
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Make the Input Box Fill in the Screen Width
The layout is currently designed so that both the EditText and Button widgets are only as big as necessary to fit their content, as shown in figure 2.
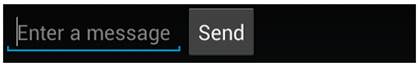
Figure 2. The EditText and Button widgets have their widths set to "wrap_content".
This works fine for the button, but not as well for the text field, because the user might type something longer. So, it would be nice to fill the unused screen width with the text field. You can do this inside a LinearLayout with the weight property, which you can specify using the android:layout_weight attribute.
The weight value is a number that specifies the amount of remaining space each view should consume, relative to the amount consumed by sibling views. This works kind of like the amount of ingredients in a drink recipe: "2 parts vodka, 1 part coffee liqueur" means two-thirds of the drink is vodka. For example, if you give one view a weight of 2 and another one a weight of 1, the sum is 3, so the first view fills 2/3 of the remaining space and the second view fills the rest. If you add a third view and give it a weight of 1, then the first view (with weight of 2) now gets 1/2 the remaining space, while the remaining two each get 1/4.
The default weight for all views is 0, so if you specify any weight value greater than 0 to only one view, then that view fills whatever space remains after all views are given the space they require. So, to fill the remaining space in your layout with the EditText element, give it a weight of 1 and leave the button with no weight.
<EditTextandroid:layout_weight="1"
... />
In order to improve the layout efficiency when you specify the weight, you should change the width of the EditText to be zero (0dp). Setting the width to zero improves layout performance because using "wrap_content" as the width requires the system to calculate a width that is ultimately irrelevant because the weight value requires another width calculation to fill the remaining space.
<EditTextandroid:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
... />
Figure 3 shows the result when you assign all weight to the EditText element.

Figure 3. The EditText widget is given all the layout weight, so fills the remaining space in the LinearLayout.
Here’s how your complete layout file should now look:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<EditText android:id="@+id/edit_message"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/edit_message" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/button_send" />
</LinearLayout>
This layout is applied by the default Activity class that the SDK tools generated when you created the project, so you can now run the app to see the results:
- In Eclipse, click Run
 from the toolbar.
from the toolbar. - Or from a command line, change directories to the root of your Android project and execute:
adb install bin/MyFirstApp-debug.apk
Continue to the next lesson to learn how you can respond to button presses, read content from the text field, start another activity, and more.
Previ
Date: 2014-12-29; view: 1256
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| About resource objects | | | Starting Another Activity |