
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
I. MARKETING
Marketing is the sum of activities involved in directing the flow of goods and services from producers to consumers.
Marketing's principal function is to promote and facilitate exchange. Through marketing, individuals and groups obtain what they need and want by exchanging products and services with other parties.
As a managerial process, marketing is the way in which an organization determines its best opportunities in the marketplace, given its objectives and resources. The marketing process is divided into a strategic and a tactical phase. The strategic phase has three components – segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP). The organization must distinguish among different groups of customers in the market (segmentation), choose which group(s) it can serve effectively (targeting), and communicate the central benefit it offers to that group (positioning). The marketing process includes designing and implementing various tactics, commonly referred to as the “marketing mix,” or the “4 Ps”: product, price, place (or distribution), and promotion. The marketing mix is followed by evaluating,controlling, and revising the marketing process to achieve the organization's objectives.
II. PR
The real tasks of public relations in the business world may focus on corporate interests or those of marketing products or services; on image creation or defense against attack; on broad public relations or straight publicity. In general, the strategic goal of public relations is to project a favorable public image. Public relations is concerned with creating a favorable climate for marketing the client's products or services, including maintaining good relations with merchants and distributors as well as placing product publicity and disseminating information to trade and industrial groups. It further includes publicizing praiseworthy activities by company personnel.
To a large extent, the job of public relations is to optimize good news and to prevent bad news, but when disaster strikes, the public relations practitioner's task, in consultation with legal counsel, is to assess the situation and the damage, to assemble the facts, together with necessary background information, and to offer these to the news media, along with answers to their questions of fact. When a client is under attack, it is a public relations responsibility to organize the client's response – usually involving several complicated issues – to be both lucid and persuasive.
III. IT
Information systems are at the heart of today’s work environment. Information Technology department deals with the electronic equipment responsible for storing, analyzing and distributing information of all kinds between all divisions within the company. IT elaborates and improves new software to simplify exchanging and sharing information of the company employees. Besides, IT is to ensure information systems security which is responsible for the integrity and safety of system resources and activities. Most organizations in developed countries are dependent on the secure operation of their information systems. F.ex, financial institutions could not survive a total failure of their information systems for longer than a day or two. Information systems are vulnerable to a number of threats, which require strict controls as countermeasures and regular audits to ensure that the system remains secure. The relationship between security measures is shown in the figure.
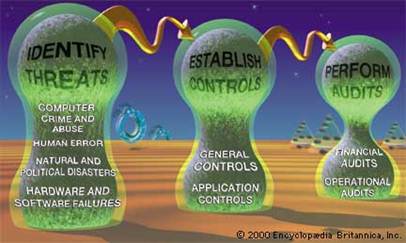 Although instances of computer crime and abuse receive extensive media attention, human error is estimated to cause greater losses in information systems operation. Disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and fires are the particular concern of disaster recovery planning, which is a part of an IT corporate business continuation plan.
Although instances of computer crime and abuse receive extensive media attention, human error is estimated to cause greater losses in information systems operation. Disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and fires are the particular concern of disaster recovery planning, which is a part of an IT corporate business continuation plan.
IV. HR
Human Resources department deals with the management of the people in working organizations. This activity comprises the following: forecasting personnel requirements in terms of numbers and special qualifications, scheduling timetable, analyzing jobs, recruiting, selecting, placing, transferring, demoting, promoting, and thus assuring qualified manpower when and where it is needed; assisting team members in their continuing personal growth, from pre-employment, preparatory job training to executive development programs; providing financial and non financial incentives for individual commitment and contribution.
Date: 2015-02-28; view: 1418
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| COMPANY STRUCTURES | | | V. FINANCE |