
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Amp;Text 2. THE STATE SYSTEM OF THE UNITED KINGDOM
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is one of the few developed countries of the world where a constitutional monarchy has survived with its ages-old customs, traditions and ceremonies. The British Constitution, unlike that of most other countries, is not complied in any single document.
The United Kingdom is governed by Her Majesty’s Government in the name of the Queen. Although the Queen is deprived of actual power, she has retained many important, though formal, functions. These include summoning, proroguing and dissolving Parliament; giving royal assent to the bills passed by the Parliament; appointing very important office holders, including ministers, judges, diplomats, bishops. She appoints the Prime Minister (usually the leader of the political party which commands a majority in the House of Commons) to form a government of State.
Under the British Constitution the Government functions through the following bodies:
· the Legislature which makes laws;
· the Executive which puts laws into effect and plans policy;
· the Judiciary which decides on cases that arise out of law.
The legislative branch is Parliament where laws are passed. The Parliament consists of two chambers: House of Lords and House of Commons. The MPs (the members of the House of Commons) are elected for a five year term at General Elections by a majority electoral system.
The executive branch which plans prospective laws and formulates policy is the cabinet of the Government. The Prime Minister is an active member of the legislative yet he is also the leading member of the executive.
The judiciary is independent, its adjudications are not the subject of ministers’ direction or control. The Courts of the United Kingdom are the Queen’s Courts, since the Crown is the historical source of all judicial power.
(British Studies. D. Kozikis, G. Medvedev, N. Demchenko Ìèíñê. Ëåêñèñ,2004)
&Text 3. THE USA POLITICAL SYSTEM
The United States is an indirect democracy – that is, the people rule through representatives they elect.
The United States has a federalist system. This means that there are individual states, each with its own government, and there is a federal, or national, government. The Constitution gives certain powers to the federal government, others to the state governments, and yet other powers to both.
Within the national government, power is divided among three branches: the legislative, executive and judicial branches.
The legislative branch consists of Congress, which has two parts – the House of Representatives and the Senate. Congress’s main function is to make laws. There are 100 senators (two from each state) and 435 representatives (the number from each state depends on the size of the state’s population).
The President is the head of the executive branch and the country. The executive branch administers the law. In addition to the President, the Vice-President, and their staffs, the executive branch consists of departments and agencies. There are now 14 departments, each with different responsibilities. The President appoints the department heads known as Secretaries, who together make up the President’s Cabinet.
The judicial branch interprets the laws and makes sure that new laws are in keeping with the Constitution. There are several levels of federal courts. The Supreme Court is the most important. It has nine members, who are appointed for life.
(Spotlight on the USA. Randee Falk. Oxford University Press. 1993)
9. Complete the sentences with the proper word using the words from the chart of Task 6.
1. The President of the USA as the head of the … power is assisted by the Vice-President and the Cabinet.
2. The House of … in the Republic of Belarus consists of 110 deputies.
3. The members of the Council of Republic are … at the meetings of the deputies of the local Councils.
4. According to … the head of the state is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces of the republic.
5. The Supreme Court in the USA comprises the Chief … and eight associate ….
6. In order to become a law a bill should be approved by the two chambers of the … body and should get the approval of the head of the state.
7. The … in the UK is independent but the courts are the Queen’s Courts.
8. A person can take part in … when he/she is a citizen of the country and has become of age.
10. Can you explain the difference in the meaning of the following terms? Make the examples of your own to show this difference.
1)  policy – politics
policy – politics
2) freedom – right
3) bill – law
4) vote – ballot
5) enforce – strengthen
6) appoint – adopt
7) elaborate – introduce
 Try to do “General Knowledge Quiz” in the Supplement to check, if you know a lot about the state structures of the Republic of Belarus, the UK and the USA.
Try to do “General Knowledge Quiz” in the Supplement to check, if you know a lot about the state structures of the Republic of Belarus, the UK and the USA.
11. Complete the text with the proper word from the box below.
represented, implemented, branches, approved, political, judiciary, laws, chambers, executive, elected
POLITICAL PROFILE OF A COUNTRY
When we speak about the (1) … system of any country we take into consideration three (2) … of power – legislative, executive and judicial irrespective of the head of the state.
The legislative branch is usually (3) … by the Parliament and its main function is to make laws. In most countries the parliament includes two (4) … or houses. The members of the parliament are (5) …for different terms according to the regulations of the sovereign country.
The (6) … branch is, actually, the government or the Cabinet of Ministers. The Prime Minister is often at the head of the executive. The main function of this branch of power is to implement (7) … which are adopted by the Parliament.
The (8)… is empowered to observe and control if the laws are executed according to the Constitution of the country.
The system of adopting the law works as follows. The bill (draft) is introduced by the department of the government or some committee to the lower chamber of the Parliament. If it is (9) … the bill goes to the upper chamber. The bill becomes the law only after it is approved and signed by the head of the state. The way how the law is (10)… is supervised by the Court.
12. Read the list of different functions of the branches of power. Sort out the functions into four categories as belonging to the
Ø head of state
Ø legislative branch
Ø executive branch
Ø judicial branch
| 1. introduces a bill | 8. determines if a law violates the Constitution |
| 2. is an integral part of the legislature | 9. elaborates the basic guidelines of the domestic and foreign policy |
| 3. approves laws | 10. is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces |
| 4. implements laws | 11. adopts laws |
| 5. watches the laws observe | 12. levies taxes |
| 6. gives consent for the appointment of the top officials | 13. appoints top officials |
| 7. is the head of the executive branch | 14. has the right of veto |
13. ^ In pairs compare the state structures of the Republic of Belarus, the UK and the USA according to the following outline:
Ø the type of the statehood;
Ø the head of the state and his / her powers;
Ø the organization and main functions of the main branches of power;
·  legislative
legislative
· executive
· judicial
Reading and watching for information on forms of governance, the system of checks and balances, separation of powers
14 a. 8 Watch a YouTube video fragment “Form of Governance” and arrange the political spectrum of the forms of the government according to the given explanation:
| Form of government | Explanation | ||
| a | monarchy | rule of majority | |
| b | oligarchy | no government | |
| c | democracy | rule by one | |
| d | republic | rule by a group | |
| f | anarchy | rule of law |
14 b. _Work in groups of 3 or 4. Share your ideas on the following issues:
Ø What examples of the history of Ancient Greece and Rome given in the video illustrate the idea that “the essence of freedom is the proper limitation of government”?
Ø Why is there no word “democracy” either in “The Declaration of Independence” or in the American Constitution?
15. Complete the text with the proper word, making a derivative from the word on the right.
| CHECKS AND BALANCES One of the unique characteristics of the American systems of … is the system of “checks and balances”. The men who wrote the …were afraid that one person or branch of government might get too …. After all, they had just finished fighting a bloody war against the powerful King of England because the king had taken away many of their rights. So they made sure that each branch of government could control the other branches. For example, the … can ‘check’ Congress by … or rejecting laws it passes. On the other hand, Congress can … the President if enough members feel that he is not doing a good job. And the Supreme Court can decide a law is …. | govern constitute power preside veto move constitute |
16. You have recently read the text “Checks and Balances”.
8 A) Watch a You Tube video lecture “Separation of Powers” and find out how the principle of checks and balances works in the USA.
B) Think of the examples of how this principle can be applied in different states.
C) Write several lines about the principle of Checks and Balances:
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
‘ round-table discussion
17. You are at a summer language school. You are taking part in the round-table discussion about the functioning of different political structures. Act on behalf of the Belarusian / British / American part. Describe the political system of the country you represent.
 The format of Round-table is described in Part 1, section 2B.
The format of Round-table is described in Part 1, section 2B.
’ COGNITIVE MAP FOR TEXT RECONTRUCTION
18. Read the text “Defining Democracy” below, Find the answers to the following questions:
1. What is the dictionary definition of the term ‘democracy’?
2. What is the difference between the direct and representative democracies?
3. Why are the ideas of democracy and freedom used interchangeably?
4. What does each group of freedom (political, social, economic) implement?
DEFINIG DEMOCRACY
Democracy may be a word familiar to most. According to the dictionary definition, democracy “is government by the people in which the supreme power is vested in the people and exercised directly by them or by their elected agents under a free electoral system” (Webster’s New World Dictionary. Warner Books Paperback Edition. 1990). In the phrase of Abraham Lincoln, democracy is a government “of the people, by the people and for the people.”
Democracy falls into two basic categories: direct and representative. In a direct democracy all citizens can participate in making public decisions. Modern society, with its size and complexity, offers few opportunities for direct democracy. Today, the most common form of democracy is representative democracy, in which citizens elect officials to make political decisions, formulate laws and administers programs for the public good.
Freedom and democracy are often used interchangeably, but the two are not synonymous. Democracy is indeed the set of ideas and principles about freedom.
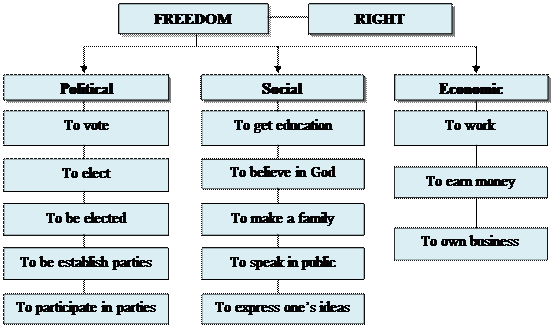
Most legal freedoms can be divided into three main groups:
Ø political freedom
Ø social freedom
Ø economic freedom
(What is Democracy? US Information agency, 1997; The individual in Society: Issues in English. I. Geniene, L. Miseviciene, etc. CfBT Educational Service, 1997)
19. _  In groups analyze the following cognitive map on the basic human rights and freedoms, tell your partners about people’s rights using the presented data. You can add any additional information. Present the result to the class.
In groups analyze the following cognitive map on the basic human rights and freedoms, tell your partners about people’s rights using the presented data. You can add any additional information. Present the result to the class.
 |
20. ^ Here are some opinions of famous people about freedom. Read and translate them. Work in pairs, choose one of the quotations, discuss it and make your comments. Present the results of your discussion to the group mates.
Ø “Man is condemned to be free.” Jean-Paul Sartre
Ø “Liberty means responsibility. That is why most men dread it.” George Bernard Shaw
Ø “It is often safer to be in chains than to be free.” Franz Kafka
Ø “Do not believe in freedom in the philosophical sense. Everybody acts not only external compulsion but also in accordance with inner necessity.” Albert Einstein
“ Finalizing 4 A
Option A. Interview a foreign student of our university, asking about:
- impressions after a year or several years in our country,
- places they have visited in our country
- people they have met here
- experiences (of shopping, going to cafes, discos, libraries etc.)
- add any other issues in your interview and present it as a video/an article/a audio-record.
and present the results of your interview to your group-mates.
Option B. Do research on one the following topics:
1. From the history of the most influential political parties in Great Britain and the USA.
2. Organization of the election campaigns in Belarus, Great Britain and the USA.
Make a Report on the results of your research and present it as if you are taking part in a student scientific conference.
” Ñ Check yourself!
I Match the terms with their definitions
| power (n) | a | political, financial, social, etc. force or influence; | |
| right (n) | b | a statute in draft, before it becomes law | |
| vest (v) | c | a plan of action adopted or pursued by an individual, government, party, business, etc. | |
| legislate (v) | d | to place or settle (power, rights) | |
| execute (v) | e | to make or pass laws | |
| judge (v) | f | to carry out, complete; to perform, accomplish, effect | |
| enact (v) | g | any claim, title, etc. , that is morally just or legally granted allowable or due to a person | |
| constitute (v) | h | to make into an act or statute; to establish by law, decree | |
| bill (n) | i | to hear and decide upon a case; | |
| policy (n) | j | to form, to compose; to give legal form to |
Score 10
II. Correct mistakes, changing the sentences below and writing the right variants.
1. The National Assembly, is a representative and legislative body of the United Kingdom.
2. The American Parliament consists of two chambers: House of Lords and House of Commons.
3. The President is the head of the legislative branch and the country.
4. Today, the most common form of democracy is direct democracy, in which citizens elect officials to make political decisions, formulate laws and administers programs.
5. When we speak about the political system of any country we take into consideration three branches of power – legislative, executive and presidential.
6. The House of Commons in the Republic of Belarus consists of 110 deputies
Score 6
III Complete the text with the derivative from the words on the right.
| GOVERNMENT AND ADMINISTRATION Britain is a parliamentary democracy with a (1) … monarch as the head of the state. The British (1) …, unlike those of most other countries, is not set out in a single document. Instead it is made up of a combination of laws and conventions. Conventions are rules and practices which are not legally (2) …, but which are regarded as vital to the working of government. In the laws the Queen is head of the (3) …, an integral part of the (4) … , head of the judiciary, the commander-in-chief of all the armed forces of the Crown and the supreme (5) … of the established Church of England. The centre of (6) … power is the House of Commons. The Commons has 651 (7) … Members of Parliament (MPs), each representing a local constituency. Once passed through both Houses, (8) … receives the Royal Assent and then it becomes law. | (1) constitute (2) force (3) execute (4) legislate (5) govern (6) parliament (7) elect (8) legislate |
Score 9
IV Read the text and do the tasks that follow.
Date: 2015-04-20; view: 1977
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Amp;Text 1. POLITICAL SYSTEM AND STATE STRUCTURE OF BELARUS | | | THE BILL OF RIGHTS |