
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
D. neither Sasha nor Masha has a dominant strategy
E. Sasha and Masha have different dominant strategies
18. In the matrix above, Masha’s best response to a decision by Sasha to play Strategy A is
- no existent
- to also choose Strategy A
- to choose Strategy B
- to choose Strategy B if it is a repeated game
- to choose the cell in which Masha’s payoff is 10.
19. The “Prisoner’s Dilemma” refers to games where
- neither player has a dominant strategy
- one player has a dominant strategy and the other does not
- both players have a dominant strategy
- both players have a dominant strategy which results in the largest possible payoff
- both players have a dominant strategy which results in a lower payoff than their dominated strategies
20. An external cost of an activity is one that is
- borne by those not directly involved in activity
- borne only by those directly involved in activity
- included in the private marginal cost curve
- present only if the activity yields pollution
- transferred from consumers to producers
21. Which factor, if it were present, would lessen the ability of the Coase Theorem to solve an externality
- the situation is already efficient
- negotiating requires hiring a very expensive lawyer
- the parties are all self-interested
- the potential gain in surplus is high
- property rights have already been assigned to one of the parties
22. The tragedy of the commons refers to the
- overuse of resources that have no price
- pollution of our natural resources
- plight of the common man
- overuse of resources that have no cost
- underproduction of external benefits
23. If a given production combination is efficient, then it must be
- Beyond the production possibilities curve
- possible to expand production of one good without lowering the amount of the other
- on the production possibilities curve
- either an attainable or unattainable point
- the best combination out of all possible combinations
24. With perfect competition, market equilibrium is considered efficient because
- prices are low
- the price consumers pay equals the profit producers receive
- no more trades remain that benefit some without harming others
- excess supply is positive
- excess demand is negative
25. Which of the following is NOT guaranteed by the efficiency of the market equilibrium?
- price represents the value of an extra unit of consumption
- rich and poor will have adequate access to the good
- price represents the cost of an extra unit of production
- neither shortage nor surplus will exist
- all mutually beneficial trades will have been made
26. If the slope of the demand curve is zero, the price elasticity of that demand curve will be
- 0
- between -1 and 0
- -1
- between -1 and -2
- - infinity
27. The long run is defined as
- one year or more
- a period in which all factors of production are variable
- the period of time between accounting reports
- a period in which only one factor of production is fixed
- a period in which at least one factor of production is fixed
28. Which of the following is most likely to be a fixed factor of production at a university?
- the number of personal computers
- the number of books in the library
- the number of professors and lecturers
- the amount of chalk (or markers)
- the number of lecture halls
29. Which of the following is most likely to be a variable factor of production at a university?
- the number of administrative staff and assistants
- the size and number of the athletic facilities
- the university brand
- the location of the university
- the number and size of university buildings
30. In general, if the price of a fixed factor of production increases,
- total costs are unchanged
- price rises
- marginal costs are unchanged
- marginal costs increase
- the profit maximizing level of output falls
31. The reason we observe the law of diminishing marginal returns to is that
- as production expands, the firm is forced to hire low quality workers
- firms become less efficient as they produce more
- workers become fatigued as they are required to produce more
- equipment breaks down more frequently as production expands
- the production facility eventually becomes congested if the firm keeps hiring workers without expanding its capital stock.
Questions 32 through 35 refer to the graph below:
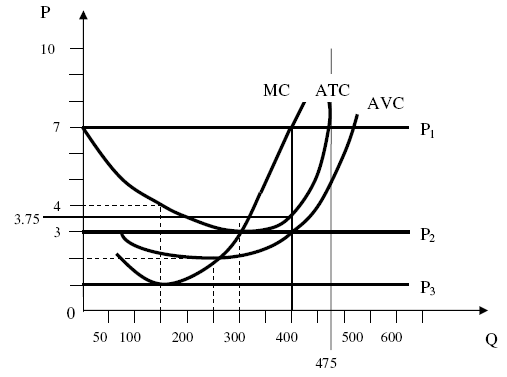
32. When the demand is P1=$7, what is the profit maximizing output?
- 475
- 400
- 300
- 250
- 150
33. When the demand is P1=$7, what is the total cost?
- $960
- $1200
- $1500
- $1600
- $1800
34. When the demand is P1=$7, how much profit (loss) this producer is making?
- $800
- $900
- $1300
- $1600
- $2400
35. When the demand is P3=$1, this firm should____________
- continue to operate in the short run and think about shutting down in the long run
- discontinue operation in the short run since there is a loss when operating
- keep operating as long as the loss is not greater than total cost
- discontinue operation in the short run since average variable cost is greater than price
- discontinue operation in the short run since average total cost is greater than price.
36. Normal profits occur when
- accounting profits are zero
- economic profits are positive
- accounting profits are positive and economic profits are negative
- economic profits are zero
- total revenues are greater than explicit and implicit costs
37. Assume the supply curve is of normal shape. If a per unit tax is imposed, the more elastic demand is, the
- less likely the deadweight loss will be affected
- smaller the deadweight loss
- larger the deadweight loss to consumers
- smaller the deadweight loss to producers
- larger the deadweight loss
38. If demand is perfectly price elastic
- the burden of a tax is shared equally
- the burden of a tax falls entirely on the seller
- the burden of a tax falls entirely on the buyer
- the burden of a tax will depend on the legal assignment of duty to pay
- deadweight loss will be infinite
39. If you were to open a business in an industry that is approximately perfectly competitive, you would expect that
- you would earn little or no profit in the short run, but higher profits eventually
- your competition would respond to your entry into the industry by aggressively advertising
- you would earn zero economic profits in the short run, and zero accounting profits in the long run
- in the long run you would earn zero economic profits and zero accounting profits.
- in the long run you would earn zero economic profits and positive accounting profits.
40. Economic rent is
- the amount you pay to rent an apartment in a free market
- the payment made to suppliers of an input
- what a landowner receives from farmers
- the difference between the payment made to the supplier of an input and the supplier’s reservation price
- the same as the input supplier’s reservation price
41. The common feature in pure monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition is
- the absence of close substitutes
- barriers to entry
- interdependent decision making by firms
- price discrimination
- downward sloping demand
42. Suppose a competitive firm and a monopolist are both charging $5 for their respective outputs. One can infer that
- marginal revenue is $5 for both firms
- marginal revenue is $5 for the competitive firm and less than $5 for the monopolist
- marginal revenue is less that $5 for both firms
- the competitive firm is charging too much and the monopolist too little
- both firms are earning profits
43. A firm is most likely to experience economies of scale if it has _________ start up costs and __________ marginal costs.
- high; increasing
- high; low
- low; high
- low; decreasing
- decreasing; increasing
44. Economies of scale exist when
- constant returns to scale are present
- input prices are falling
- average costs fall as the scale of production grows
- a 10% increase in all inputs causes a 9% increase in output
- firms become extremely large.
45. A firm that emerges as the only seller in an industry with economies of scale is termed a(n)
- cartel
- oligopoly
- monopsony
- natural monopoly
- either (A) or (D)
46. If a monopolist finds that its marginal revenue exceeds its marginal costs at the current level of output, it should
- do nothing; it has maximized profits
- contract production and raise price
- expand output while keeping price constant
- expand output and reduce price
- set price equal to marginal cost
47. The profit maximizing rule MR=MC applies to
- all firms
- monopolists only
- perfect competitors only
- all firms except perfect competitors
- all firms except oligopolists
48. When a monopolist sells additional units,
- total revenues always rise
- marginal revenues are constant
- total revenues always fall
- marginal revenues rise
- total revenues may rise, fall, or remain unchanged
49. Price discrimination means charging
- the same consumers the same price
- different prices to different consumers because production costs are different
- the same price to all consumers because production costs are different
- different prices to different consumers when production costs are the same
- higher prices to consumers with lower incomes
50. Patents and copyrights, which confer market power, exist to
- protect the consumer from low quality imitations
- ensure excessive profits to holders
- protect and encourage research, development and creative expression
- reduce competition in all sectors of the economy
- magnify the dominance of large firms
Date: 2015-12-17; view: 1325
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| C. coincides with the demand curve | | | D. Price equal to marginal cost |