
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Sensitivity of demanded and supplied quantities to price.
Price elasticity of demand – measures the percentage change in quantity demanded in response to a change in market price.

If the absolute value is more than 1 – elastic. Perfectly inelastic – the curve is vertical.
Cross elasticity of demand – change in the demand for a good in response to the change in price for another good.
If cross elasticity is positive – goods are substitutes. If negative – complements.
Price elasticity of supply – change in quantity supplied related to changes in price. Perfectly inelastic is a vertical line.
21. Consumer choice & preferences
Consumer choice is a theory of microeconomics that relates preferences to consumer demand curves. The link between personal preferences, consumption, and the demand curve is one of the most complex relations in economics. Implicitly, economists assume that anything purchased will be consumed, unless the purchase is for a productive activity.
For an individual, indifference curves and an assumption of constant prices and a fixed income in a two-good world will give the following diagram. The consumer can choose any point on or below the budget constraint line BC. The decision is made at the point, where an indifference curve touches the budget line.
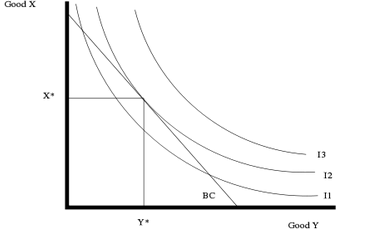
The choice could be affected by a substitution effect, Income effect, Price effect as sum of substitution and income effects.
Date: 2015-02-03; view: 1005
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Allocation of scarce resources | | | Effects of price change |