
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
IELTS writing task 1 – process diagrams – an introduction
RUSSIA – a promising, dynamic and never dull business environment
| Strengths Large market Availability of high-quality labour Stable political situation (government does not do any radical reforms, it continues the on-going projects, policies and reforms) Support of start-ups and young entrepreneurs In the middle of global rankings Service sector becomes more important Support of innovations Geographical proximity and historical links to emerging markets An increasing number of companies using project oriented management and best practices in running a business Federal government commitment to support innovations The introduction of public private partnership practice in executing big infrastructure projects Introduction of cluster policies Rich resource base Growing wealth Large domestic market Sound economic policy Low sovereign debt levels Sound external liquidity situation | Weaknesses High level of corruption Complexity of tax system Lack of regulatory transparency Government bureaucracy Weak contract legislation Insufficient business ethics Deals are often made on the basis of trust Lots of Russian business registered in foreign countries (offshoring) To get to the Russian market it is important to establish good relations with local authorities Low competitiveness of the local businesses Weak development of regions, all activities concentrated in the country capital Dependence on the global energy landscape State interventionism Weak institutions and corruption Demographics, infrastructure, education and health Low degree of diversification |
| Opportunities Large consumer market with rising middle class EU is the main trading partner – opportunities to develop strong relations with EU and execute mutual cross-border programmes aimed at social and economic development (LT-PL-RU, Tempus, Interreg) – The European neighborhood policy (ENP), Euroregions – have made little headway Diversification of the economic base Development of sme sector Improvement of transparency and corporate governance | Threats Positive economic developments are mostly attributable to high energy prices Political tensions and differing values in developing the relations with EU Energy is the most pressing topic between EU and Russia The development of alternative energy sources The uncertain direction of social cohesion Losing competitiveness Lower oil prices Shrinking population Emigration of population |
There is no intellectual understanding of RussiaJ)
Foreign investment:
- Russian government is putting a lot of effort into attracting more investment into the country and improving the investment climate in general
- Investment fund
- Government undertakes various measures to stimulate investments outside the resource-based industries (special economic zones, tax incentives, export promotion)
- Development bank
- Russia enjoys the highest percentage of satisfied foreign investors. Over 80% of foreign businesses indicate that they are generating very attractive returns on their businesses (ABN-AMRO report)
Factors of positive economic development:
- High prices for energy resources
- Stable macroeconomic policy (fiscal surpluses, reduction of debt levels
- Inflow of foreign capital
- Control of inflation
- Domestic demand
Russian rankings
- Ease of doing business index (112 out of 185)
- Index of economic freedom (51.1), 139th freest in the world
- UNDP Human development index – 55, ranking with high human development
- Global competitiveness index – 64 out of 148
Long term social and economic development plan until 2020 of the Russian Federation (Russia 2020)
Russia may not become of the strongest economies overnight but it is the matter of long-term perspective.
The diagrams for the presentation:
- Share of Russian GDP
Oil and gas represent around 25 % of GDP
- Growh in the number of smes figure
Strategic industries for Russian development
40 industries
- Production of military equipment
- Aircraft
- Spacecraft
- Ciphering tools
- Treatment and trade of radioactive and nuclear materials
- Fields highly endowed with natural resources
EU strategies in developing relations with Russia:
- Enlargement process
- ENP
- Four common spaces with Russia (economics, education and research and internal and external security)
Important notes:
A well –developed SME sector increases competition increases competition and is an important source of jobs and a generator of innovations.
Today we face the challenge of diversifying Russia’s economic structure and reducing its reliance on natural resource sectors has loomed large on policy agenda for well over a decade. Attention has therefore increasingly focused on modernization and in particular, on innovation, as the keys to Russia’s successful development over the long term.
The Russian economy is at crossroads.
Shifts in the global economy are affecting the country due to its strong reliance on oil and gas exports.
Russia is at a critical turning point in its economic, social and political development.
The economy was hit hard by the global financial crisis of 2008.
Russia’s competitiveness in 2012
The Russian Federation ranks 67th in The Global Competitiveness Report 2011–2012. A strong macroeconomic environment (22nd) owing to low government debt and a government budget that has moved into surplus is not enough to compensate for the country’s weak and deteriorating public institutions (133rd) and its struggling innovation capacity (85th). The country also suffers from inefficiencies in the goods (134th), labour (84th) and financial (130th) markets, where the situation has deteriorated in recent years.
Weak market competition (136th), caused by inefficient antimonopoly policies (124th), restrictions on trade and foreign ownership and a lack of trust in the financial system (134th), contribute to Russia’s vast resources being inefficiently allocated, hampering economic productivity. As the country’s economic development advances, its lack of business sophistication (119th) and low rates of technological adoption (137th) will present challenges for its sustained progress, although the high level of education enrolment, especially at the tertiary level, and a large domestic market (7th) can be exploited to improve Russia’s competitiveness.
Russia’s sustainable competitiveness will likely be affected by environmental and social factors, in addition to productivity, which is captured by the global competitiveness index. The country ranks particularly poorly in environmental sustainability, with some of the poorest ratings globally for three indicators: the strength of environmental regulations; the number of international environmental treaties ratified by the country; and the quality of the natural environment. Russia’s social sustainability performance lags behind Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) economies and is lower than in China and Brazil, although Russia outperforms India. In this regard and contrary to most other competitiveness measures, Russia’s profile differs from its BICS peers (Brazil, India, China and South Africa) (see Figure 1).
Evolutions in the global energy landscape guide the dynamics of oil and gas prices, which currently determine to a large degree Russia’s gross domestic product (GDP) and fiscal revenue. High oil prices currently support a strong macroeconomic position. This, however, also creates deep uncertainties about the country’s future should energy prices drop.
IELTS writing task 1 – process diagrams – an introduction
The process diagram is in many ways the odd one out in academic task 1 and it requires some different language from the other task types. This lesson shows you some of the skills you need to tackle a process diagram. In it, I talk you through some of the difficulties in describing a process and suggest some basic techniques to help you understand the diagram and write the description. You will also find a sample task and description.
Reading a process diagram – find the beginnings and ends
The first step in learning to write about a process diagram is to see where the process starts and ends. Sometimes it is evident, frequently it is less so. This is important information as it will help structure your writing. The obvious thing to do is to start at the beginning and carry on until you get to the end.
An example
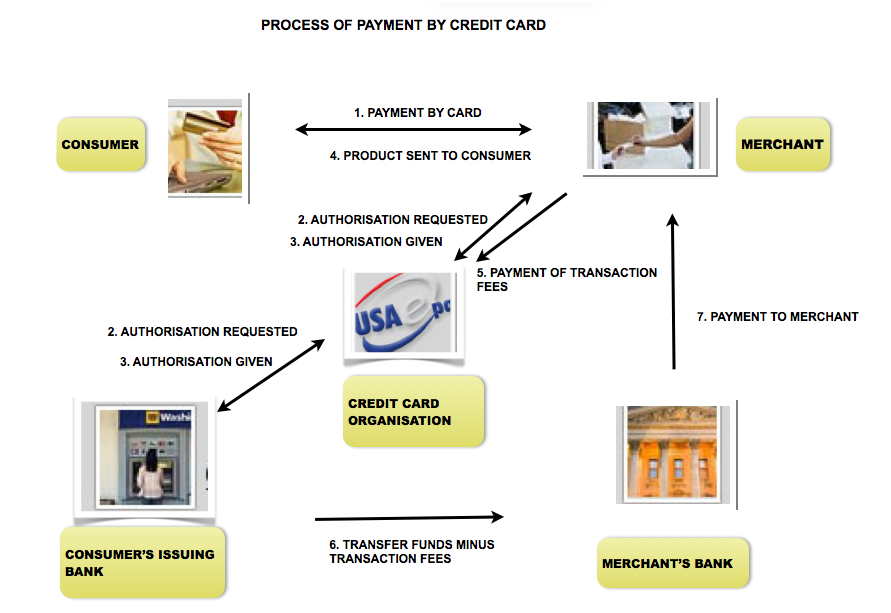
Where is the beginning here? The customer pays by credit card (item 1). Where is the end? The merchant receives his money (item 7). We now know part of the structure of our report.
Date: 2014-12-21; view: 1901
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| SWOT ANALYSIS RUSSIAN ECONOMY – CURRENT STATE | | | Understand the different stages of the process |