
Proclus, viii , 3 , 25 n70, 30 , 129 n130, 158 , 197 -99, 244 -48;
attitudes toward earlier literature, 14 , 180 -83;
attribution of Chrestomathy to, 177 -78, 181 n65, 201 -2;
classification of types of poetry by, 188 -97, 258 -59;
commentary on Euclid by, 30 -31, 173 , 224 -25;
commentary on Plato's Parmenides by, 225 -26;
commentary on Plato's Republic by, 66 -71, 164 , 170 , 175 , 178 -79, 181 -97, 199 , 226 -32, 318 (see also Er, myth of);
commentary on Plato's Timaeus by, 30 , 65 , 167 -69, 175 , 176 , 181 , 189 , 190 n99, 199 n143, 221 , 228 -29, 312 -14 (text);
defense of Homer by, 19 , 64 n66, 70 , 140 , 153 -54, 163 -64, 169 -70, 172 -73, 178 -79, 181 -97, 208 , 216 , 226 , 230 , 235 ;
demonology in, 98 -99, 217 -21, 226 -32, 258 -59;
interpretation of Iliad by, 199 -221, 315 -17;
interpretation of Odyssey by, 221 -32, 315 -17;
life of, 162 -63, 174 -76;
Neo-platonic doctrines in, 162 -71, 188 -97;
and Numenius, 66 -71, 73 -74;
physical allegory in, 219 -21;
and Porphyry, 164 , 170 , 174 -75, 178 -79;
Pythagorean thought in, 39 -40, 209 -10, 216 -18;
and theologoi , 30 -31;
use of Homer's blindness by, 8 , 9 -10, 177 n51, 196 , 199 -200, 211
― 362 ―
Procopius of Gaza, 160
Prometheus, 103 -4
Proteus, viii , 17 , 37 , 172 , 226 -27
Prudentius, x , 145 -48, 158 , 283 , 290
Ps.-Dionysius, 232 n270, 246 -47
Ps.-Plutarch, 11 n27, 14 , 20 n52, 36 n125, 41 , 110 , 112 -13, 118 , 251 -53, 268 , 320 , 322
Pythagoreanism, ix , 2 , 9 , 15 , 19 , 21 , 237 , 238 ;
allegorical interpretations in, 31 -43, 73 -75, 115 , 178 , 270 -72, 320 -24;
doctrine of souls in, 73 -74, 101 -2, 118 -19, 271 ;
Philolaus as source on, 28 ;
sects in, 36 ;
use of Plato's myths by, 38 , 128 .
See also Numenius; Platonism; Plotinus; Porphyry; Proclus
R
Rahner, H., 242 , 243
Raphael, 8 -9
Renaissance, x , 1 , 9 , 20 , 146 , 186 n81, 223 , 234 , 240
Rhea, 223 -14
Rhetoric, 20 , 40 , 57 , 287 , 193 , 201 , 268 , 273
Richard of St.-Victor, 287
Ricoeur, E, 302
Romances, Greek, 148 -53, 157 , 160
Ross, D., 165
Rufinus, 263
S
Sallustius, 239 -43, 148 , 171 , 188
Sappho, 176
Sarpedon, 215 n214
Satire, 55 , 58 -59, 220 -21, 275 , 286
Saturnalia of Macrobius. See Macrobius
Schlegel, E, 301
Schleiermacher, E, 301
Scholia on Homer, ix , 20 , 32 , 38 , 52 , 94 , 112 , 114 , 194 n124, 198 , 219 , 254 , 320 -24
School of Chartres. See Chartres, School of
Schrader, H., 208 , 110
Scipio, dream of (in Cicero's De re publica ): commentary by Favonius Eulogius, 272 -73;
commentary by Macrobius, 66 , 71 , 249 , 269 -73, 289 , 318 -19
Second Sophistic, 57 , 193 , 201
Seneca, 13
Servius, 224 n246, 250 , 262 -64, 269 -70, 282
Severus, 84
Sheppard, A., 185 n77, 290 -91, 200 , 201 n150, 208 n180, 210 n189, 214 -15, 247 , 304 n14
Sibyl, 248
Simonides, 29
Sirens, 7 , 10 , 37 , 52 , 230 -32, 243 , 275 , 281 , 295
Skylla, 51
Socrates: attitudes toward myth and poetry, 23 , 25 , 102 , 224 , 140 , 180 -85, 196 , 197 , 237 , 243 ;
condemnation of Homer by, 16 -29, 70 , 200 , 124 , 153 -54, 172 -73, 182 -85, 196 -97, 198 , 215 -26, 260 ;
etymological speculations and, 38 -39, 165 -66, 214 ;
in text of Philip the Philosopher, 307 ;
on uses of texts, 21 , 159 , 252 , 300 -1;
as voice of Plato, 64 -65.
See also Plato
Sodano, A. R., 108
Solon, 176
Sontag, S., 299
Sophistic, Second. See Second Sophistic
Spercheios, 18
Speusippus, 34 , 39
Stesichorus, 195 -96
Stobaeus, 42 , 109 , 113 -15
Stoicism, ix , 13 -24, 21 , 40 -41, 56 , 94 , 109 , 251 , 260 n105;
allegorical interpretation in, 25 , 81 , 143 , 164 n5, 210 n291, 219 , 260 , 265 -66;
as source for Philo's allegorizing, 45 -51, 75 -76;
theology in, 26 , 261
Strabo, 24 , 26 -27, 121 , 122 , 138
Structuralism, 201
Styx, The. See Porphyry
Suda , 64 n66, 176 , 177
Symmachus, 263 , 267 -68
Synesius, 144 n1
Syrianus, 134 , 164 n5, 176 -77, 197 -98, 200 , 206 , 208 , 210 , 244
T
Tate, J., 2
Taylor, T., x , 301 -2
Telemachus, 7 n13
Telephus of Pergamon, 16
Tethys, 252
Thales, 252
Theagenes and Chariclea. See Heliodorus; Philip the Philosopher
― 363 ―
Theagenes of Rhegium, 15 , 32 , 322
Themis, 219
Theoclymenus, 2
Theodoret, 65 n68, 260
Theophanes the Keramite, 148 n12
Theophilus of Edessa, 238
Thetis, 17 , 203 , 215 n214, 250 n63, 265 , 277
Thomas Aquinas, Saint, 240 , 241 , 260 n105, 289
Thrasyllus, 84
Tigerstedt, E. N., 34 n114
Timon of Phlius, 58
Tiresias, 2 , 8 , 10 , 22 , 130 , 132 . See also Homer
Trojan War: as metaphor, 19 , 100 , 199 -202, 221 , 260 n105, 294 ;
as poetic fiction, 285 , 287 , 294 -95;
in Origen, 81
Trouillard, J., 167
U
Ulysses (Ulixes), 274 , 281 -82, 296 . See also Odysseus
V
Varro, 45 , 46 , 260
Victorinus, Marius, 249 , 256 -57
Virgil, 13 , 146 , 147 , 233 -34, 235 , 274 ;
in Dante, 288 -90, 292 -97;
and Homer, 294 -97;
Macrobius's treatment of, 264 , 267 -70;
as philosopher, 285 -87.
See also Allegory; Augustine of Hippo; Servius
W
Wallis, R. T., 86
Walzer, R., 240 -41
Wolfson, H. A., 284
X
Xanthus, 219 , 220
Xenocrates, 34 , 169
Xenophanes of Colophon, 11 , 15 , 35 , 49 , 260
Y
Yeats, W. B., 206
Z
Zeller, E., 34
Zeno, 56 , 58 -59
Zeus, 99 ;
allegorical treatment of, 219 -21, 231 , 238 , 246 -47;
birth of, 104 -6;
and Pandarus, 17 ;
as solar deity, 137 , 265 -66, 278 -79.
See also Homer, Iliad ; Jupiter; Kronos
Ziehen, L., 24
Preferred Citation: Lamberton, Robert. Homer the Theologian: Neoplatonist Allegorical Reading and the Growth of the Epic Tradition. Berkeley: University of California Press, c1986 1986. http://ark.cdlib.org/ark:/13030/ft7g50089t/
_uacct = "UA-294364-1"; _udn="content.cdlib.org"; urchinTracker();
Date: 2015-12-17; view: 1024
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Ancient and Medieval Passages Cited | | | HOME-SCHOOLING: Socialization not a problem |