
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Receive the Intent
Every Activity is invoked by an Intent, regardless of how the user navigated there. You can get the Intent that started your activity by calling getIntent() and retrieve the data contained within it.
In the DisplayMessageActivity class’s onCreate() method, get the intent and extract the message delivered by MainActivity:
Intent intent = getIntent();String message = intent.getStringExtra(MainActivity.EXTRA_MESSAGE);
Display the Message
To show the message on the screen, create a TextView widget and set the text using setText(). Then add the TextView as the root view of the activity’s layout by passing it to setContentView().
The complete onCreate() method for DisplayMessageActivity now looks like this:
@Overridepublic void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Get the message from the intent
Intent intent = getIntent();
String message = intent.getStringExtra(MainActivity.EXTRA_MESSAGE);
// Create the text view
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setTextSize(40);
textView.setText(message);
// Set the text view as the activity layout
setContentView(textView);
}
You can now run the app. When it opens, type a message in the text field, click Send, and the message appears on the second activity.
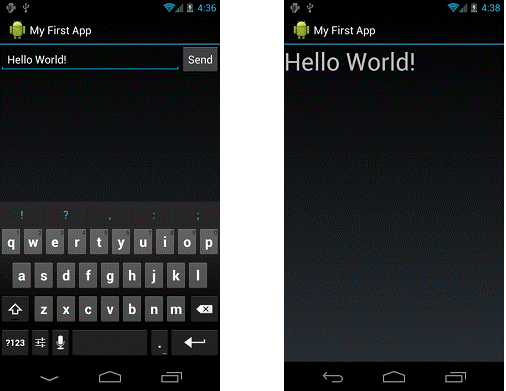
Figure 2. Both activities in the final app, running on Android 4.0.
That's it, you've built your first Android app!
To learn more about building Android apps, continue to follow the basic training classes. The next class is Managing the Activity Lifecycle.
Date: 2014-12-29; view: 1288
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Add it to the manifest | | | The Middle Ages - 1066 and all that |