
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Drug calculations
Dose calculation is usually based on either body surface area (mg/m²) or body weight (mg/kg) of the patient. Body weight is used more frequently for ease of calculations.
The calculation of body surface area (BSA) used to require both weight and height.
To calculate drug doses, use the following formula:
Dose required/ Present Standard Quantity of Drug X Present Quantity of Liquid in which Standard Quantity of Drug is Dissolved
In other words:
What you want/What you have X What it is in (dilution)
For example: a patient (child) is prescribed 90mg of Paracetamol and the medication supplied is 120mg of Paracetamol in 5mls:
90 / 120 X 5 = 3.75mls
Medication errors arising from poor mathematical skills of nurses are an ongoing problem
To enhance safety:
Take time working out calculations
Recheck answers
Do not be rushed by colleagues/patients/parents/ carers
Answers that look wrong probably are wrong and an initial mental estimate of the dose may be useful.

Remember: 1 cc is the exact same amount as 1 ml!
Do YOU know the answers to the following?
1 gram = ______ milligrams (mg)
0.001 gram = _____ milligrams (mg)
1 kilogram = _____ grams (g)
0.001 kilogram (kg) = _____ gram (g)
1 liter (L) = _____ milliliters (ml) 0.001 liter (L) = _____ milliliters (ml)
1 milliliter (ml) = _____ cubic centimeter (cc)
1ml = ____ minims
4-5 ml = _____ dram
30 ml = _____ ounce
500 ml = _____ pint
1000 ml = _____ L = _____ quart
60 mg = _____ grain
1 kg = _____ pounds
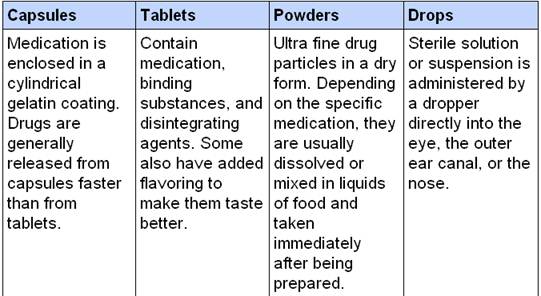
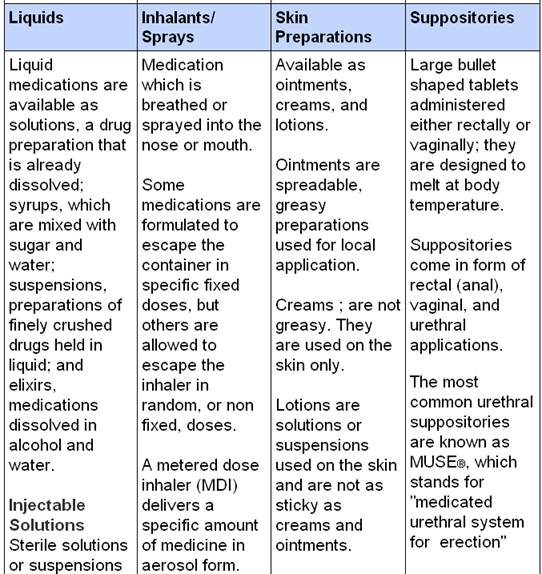
Forms of medicines

Date: 2014-12-29; view: 1393
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Bioavailability | | | Topical administration |