
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
E. All of the above.
20. In which of the following combinations would a change in price result in the largest decrease in equilibrium quantity?
A. Inelastic demand, inelastic supply
B. Inelastic demand, elastic supply
C. Elastic demand, elastic supply
D. Elastic demand, inelastic supply
E. None of these choices would influence the equilibrium quantity
Use the following to answer question 21:
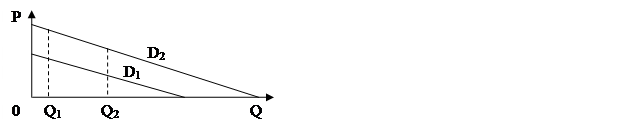
21. Given the figure above, over the same output range Q1-Q2:
A. Demand curve D1 is more price sensitive than demand curve D2.
B. Demand curve D2 is more price sensitive than demand curve D1.
C. Both demand curves have the same price elasticities.
D. Elasticities cannot be determined without supply information
E. Elasticities cannot be determined without price information being given
22. The government would like to discourage the consumption of a particular good by placing a per unit tax on it. This policy would be more effective if:
A. The good had no substitutes
B. The good was a necessity
C. The good was a luxury good
D. The good formed only a small part of consumersí budgets
E. The good had a vertical supply curve
23. If demand for cloggs increased by 11 % at each price when income decreased by
9% then the income elasticity of demand at quantity 100 is _____, and cloggs are ______:
A. 11/9, a luxury good
B. - 9/11, an inferior good
C. -11/9, an inferior good
D. 9/11, a necessity
E. -11/9, a normal good
24. Mary likes apples. Assuming she can get them free of charge, she will stop eating apples when:
A. The total utility from eating apples equals zero.
B. The substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
C. The ratio of marginal utility of apples divided by total utility is equal to one.
D. The marginal utility from eating apples is zero.
E. The marginal utility from eating apples is increasing at a decreasing rate.
25. Don was spending all his monetary income on jam and spam. After a drop in the price of jam, he started to buy more spam. This can be explained by:
ņ. Income effect.
B. Substitution effect.
C. Substitution effect, whose influence dominated income effect for spam.
D. Income effect, whose influence dominated substitution effect for spam.
E. Income and substitution effects for spam reinforcing each other.
26. Suppose that, holding the price for good X constant, we doubled the price for good Y and tripled the consumerís income. Then, on a graph where X is on the horizontal axis, the budget line will:
A. Shift out.
B. Rotate counter-clockwise.
C. Shift in, and rotate clockwise.
D. Shift out, and rotate clockwise.
Date: 2015-12-17; view: 750
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| E. The studentís demand for books is unit price elastic. | | | The correct answer is (e), by construction. |