
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
PSC # 6 Work, Power & Conservation of Energy 2011
1) A projectile is shot upward from the Earth with a speed of 20 m/s. Using energy considerations, where the total mechanical energy of the system is conserved, how high is the projectile when its speed is 8.0 m/s? Ignore air friction.
2) A small dust particle of mass 10 mg collides with a spacecraft with a relative velocity of 40 km s-1, and embeds itself in an aluminum shield of thickness 50 cm. What is the average stopping force exerted on the particle, if it penetrates a depth of 50 cm? Do this problem with 2 different methods. Use ‘suvat” equations for method 1, and energy considerations for method 2.( See Adams and Allday, worked example 1 page 70)
3) A 40.0-kg wagon is towed up a hill inclined at 18.5º with respect to the horizontal. The tow rope is parallel to the incline and has a tension of 140 N in it. Assume that the wagon starts from rest at the bottom of the hill, and neglect friction. How fast is the wagon moving after moving 80 m up the hill?
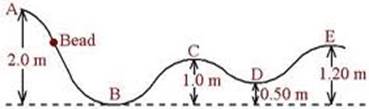
4) A bead (a small hard ball) slides from point A as shown in the figure. If the frictional forces are negligible and the bead has a speed of 2 m/s at A, what will be its speed at points B, C, D and E?
5) A 0.444 kg mass is attached to a spring with a force constant of 26.8 N/m on a frictionless horizontal surface and released from rest a distance of 3.15 cm from the equilibrium position of the spring. What is the speed of the mass when it is halfway to the equilibrium position?
6) * A 500 MW hydroelectric power station operates with water falling 100 meters and falling through an electric generator. Assuming the transfer of gravitational potential energy (GPE) to electricity is 100% efficient; calculate the mass flow rate (the number of kg/s of water) that is passing through the turbines.
7)  * A tennis ball of mass 57.0 g is held just above a basketball of mass 590 g. With their centers vertically aligned, both balls are released from rest at the same time, to fall through a distance of 1.20 m, as shown in the figure.
* A tennis ball of mass 57.0 g is held just above a basketball of mass 590 g. With their centers vertically aligned, both balls are released from rest at the same time, to fall through a distance of 1.20 m, as shown in the figure.
a) Find the magnitude of the downward velocity with which the basketball reaches the ground.
b) Assume that an elastic collision with the ground instantaneously reverses the velocity of the basketball while the tennis ball is still moving down. Next, the two balls meet in an elastic collision. To what height does the tennis ball rebound?
Date: 2015-12-11; view: 1184
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| For further information | | | Respondent was not entitled to withhold payments under the Sales and Licensing Agreement. |