
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
During vigorous activity
| Micelle |
lactic acid accumulates in muscles as a result of incomplete oxidation of glycogen (the energy source). This incomplete oxidation is itself due to a lack of oxygen. When activity stops, some lactic acid is oxidized (to carbon dioxide and water) and some is converted back to glycogen.
 Esters occur widely in nature and have many practical uses. Some give the characteristic smell and flavor to fruits, such as isoamyl ethanoate (A) in bananas. Many waxes and oils consist mainly of esters, such as myricyl palmitate (B) in beeswax and glyceryl tristearate (C) in tallow. The painkilling drug aspirin is an ester-hydroxyl-benzoic acid ID). The plastic Lucite, used for making toothbrush handles and spectacle frames, is a polymer of the ester methyl methacrylate (E). Coconut oil, used in soapmaking and obtained from the fruit of the coconut palm tree (far right), contains various fatty acid esters.
Esters occur widely in nature and have many practical uses. Some give the characteristic smell and flavor to fruits, such as isoamyl ethanoate (A) in bananas. Many waxes and oils consist mainly of esters, such as myricyl palmitate (B) in beeswax and glyceryl tristearate (C) in tallow. The painkilling drug aspirin is an ester-hydroxyl-benzoic acid ID). The plastic Lucite, used for making toothbrush handles and spectacle frames, is a polymer of the ester methyl methacrylate (E). Coconut oil, used in soapmaking and obtained from the fruit of the coconut palm tree (far right), contains various fatty acid esters.
Esters
Esters are organic compounds that result from a condensation reaction between an acid (usually a carboxylic acid) and an alcohol. A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two molecules link together, usually with the expulsion of a small molecule such as water or ammonia. Carboxylic acids are explained in the preceding article on organic acids. Alcohols are also covered in a preceding article in this section on organic chemistry. A condensation reaction involving esters is called esterification. It is an important chemical reaction in organic synthesis, the artificial production of chemical compounds.
An ester is named after the alcohol and acid from which it is derived. Ethanoic (acetic) acid gives ethanoates (acetates) such as ethyl ethanoate. Butanoic (butyric) acid gives butanoates (butyrates). Animal fats, which are esters of carboxylic acids with the alcohol glycerol, are called triglycerides.

|
Banana flavor
c^coocHjCapHici-y.,
| Beeswax |
| CH3(CH2)14COO(CH2)29CH3 |
| Myricyl palmitate |
| Tallow (candle wax) CH2OCO(CH2)16CH3 |
| CH OCO(CH2)16CH3 CH2OCO(CH2)16CH3 Glyceryl tristearate |
| Aspirin |
| COOH |
| CH3 2-(Acetyloxy)benzoic acid |
| Lucite polymer of CH, |
| CH2 = CCOOCH3 Methyl methacrylate |
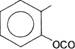 Isoamyl ethanoate
Isoamyl ethanoate




Esters do not generally dissolve in water. They have boiling points slightly higher than hydrocarbons (compounds solely of hydrogen and carbon) of similar molecular weights. Low molecular weight esters are usually colorless liquids. High molecular weight esters are generally solids. They frequently have pleasant odors and are responsible for the fragrance and flavor of many flowers and fruits. Cyclic esters are known as lactones. These are esters whose carbon atoms are bonded in the shape of rings.
Formation ofesters
Esterification (the making of an ester) generally takes place in a solvent other than water. Solvents dissolve substances. In this case, the solvent is usually an alcohol. Acid is the substance dissolved in the alcohol. The chemical reaction between the alcohol and the acid produces an ester and water. New esters can also be made by mixing an alcohol with an ester. Although an organic ester may be said to correspond to a salt in inorganic chemistry, it is formed in a different way.
Esterification has been studied extensively by physical chemists since the middle of the nineteenth century, because it involves an equilibrium. In other words, it is a reversible reaction. Hydrolysis (a chemical process that changes compounds by taking up the elements of water) is the reaction that splits the ester to give the parent acid and alcohol. It is usually catalyzed (speeded up) by dilute mineral acid or a base. This is done in the presence of water at a high temperature.
Esters can also react with bases. Such a reaction is irreversible. It causes the ester to break down into its two basic parts, an acid and an alcohol. Since bases react with acids to

Organic chemistry: Esters 87

|
The subtle flavors of winesdepend largely on the presence of small amounts of esters. They continue to form gradually after fermentation has ceased, while the wine "ages" in the racked bottles stored in a cool cellar.

|

|
form salts, the reaction of an ester and a base produces an alcohol and the salt of the acid. This type of hydrolysis is historically called saponification. It is one of the oldest chemical reactions known. Soap is made by saponification of natural fats and oils (lard or tallow) with lye (sodium dissolved in water or potassium hydroxide). This process is explained in the preceding article on organic acids.
Uses of esters
Low molecular weight esters (such as ethyl ethanoate and butyl ethanoate) are used industrially as solvents for lacquers, resins, and varnish. Solvents dissolve other substances. High molecular weight esters may be used as softeners for plastics. The plastic polymethyl methacrylate is a glass substitute more commonly known as Lucite or Plexiglas. It is made using the ester of an unsaturated acid. Polyethylene terephthalate is the basis of textile fibers such as Terylene, Fortrel, and Dacron. It is also used in sheets as photographic film (Mylar). It takes several stages of esterification to make this complex ester.
Aspirin is an ester, the product of the reaction between salicylic acid (a type of organic acid) and acetic anhydride (obtained from acetic acid, another organic acid). Cellulose is a substance that forms the walls of plant cells and the woody parts of trees and plants. Cellulose esters are used in photographic films, as a textile fiber (rayon), and in explosives. Natural oils and waxes are largely simple esters. Beeswax is mainly myricyl palmitate. Menthyl acetate is the ester found in peppermint oil.
Low molecular weight esters have characteristic fruitlike odors. The flavor and odors of many fruits and flowers are due to a complex mixture of minute traces of esters. Thus, esters have been widely used as synthetic flavors and in perfumes. Different esters can duplicate the taste and smell of bananas (isoamyl ethanoate), rum (isobutyl propanoate), pineapple (butyl butanoate), apple (isoamyl valerate), and
wine/cognac (ethyl decanoate). Wines have hundreds of esters in trace amounts contributing to their flavor. The ethyl esters of the wine acids form slowly, adding to the unique bouquet of vintage wines, rum, and brandy.
Lactones are usually encountered in their most stable form—the five- and six-membered rings respectively known as gamma- and delta-lactones. Both types are widely distributed in nature, especially in plants. Large ring lactones (with 15 or 16 carbon atoms) have musky odors. Several of the unsaturated lactones found in plants are used as drugs.
Many old aircraft,and
some modern lightweight ones, have surfaces made by fixing fabric (such as linen) onto wooden frames. A key stage involves painting the fabric with a quick-drying lacquer or "dope." Typically, this consists of a cellulose compound dissolved in a volatile ester, such as amyl ethanoate.
Nitrogen compounds
|
| © |
| Ammonia |
Tertiary amine
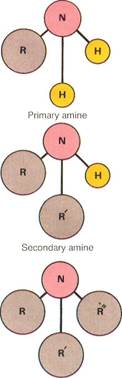
Ammonia,NH3, is a simple nitrogen compound and the "parent" of amines. In a primary amine, one of ammonia's hydrogen atoms is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (R). Substitution by further groups gives secondary and tertiary amines.
There is a wide range of organic compounds that contain nitrogen. These include amines, amides, nitriles, oximes, and nitro compounds. Among the most important are amino acids. These are covered in an article later in the biochemistry section.
Amines can be considered to be derivatives of ammonia, since they are obtained from the ammonia compound. They are classed as either primary, secondary, or tertiary. The classification depends on the number of hydrogen atoms "replaced" by organic groups. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the compound is a primary amine. If two hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups, it is a secondary amine. If three organic groups are attached to the nitrogen atom, it is a tertiary amine. A tertiary amine has no hydrogen atoms connected directly to the nitrogen atom.
Aliphatic amines are named after the parent hydrocarbon. Thus, if an amino group replaces one of the hydrocarbon atoms in methane, the resulting compound is aminomethane (formerly called methylamine). The names of secondary and tertiary amines are more complicated and not used too often. Many aromatic amines (such as aniline) and nitrogen ring compounds are still known by their trivial names, because their proper names are unwieldy.
Amines play important roles in biochemical systems. They are widely distributed in nature as amino acids (the building blocks of protein), alkaloids (organic bases found in plants), and vitamins. Manufactured amine derivatives are medicinal chemicals (sulfa drugs and anesthetics) and starting substances for synthetic fibers such as nylon. Aniline (aminobenzene) is the most important industrial amine. It is highly toxic. It can be used to make a whole family of dyestuffs.
Date: 2015-12-11; view: 1668
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Kinds of carboxylic acids | | | Structure and properties of amines |