
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Proportion of the news’ effect on competitor(s)’ return
Finally, to stick to our question of the influence of important news on competitors, the third test is run. To find the important news 10% of the returns with the highest deviation from the mean is identified. Since these events happen from time to time we cannot add autoregressive part in the regression. Also, instead of having company A’s returns as the dependent variable, we regress competitors’ returns at time t  on firm A’s significant returns
on firm A’s significant returns  .
.

Here the p-value of  will show if the significant returns of company A have effect on the competitors’ returns. And the value of
will show if the significant returns of company A have effect on the competitors’ returns. And the value of  will show the scale of the effect. If the value of
will show the scale of the effect. If the value of  is significantly negative we make a conclusion that significant positive (negative) news for company A has a negative (positive) effect on its competitor.
is significantly negative we make a conclusion that significant positive (negative) news for company A has a negative (positive) effect on its competitor.
Justification
The ratio response part of the testing is designed to provide RN (competitors’ stocks reacted strongly in the opposite direction) and Neg (competitors’ stocks reacted in the opposite direction) ratios. They are then compared to the opposite ratio. The opposite ratio is a proxy to correlation between the competitors’ stock returns. If the RN or Neg ratio is higher than the opposite ratio, which would imply that on average significant news brought more information, which led to Situation X, than just any random news.
If the RN or Neg ratio happened to be higher than 0.5 we can try to use computers. They would trade in competitors’ stocks in the opposite way and due to the fact that the ratio is higher than 0.5, on average they are going to earn profits. If RN ratio happens to be higher than 0.5, then the profits would be high. But if only Neg ratio happens to be above 0.5, then the profits are still going to be earned, but not as high.
The proportion of competitors’ effect on stock price return is meant to provide explanation of a company’s stock return. If the values of  and
and 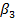 for a company A are significantly negative, then we can imply that Situation X on average happens more often than Situation Y. With the use of intraday data, computers may analyse competitors’ returns. If the returns are positive (negative), then a short (long) position should be opened for company A’s stock. However, the intraday time frame for determination of the direction of competitors’ returns cannot be calculated in this dissertation due to the absence of intraday data. Since the data included all the observations, computers can perform trades on any day, not necessarily those with significant returns.
for a company A are significantly negative, then we can imply that Situation X on average happens more often than Situation Y. With the use of intraday data, computers may analyse competitors’ returns. If the returns are positive (negative), then a short (long) position should be opened for company A’s stock. However, the intraday time frame for determination of the direction of competitors’ returns cannot be calculated in this dissertation due to the absence of intraday data. Since the data included all the observations, computers can perform trades on any day, not necessarily those with significant returns.
Similarly, proportion of news’ effect on competitors’ return explains competitors’ reaction to company A’s news. If the value of  is significantly negative, we can conclude that on average Situation X effect is dominant. Then computers can take advantage of the Situation X and perform trade accordingly. To do so, first they check if the returns are significantly positive (negative) on an intraday scale after the news release for company A. If that is the case they open a short (long) position in the competitor(s)’ stock(s).
is significantly negative, we can conclude that on average Situation X effect is dominant. Then computers can take advantage of the Situation X and perform trade accordingly. To do so, first they check if the returns are significantly positive (negative) on an intraday scale after the news release for company A. If that is the case they open a short (long) position in the competitor(s)’ stock(s).
Hypothesis
Date: 2015-12-17; view: 974
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Ratios of response to significant news analysis | | | Ratios of response to significant news analysis |