
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Section 1. Stages of ship construction
The corporation is by far the most complex of the three business structures.
As defined by the Chief Justice Marshall's famous decision in 1819, a corporation " is an artificial being, invisible, intangible, and existing only in contemplation of the law." In other words, a corporation is a legal entity, distinct from the individuals who own it.
Ex. 13
Analyze the ways of noun formation and translate them into Russian.
Legality, fluctuation, availability, requirement, disadvantage, similarity, importance, knowledge, mobility, intelligence, ownership, formation, restriction, approval, decision, flexibility, taxation, freedom, responsibility, investment, insurance, coverage, termination, illness, financing, experience, contribution, agreement, consideration, elimination, dissolution, disposition, permanence, investor, stockholder, lender, disability, accountant, misunderstanding.
Ex. 14
Complete the sentences. Put the necessary verbs into a passive form.
build make spend send
hold take over steal tell
1. They ..................... by an American company last year.
2.Their new factory .................. on the outskirts of town.
3. Over $ 3 million ................... on advertising last year.
4.A prospectus ...................... to all potential investors.
5.Why .............. clients ................ in advance about this increase in fees?
6.An extraordinary general meeting .................. next Wednesday.
7. The share offer ...................... by a leading merchant bank.
8. They claim that plans for the new aircraft ................. by a competitor.
Ex. 15
Find the sentences in the text in Passive Voice and analyze them.
Ex. 16 Grammar focus. Conditional sentences (types 1 and 2).
Model 1: If I see a nice jumper in the shop, I'll buy it.
What will you do if you don't have enough money?
Model 2: If I were Prime Minister, I'd increase income tax.
What would you do if you saw a ghost? What is the difference between these models?
Complete the following sentences:
a) 1. I'll be happy if...
2. If I have a lot of money....
b) 1. If I had 1 million dollars...
2.1 would be very upset if...
Ex.17 Put the verbs in brackets into the correct form.
Model: If share prices continue to fall, we... 'll lose (lose) a lot of money.
If we…paid (pay) the transport costs, would you reduce the unit price?
1. If the men call off the strike, we.... (negotiate).
2. If our competitor. ..(go) bankrupt, we'll increase our market share.
3. If we.. .(change) the packaging, we'd sell more.
4. If we asked for easy credit terms, they (not agree).
5. If a firm... (offer) me a bribe to get an important contract, I'd ask "How much?"
Ex.18 Make up chains of sentences ( 5-7 sentences):
If I won 5 million I 'd buy a plane
If I bought a plane, I'd go to Las Vegas, etc.
Compare the last sentences of your chains with your partner.
Ex.19 What would you do if:
a) you could speak perfect English?
b) you found burglars in your flat?
c) you lost your job?
d) you found a purse?
e) you met a famous film-star?
f) your friend invited you to the party?
Ex.20 a) Work in pairs. How would you feel in the following situations? Would you be pleased, sorry or angry if:
1.you picked up a bargain in the sales?
2. you paid next to nothing for something?
3. you were overcharged in a restaurant?
4. you were overdrawn at the bank?
Glossary:
Access: the means of getting to something.
A corporation has a greater access to capital than does a sole proprietor.
Articles of co-partnership: the agreement telling the terms and conditions of a
partnership.
The articles of co-partnership should also provide a method of selling the
businesses.
Articles of incorporation: the agreement telling the terms, conditions and purposes of
a corporation. These must be filed in the state where the corporation is
chartered.
My lawyer will draw up the articles of incorporation
Asset: (often plural) anything of value to a company. Anything which can be sold or
converted into cash.
The partners each own a share of the assets of the partnership. Inventory is a
current asset because it will be sold during that business year.
Bankrupt: unable to pay one's debts and legally released from the liability .
His business went bankrupt because of poor management and bad financial
decisions.
Bills: debts; money which must be paid to someone for a service or product received.
The bill for my telephone service arrives today. Most suppliers want you to
pay the bill within thirty days.
Board of directors: a group of persons elected by stockholders to run a corporation.
The board of directors has decided to pay a dividend of $5 per share.
Capital: he money which owners or stockholders invest in a business.
We need some capital in order to purchase new production equipment .
Chief executive officer (CEO): the top manager or director of a company .
The board of directors has hired a new chief executive officer for the corporation.
Comply: obey.
The corporation must comply with all the regulations which pertain to it.
Corporation: a group of persons granted a charter to do business as a separate unit with its
own rights and responsibilities.
Large businesses are operated as corporations because capital can be easily
raised and liability is limited.
Dissolve: to break up a partnership or corporation.
The partnership was dissolved because the two partners wanted to have their own
businesses.
Dividends: a share of the profits of a corporation which is given to the stockholders.
The dividend will be paid to owners of record on June 30.
Enterprise: a business, particularly one privately owned.
If the sole proprietor wants to quit,he can simply find someone to purchase his
enterprise.
Entity: a separate unit for ownership or legal purposes.
As a separate entity a corporation can own property apart from the individual
stockholders.
Expertise: special knowledge or ability.
This accountant has expertise in financial planning.
Financial: refers to money or the management of money.
This company is in good financial condition.
The sole proprietor makes all his own financial decisions.
Income tax: a tax which is based on the amount of money a person or company receives for
labor, services, or products, and which cannot be added to the price of the labor,
services, or products .
The owner of a sole proprietorship pays personal income tax on the profit he
receives.
The business itself pays no tax.
Inventory: the amount of goods, merchandise, or materials on hand.
Once each year the owners of the store must record all their inventory in order
to know which goods they have on hand.
Some new computerized cash registers are able to keep track of inventory
Liability: (often plural) debt or legal responsibility.
The assets and liabilities of the company must be listed on the balance sheet.
The liability of a corporation is limited to its assets.
The sole proprietor has all the liabilities of his business.
Limited: restricted;not allowed to exceed a certain amount.
A corporation's liability is limited to the value of its assets.
Ownership: refers to a right a person has to things that belong to him.
The ownership of a sole proprietorship can be transferred if the proprietor
wants to sell it.
In order to sell a car, you must have an ownership certificate.
Private ownership of property is an American tradition.
Partnership: a business owned by two or more individuals.
The owners of a partnership share in the operation and profits of the business.
Profits: the amount of income above costs.
The profits have increased due to a decrease in the cost of raw materials.
Proprietorship: ownership of a small business.
This restaurant is operated as a sole proprietorship. It is owned by one
individual.
Purchase: buy.
The individual owner can decide whether or not to purchase new tools and
equipment.
Section 1. Stages of ship construction
Words and Terms to be Remembered
| construction assembly prefabrication shipyard building berth route sequence weld rivet mould erect tightness | launch trial trip design office digital master plan numerical stockyard blast corrosion torch ways subassemble |
Read the text and find the answers to the following questions.
1. Why is shipbuilding one of the most important assembly industries?
2. What is a building berth?
3. What must the naval architect and the shipowner coordinate?
4. What are the production stages in ship construction?
Shipbuilding is one of the most important assembly industries in the world. There are more individual pieces in the ship than in any mobile structure made by man. The shipyard is the place where all the pieces of structure are brought together, put into their proper positions and made into the living ship. The place where the ship is built in the shipyard is known as the building berth.
Ships are designed by naval architects. The largest shipping companies have their own naval architects. In Europe and Japan shipyards employ naval architects to design a ship for a customer, or offer basic designs which can be varied to suit the customer's needs. Shipowners may also go to independent firms of shipping consultants and ask their naval architects to design a ship for them.
When shipowners decide to order a new ship, they tell the naval architect the cargo they want the ship to carry. They also tell him what routes the ship will ply and the desired speed. They put limits on the ship's dimensions and on the price that they are prepared to pay. The ship must also comply with the rules of the classification society and international regulations. Economic, engineering and safety factors all govern the design of a ship. The building of a ship follows a well-ordered sequence of events:
1) Securing contract for building;
2) Preparing the working drawings, the moulds, etc.;
3) Ordering of material for construction;
4) Machine-shop processes;
5) Erection operations at the building berth;
6) Welding or riveting the portions of the ship together;
7) Testing watertight or oiltight parts for "tightness";
8) Launching;
9) Fitting out and installing the main and auxiliary machinery;
10) The trial trip and delivery.
After the vessel has been ordered, the plans are completed in the drawing-office. Today shipbuilding begins in the design office, where computers are used to help develop a variety of designs. The preferred design is refined on the drawing board and then translated into digital signals and fed back into the computer. The final plans must be approved by a classification society such as Lloyd's Register of Shipping. This is necessary if the owner wants his ship to be classed. While the ship is being built, constant checks are made to make sure she is being built to the standards of the society. Classification will show that the ship is seaworthy and able to carry the cargo she has been designed to carry. The plans required by the classification society for the new ship may be termed the master plan, and at this stage all the technical data concerning speed, power for propulsion, deadweight, cubic ballast, bunker capacities, trim, shape and propeller design are finally checked. Then follows the preparation of the lines plan, the working model, the plans required by the engine builders and the drawings of stern casting and forgings. The final design is studied for practical production modifications, and then, using computer-aided manufacturing techniques, the design is passed on to numerically controlled cutting and bending machines. Additional computer programs are used to ensure that as many ship parts as possible are cut from each steel plate to avoid wasting material.
Nowadays a shipyard is organized so that each stage in the building of a ship is done in a continuous chain of shops. Each shop is linked by conveyor rollers and moving cranes on rails. First of all, steel plates and bars are taken from the stockyard to the preparation shop. Here they are cleaned by shot (sand) blasting and are coated with a primer paint to prevent corrosion. Then they are cut and shaped automatically by machines. Cutting is done by gas torches and shaping by giant presses. After that, the pieces are welded together in prefabrication (assembly) sheds to form sections. The prefabricated sections are then transferred to the building berth where they are lifted into position by giant cranes. Most ships are assembled on sloping ways which extend inland from the water's edge. Other ships are built in dry docks or graving docks. On the ways or in the dock a temporary framework supports the ship while it is being built. The ship's keel, the bottommost line of plates along her centerline is laid within the framework. Construction proceeds upward and outward. Large segments of the ship are subassembled in the shipyard shops, then brought to the ways and welded into place.
 Exercises and assignments
Exercises and assignments
Ex. 1. Give all the words that can be derived from the following verbs. Find in the text the sentences in which these verbs or their derivatives are used and translate them into Russian.
Assemble, fabricate, industry, consult, construct, erect, weld, draw, numerate, employ, blast, deliver, prefer, modify, regulate.
Ex. 2. Match the words on the left with their synonyms on the right:
| blast deliver mould drawing contract sequence framework digital construct employ ways assemble check stockyard modification | built succession blow change storehouse building berth engage hand (over) pattern numerical support agreement plan control collect |
Ex. 3. Review the vocabulary items. Match the definition with vocabulary item.
| Vocabulary item | Definition |
| 1) shipyard | a) patterns conforming exactly to the shape of parts of a ship by the aid of which these elements can be fashioned to the required form |
| 2) building berth (ways) | b) a way taken or planned from one place to another |
| 3) rivet | c) fit or put together, collect the parts of (a ship) |
| 4) assemble | d) fasten with metal pins various structural parts composing a ship's hull |
| 5) weld | e) a place for construction and fitting out of vessels |
| 6) route | f) portion of land near the water in a shipyard specially prepared for constructing a ship |
| 7) mould | g) join pieces by hammering, pressure or fusing |
Ex. 4. Fill in the blanks. Make use of the appropriate words from the text.
1. Ships are designed by _________.
2. The ship must comply with _________.
3. The shipbuilding begins in the _________ where computers are used.
4. Steel plates and bars are taken from _________ to _________.
5. The steel plates are coated with _________ to prevent _________.
6. The pieces are welded together in _________ to form _________.
7. A temporary _________ supports the ship on the building berth.
8. The place where the ship is built in the shipyard is known as _________.
9. The shipowner tells the naval architect what _________ the ship will ply and _________.
10. Economic, engineering and _________ factors govern the design of a ship.
Ex. 5. Study this diagram which shows each stage the plates and bars go through on their way to the building berth; read the following sentences and arrange them in the correct sequence. The first has been done for you.
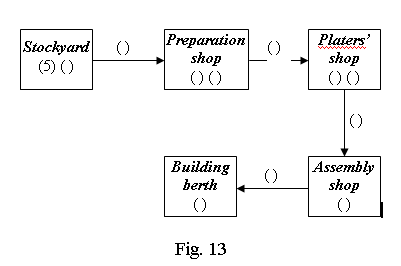
(1) The units are carried to the building berth by giant cranes.
(2) In the platers' shop they are cut to the correct size by gas torches.
(3) They are conveyed to the preparation shop by magnetic cranes.
(4) In the assembly shop they are joined together to form larger units.
(5) The steel plates and bars are off-loaded from lorries or railway wagons.
(6) At the building berth the units are welded together to form the hull.
(7) They are transferred to the platers' shop by conveyor rollers.
(8) In the preparation shop they are coated with primer paint to prevent corrosion.
(9) They are transferred to the assembly shop by cranes or conveyor rollers.
(10) In the platers' shop they are shaped by different presses and rollers.
(11) The steel plates and bars are stored in the stockyard ready for processing.
(12) In the preparation shop they are cleaned by shot blasting.
Date: 2014-12-28; view: 3035
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| The Corporation | | | Section 1. General classification of civil ships |