
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
RESEARCH OF INDUCTION MOTOR IN UNBALANCED MODES
Purpose of the work – to investigate working characteristics of induction motor using different types of unbalancing of rotor and stator windings.
Equipment and devices
Induction motors with phase and short-circuited rotor are investigated in this work; measuring kit “K-50”; electromagnetic ammeter (scale 10 A); three-phase rheostat at the circuit of rotor winding of induction motor with phase rotor; lamp stroboscope.
Direct current generator, regulating rheostat Rr having the resistance value about 300-400 Ohm and current about 1 A; one-phase loading rheostat; ammeter (scale to 10 A) and voltmeter (scale to 250V) of permanent-magnet system in generator armature winding.
Terminals of all equipments devices are put on the test bench.
Work contents
1. To make a scheme from laboratory work 3.3 (see figure 6.1, a ). Stator winding must be connected in star.
2. To set up the induction motor startup, and load using direct current generator, to measure currents and power of the induction motor by the phases and rotation frequency.
3. To investigate induction motor work in the single-phase mode, at opened knife-switch "Ð".
4. The winding of stator is connected in delta; to startup and load of induction motor in the symmetric mode. To measure currents and power of induction motor windings phases and rotation frequency for load current quantity.
5. To investigate the work of induction motor having stator windings opened delta connection, and the load current according to item 4.
6. To investigate the work of induction motor with a phase rotor at symmetric and unbalanced resistance of rotor windings.
7. To carry out startup of induction motor with a phase rotor at the open state of one rotor phase.
Work explanations
The unbalanced modes of induction motors operation appeared in the following cases: 1) during distortion of symmetry of network voltage;
2) during unbalanced resistances in the stator and rotor circuits;
3) during the asymmetrical scheme of motor winding connection. Such modes can appear because of disrepairs and breakdowns.
1. The cutting out of network linear wire or burning out of one of safety devices (figure 6.1) is one of the most widespread abnormal modes of induction motors work. Motor is moved into the one-phase mode independent on the stator connection scheme. Field of stator is immovable, is pulsates and it can be decomposed into two circular revolved fields. These fields have identical frequencies of rotation n1 but they revolve in different directions.
Field, which direction of rotation coincides with the rotor rotation is named direct one. Rotor slip relatively to this field is determined by the expression
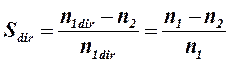
The field, which direction of rotation is opposite to the rotation of rotor, is named reverse. Rotor slip relatively to this field
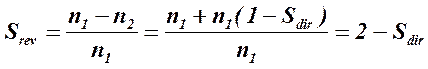
The magnetic fields of positive and negative sequence are induced in the rotor winding corresponding EMF, which create the currents of positive and negative sequences in the reserved winding. These currents are interacted with the fields and create the electromagnetic torques of positive and negative sequence:
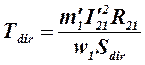
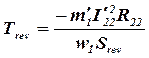 ,
,
where R21=R22
A resulting torque influences to the machine rotor
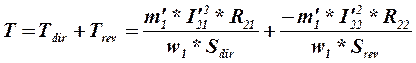
The analysis of mechanical characteristics (fig. 6.2) shows that if Sdir=1 we have T=0, i.e. starting torque is absent. For the motor rotation it must be rotated by the external force in any direction. If linear wire is cut rotor continues to work, rotating in the same direction and consuming bigger current from the network. Motor having a switch-off phase can work protractedly if load is in 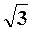 times less, than rated load in the symmetric mode.
times less, than rated load in the symmetric mode.
Induction motor work if one phase of the stator winding is cut is connected in star similar to above-mentioned.
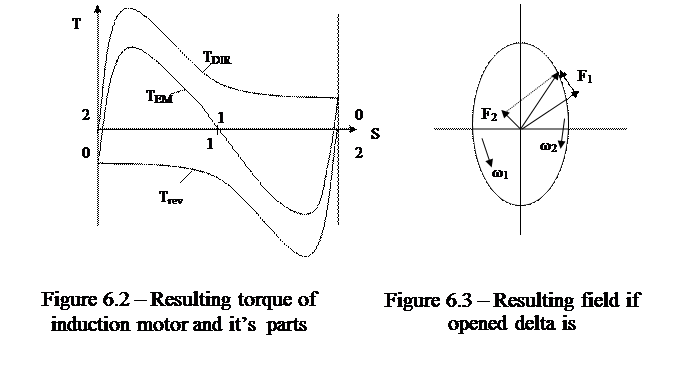
2. The scheme of the opened delta is possible at the cutting of one of phases of the stator winding, connected in delta (fig. 3.1,b).
Magnetic field, created by the stator winding is revolved on the ellipse (fig. 6.3). It creates torque at the steady part of mechanical characteristic. Torque is insignificantly different from a torque during the normal work. A starting moment is small; it worsened starting conditions, in separate cases motor can not rotate.
Load on motor axle must be decreased to 70% of rated one during the prolonged the motor operation.
 | |||||||||||
 |  | ||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
|




|
|
|




|
|
|

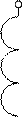 | 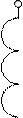 | ||||||
 | |||||||
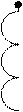 | |||||||
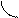
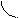

3. Induction motor having the unbalanced resistance in the rotor circuit.
Unbalanced rotor occurs in the following cases:
1) cutting of the pins of short-circuited rotor winding;
2) cutting of phase rotor winding;
3) inequality of additional resistances in the phase rotor circuit.
The currents of positive I21 and negative I22 sequences appear in the rotor winding having frequency Sf1. The currents of rotor and stator positive sequence create common direct field. This field in interaction with a current I21 creates the of positive sequence torque Tdir (curve 1 in the fig. 6.5).
Currents I22 create the field, revolved in opposite direction with frequency n2Ð= Sn1 relatively to the rotor, and relatively to stator with frequency
n2C= n2- n2P= n1(1- S1)- n1S=(1-2S1) n1
and they induce the current in stator I12 having frequency
f2C = (1-2S1) f1,
which are passed through a network and at small S1 current beatings are resulted. Superposition of the currents is harmful for the other consumers of this network.
Current beating having the frequency f1-f1(1-2S1)=2Sf1 causes of ammeter pointer oscillation plugged in the stator circuit.
Currents of negative sequence I12 of stator create the negative sequence field, which interacted with I22 creates the electromagnetic moment of negative sequence (curve 2 in figure 6.5).
Resulting electromagnetic torque on machine axle is
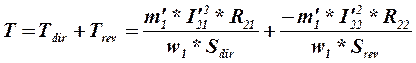
presented by a curve 3 in figure 6.5.
Motor has two regions of steady work: at S=Srated and at 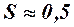 as it is seem from fig. 6.5. If the cutting of rotor phase happened during the operation of the motor having load less, then rated, rotor frequency of rotation will be almost invariable (point "à" in fig. 6.5). If load exceeds rated one, a motor will be rotated having half of previous frequency - on the second steady part of mechanical characteristic (point «b»).
as it is seem from fig. 6.5. If the cutting of rotor phase happened during the operation of the motor having load less, then rated, rotor frequency of rotation will be almost invariable (point "à" in fig. 6.5). If load exceeds rated one, a motor will be rotated having half of previous frequency - on the second steady part of mechanical characteristic (point «b»).
Motor can be sent to the basic steady part of characteristic (point “a”), if large resistance is put into the rotor circuit and this resistance is decreased slowly at the motor startup (when small load is on the axle). A motor is “got stuck” having half frequency of rotation and small additional resistance or if this resistance is decreased sharply.
The work fulfillment order
1. To construct a scheme for the working characteristics removal (fig. 3.1 for laboratory work ¹ 3). To startup the motor at the disconnected kit (switch "Switching of phases" must be in position "Î").
After the motor acceleration to excite a generator to U =220 V, induction motor must be load , setting Rload at the circuit of armature of generator a current about 6À, and the readings of kit Ê-50 put in the table 6.1. Frequency of rotation is defined by the stroboscope method (laboratory work 3.2).
Table 6.1 - Investigations results of the unbalanced operations modes of induction motors
| Type of induction motor | Winding connection | Working regime | Phases | n2 | |||||
| IA | ÐÀ | IB | PB | IC | PC | ||||
| À | W | À | W | À | W | rpm | |||
| Short-circuited rotor | Symmetrical Syngle-phase | ||||||||
| Symmetrical Open delta | |||||||||
| Phase rotor | Symmetrical Cutting of the phase wire |
2. To move induction motor into single-phase mode, by opening knife-switch "Ð" (fig. 6.1, à). Supporting the previous load, to put the readings of kit Ê-50 into the table 6.1, define rotor rotation frequency.
3. Winding of induction motor must be connected in delta. To carry out experiment in accordance with item 1.
4. To investigate the of the induction motor work with stator winding in the opened delta connection, for what a knife-switch of "Ð" must be broken (fig. 6.1, b). Supporting the previous load, to put the readings of the kit Ê-50 in the table 6.1, to define frequency of rotor rotation.
5. To construct a scheme and perform the motor having a phase rotor startup (fig. 6.4). To perform induction motor load at symmetric resistance in the rotor winding (winding of rotor is short-circuited), to put the readings of the kit K-50 in the table 6.1; to define n2.
6. To perform the phase cutting of rotor winding, measure currents in stator and to define n2. To perform analogy measurements for the several values of motor load.
7. To perform the startup of the motor with open phase during different values of the staring rheostat, different velocity of the rheostat leading out. Obtain the steady motor operation if frequency of rotation is halved (point "b" in figure 6.5).
Control questions
1. Why is a starting torque in single-phase mode equal to zero?
2. How will power of the motor change during working a single-phase network if moment of resistance is mauntained?
3. Why does a motor continue to rotate during the linear wire cutting of the linear ware during motion?
4. Why is current beating arisen in stator during unbalanced resistances in the rotor circuit?
5. In what cases while the phase of rotor cutting of motor can develop frequency of rotation, equal to the 50% compared with rated frequency of rotation?
A report must contain:
1. Experiments carrying out schemes.
2. Table, calculations frequency of rotor rotation determination.
3. Analysis of the obtained data in a table.
4. Answers the questions.
Date: 2015-02-16; view: 3305
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Work fulfillment order | | | MuHL 570 |