
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
II. The Conduct of Monetary Policy
The Monetary Policy Instrument
A monetary policy instrument is a variable that the Fed can directly control or closely target.
- The Fed could fix the exchange rate as its policy instrument. But then it could not pursue an independent monetary policy, so for that reason the Fed does not fix the exchange rate.
- The Fed, similar to most central banks, chooses to use a short-term interest rate as its monetary policy instrument. The interest rate the Fed targets is the federal funds rate, the interest rate on overnight loans (of reserves) that banks make to each other. Although the Fed can change the federal funds rate by any reasonable amount, it normally changes the federal funds rate one quarter of a percentage point at a time.
- The federal funds rate is determined in the market for reserves.
-
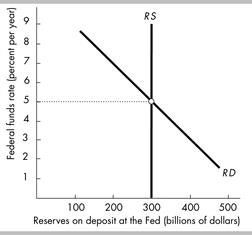 The higher the federal funds rate, the greater the opportunity cost of holding reserves rather than loaning them. So the higher the federal funds rate, the smaller the quantity of reserves demanded. As shown in the figure, the demand curve for reserves is downward sloping.
The higher the federal funds rate, the greater the opportunity cost of holding reserves rather than loaning them. So the higher the federal funds rate, the smaller the quantity of reserves demanded. As shown in the figure, the demand curve for reserves is downward sloping. - The Fed’s open market operations determine the supply of reserves. Because the Fed determines the quantity of reserves, the figure shows that the supply curve of reserves is vertical at this quantity.
· An Open Market Purchase: The Fed buys government securities from a bank and pays for the purchase by increasing the bank’s reserves. The supply of reserves increases.
· An Open Market Sale: The Fed sells government securities to a bank and receives payment for the sale by decreasing the bank’s reserves. The supply of reserves decreases.
- The figure shows the market for reserves. In the figure the equilibrium federal funds rate is 5 percent.
· If the Fed wants to lower the federal funds rate, the Fed undertakes an open market purchase of government securities. The quantity of reserves increases and the federal funds rate falls.
· If the Fed wants to raise the federal funds rate, the Fed undertakes an open market sale of government securities. The quantity of reserves decreases and the federal funds rate rises.
FOMC Decision Making and the Market for Reserves
After assessing the current state of the economy using the Beige book (which is now online), the Fed turns to forecasting three key variables: the inflation rate, the unemployment rate, and the output gap. Based on those forecasts, The FOMC formulates its monetary policy and decides upon its target federal funds rate. The FOMC instructs the New York Fed to use open market operations—the purchase or sale of government securities in the open market—to hit its federal funds target rate.
Date: 2015-12-11; view: 1145
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| III. Generational Effects of Fiscal Policy | | | IV. Extraordinary Monetary Stimulus |