
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Run on the Emulator
Whether you're using Eclipse or the command line, to run your app on the emulator you need to first create an Android Virtual Device (AVD). An AVD is a device configuration for the Android emulator that allows you to model different devices.
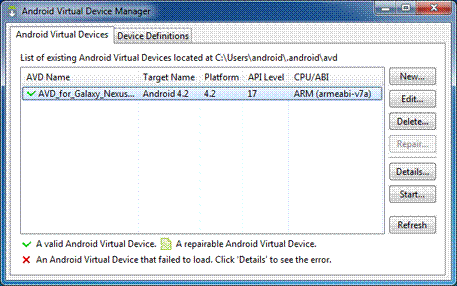
Figure 1. The AVD Manager showing a few virtual devices.
To create an AVD:
- Launch the Android Virtual Device Manager:
- In Eclipse, click Android Virtual Device Manager
 from the toolbar.
from the toolbar. - From the command line, change directories to <sdk>/tools/ and execute:
- In the Android Virtual Device Manager panel, click New.
- Fill in the details for the AVD. Give it a name, a platform target, an SD card size, and a skin (HVGA is default).
- Click Create AVD.
- Select the new AVD from the Android Virtual Device Manager and click Start.
- After the emulator boots up, unlock the emulator screen.
To run the app from Eclipse:
- Open one of your project's files and click Run
 from the toolbar.
from the toolbar. - In the Run as window that appears, select Android Application and click OK.
Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts it.
Or to run your app from the command line:
- Change directories to the root of your Android project and execute:
- Make sure the Android SDK platform-tools/ directory is included in your PATH environment variable, then execute:
- On the emulator, locate MyFirstActivity and open it.
That's how you build and run your Android app on the emulator! To start developing, continue to the next lesson.
Date: 2014-12-29; view: 1375
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| You should also read | | | Create a Linear Layout |