
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Roentgen-anatomy| features of the respiratory organs in children |kids|.
Thorax in newborn is short and wide. Intervertebral intervals|spaces| are wide. | The sternum consists of separate ossificated nucleus.
A diaphragm at children|kids| under one year age is located on either side at the level of anterior parts of the 5th-6th ribs.
In newborn trachea is short (4-5 sm|). At children|kids| under age 3-4 years on the mediastinum background |a trachea and main|head,leading| bronches are differentiated as lengthened brithness|.
Lungs The obiqua interlobal fissures in newborn are located highly, therefore inferior pulmonary lobes|bottom|lobes are greater than superior|upper,top|. Interlobar fissures do not extend to|by| the roots, in this connection an inflammatory|hot-tempered,ardent| process in sub-root areas|zones| can pass|turns| from one lobe|part,stake,portion,share| to other. In the bronches mucus shell lot of circulatory and lymphatic vessels are located, that is why|that is why| at inflammatory|hot-tempered,ardent| processes, communicating|passable| of bronches is often violated|excited| (hyperinflation, atelectasis |).
Lungs vessels. The pulmonary trunk|barrel| diameter at children|kids| is greater, than aortal one (to 10 years). The segmentar and sub-segmentar arteries at children|kids| under age 3 years relatively|in relation to| short, that is why|that is why| on the sciagram their transversal cuts are form the outlined focal| shades|shadows| of round and oval form|shape|.
The lungs roots at the children|kids| of early age are located at the same level, their structure is homogeneous.
The computer tomography anatomy of the thoracic cavity organs. It is accepted to execute|implements| computer tomography| at certain|definite| anatomic levels. In accordance with|according to| these levels is developed a computer roentgen-anatomy| | (fig.15.10, A|but|, B, C, D, E, F, and G).
I. An apex|top| level or level of the|upper,top| superior thoracal aperture (0 mm|) passes through incisura|cutting| and sterno-clavicular joints|halving,compounds,junctions,joints,coupling|, 7th cervical or 1st thoracic vertebra and 1st or 2nd ribs. Pulmonary parenchyma| conforms S1|tops|. A trachea is visualizing in the| center, in front of the trachea is thyroid | gland |, |but|between the trachea and vertebra column – esophagus, |bacthe anterolateral from trachea the brachiocephalic veins and brachiocephalic arteries are located. The para-tracheal lumphatic nodes are visualized| round|about| the trachea (their diameter in a norm|standard| no more than 5 mm|). The vascular pattern at this level has the appearance of shallow|small| roundish or short line-like shades|shadows|.
II. The level of sternoclavicular joint (20 mm|) - along the clavicle inferior|bottom| surface, through|from,because of| the handle of sternum|, areas of superior|upper,top| ribs and 2nd thoracic vertebra. Pulmonary parenchyma | is the lungs superior lobe apex|tops| segments|upper,top|. A vascular pattern has the appearance of roundish shades|shadows|. The brachiocephalic| veins are located at front trachea with diameter about 2 sm|. The common|common| carotid aryery is located between the left brachiocephalic| vein and anterior-left trachea | wall, behind from it - |left subclavian artery. Between a right brachiocephalic| vein and anterior trachea wall located right arterial brachiocephalic| trunkus|barrel| wider than the alongside located arteries. Between a trachea and the 2nd thoracic vertebral body situated esophagus, sometimes there is air in it|what|. On either sides of the trachea there are peratracheal limphatic nodes with the diameter of 5 mm.
III. The level of aortal arc (60mm) – from breast bone|, separate ribs areas, 4th thoracic vertebrae and the shoulder-blade superior|upper,top| third part. Pulmonary parenchyma| in anterior departments shows itself anterior segments, in middle are back segments of both superior|upper,top| lobes|parts,stakes,portions,shares|; in dorsal| departments are lungs inferior lobe apexes|tops| segments. The lungs vascular pattern nearer to|by| the roots has the appearance of the rounded and linear shades|shadows| which appear due to transversal and slanting to the cut of segmentar and subsegmentar vessels. Arteries and veins on lungs periphery| on this cut look like identical. Behind from the located ascending aorta that adjoins to|by| the anterior wall of trachea, and|but| on the right|it|--- is superior|upper,top| vena cava. Between it|it| and in anterior-right| trachea wall in cellulose there are limphatic nodes. The arc of aorta issituated from anterior |ahead|to back|backwards|, esophagus adjoins to|by| it|it|. The descending aorta is situated near the 4th thoracic vertebra anterior-left| contour.
IV. Level of the trachea bifurcation (70mm). T|he superior|upper,top|lobe lobe anterior segment is adjoins to anterior thoracic wall by the wide basis|foundation|. In right lung it medialy adjoins to|by| the ascending aorta right auricle and superior|upper,top| vena cava, and|but| in left lungs — to|by| the pulmonary trunk|barrel| In the central areas of this cut there are the segments of middle lobe|part,stake,portion,share| of right lungs and uvular segments of superior|upper,top|lobe lobe of left lung; the apexes|tops| of these segments are directed to|by| the proper roots, their wide basis|foundation| adjoins to|by| the anterior-lateral thoracic wall surface. The back departments of this cut occupy|borrows| the superior|upper,top| segments of the lungs lower|bottom| lobes|parts,stakes,portions,shares|. The apexes|tops| of these segments are directed to|by| the roots. The transversal cuts of right and left main|head,leading| bronches visualised| between an ascending aorta and body of the 5ththoracic vertebra. There is ascending aorta at the front of trachea bifurcation; the esophagus- behind and to the left of it|to the left fro.The superior|upper,top| vena cava is traced on the right side of the ascending aorta, on the left|on the left|-left pulmonary artery. The descending aorta is visualized between the left main|head,leading| bronchus back wall and body of the 5th thoracic vertebra. At this level right lungs root superior-lobe| part|portion| (superior-lobe| | right pulmonary artery) is traced on the right|to the right|, and|but| to the left|on the left|- segmentar bronches of the apex|top|, back, anterior and uvular segments.
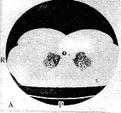
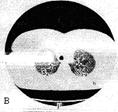
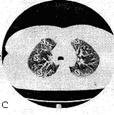
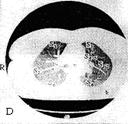
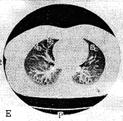
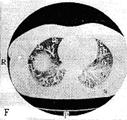
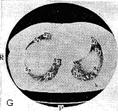
Fig.15.10 The computer tomography anatomy of the thoracic cavity organs is executed|done,implemented| in the mode|regime| of lungs (A|but|, B, C, D, E, F, G ). The lungs segments are marked by the proper numbers.
V. The level of pulmonary artery (100mm) - from the sternumbody, 7th, 6th, 5th, ribs and 7th thoracic vertebra. In the lungs - on the right|to the right| is front segment of the right lungs superior|upper,top| lobe|part,stake,portion,share|; dorsally -| middle lobe|part,stake,portion,share| and basis|foundation| of apex|top| segment of the inferior lobe|part,stake,portion,share|; to the left|on the left| - front segment of the superior|upper,top| lobe superior-lingualis| segment|part,stake,portion,share|, to the left|on the left| dorsally|- basis|foundation| of the inferior lobe apex|top| segment|b|part,stake,portion,share|.
At this level large|great,big| vessels are expressly traced: at the front-|ahead|ascending aorta, to the left -a pulmonary trunk|barrel| with its|its| branches.
Between a right pulmonary artery and bulb|onion| of aorta there is superior|upper,top| vena cava. Dorsally| from right and left pulmonary arteries there are main|head,leading| bronches. Length of right bronchus - 2,2 sm; width - 1,53 sm, left accordingly - 5 sm and - 1,3sm. Arterial vessels in lungs accompany bronches and have a general|common| topography.
VI. The heart basis level |foundation| (140 mm) – from its|its| basis|foundation|, 8th, 9th thoracic vertebrae, inferior |bottom| ribs. The front areas of the lungs: on the right|to the right| - the medial and lateral right lung segments of the middle lobe|part,stake,portion,share|, to the left|on the left| - the uvular left lung superior|upper,top| lobe segments |part,stake,portion,share|. The middle areas of both lungs are situated in the inferior lobes anterior basis segments|parts,stakes,portions,shares|. In the back departmentsof the lungs inferior |bottom| lobes lateral and posterior segments are situated|parts,stakes,portions,shares|.
The lung vessels on this level in most cases are oriented horizontally and are traced on the tomography cut from the lungs roots, gradually narrowing to|by| the periphery. The pulmonary veins on either side of the lungs are situated near|by| the left auricle.
VII .The diaphragmal level (160 mm) – from 9th-10th thoracic vertebrae, 7th, 9th, 10th ribs, xiphoid process| or inferior |bottom| segment of the sternumbody and the heart inferior |bottom| departments.
Depending on a patient constitutional feature at this level in the center of the right lungs basis| department tthe right diaphragmal cupula of different|diverse| area is situated|. The parenchyma | of the both lungs is segments, what at previous|preliminary| level.
Between the sternum and the 9th - 10th thoracic vertebrae bodies the heart is situated.
The esophagus is situated at front of|in advance of| the 9th - 10th thoracic vertebrae bodies, more left from its - descending aorta; between the 9th-10th | thoracic vertebrae bodies and esophagus is azugos vein, and|but| between the 9th-10th thoracic vertebrae bodies and aorta is hemyazigos vein.
Scheme of lungs sciagram studing:
Anterior al sciagram: 1. Common view of sciagram (an estimation of quality, simmetry patient’s positioning, common orientation - is a size and form of thorax, topography of thorasic cavity organs. 2. Study of the walls of thorax (volume and structure of soft tissues, condition of bone skeleton - bladebones, ribs, clavicles and vertebrae column, position and form of cupules of diaphragm,condition of costodiaphragmatic recess. 3. Comparative estimation of lung field – it is estimating right lungs fields with the same left lungs fields (radiolucency, form and square of fields), detailed study of lung pattern and roots of lungs. 4. Studing of mediastinum - it is a position and form of heart, pulmonary arteria and aorta, trachea and other.
Lateral sciagram: on the lateral sciagrams the studies are conduct in the same order (it is necessary to draw lungs schematically, lobes, and segments, to show sines, root and other).
In order to learn how to find the signs of lungs diseases, it is necessary to know well a norm, have a concept about a lung pattern.
Date: 2014-12-28; view: 1793
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| The thoracic organs roentgenanatomy | | | Symptoms of lungs disease |