
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Visual arts
The oldest surviving British art includes Stonehenge from around 2600 BC, and tin and gold works of art produced by the Beaker people from around 2150 BC. The La Tène style of Celtic art reached the British Isles rather late, no earlier than about 400 BC, and developed a particular "Insular Celtic" style seen in objects such as the Battersea Shield, and a number of bronze mirror-backs decorated with intricate patterns of curves, spirals and trumpet-shapes.
 The English contribution to Romanesque art and Gothic art was considerable, especially in illuminated manuscripts and monumental sculpture for churches, though the other countries were now essentially provincial, and in the 15th century Britain struggled to keep up with developments in painting on the Continent. A few examples of top-quality English painting on walls or panel from before 1500 have survived, including the Westminster Retable, The Wilton Diptych and some survivals from paintings in Westminster Abbey and the Palace of Westminster.
The English contribution to Romanesque art and Gothic art was considerable, especially in illuminated manuscripts and monumental sculpture for churches, though the other countries were now essentially provincial, and in the 15th century Britain struggled to keep up with developments in painting on the Continent. A few examples of top-quality English painting on walls or panel from before 1500 have survived, including the Westminster Retable, The Wilton Diptych and some survivals from paintings in Westminster Abbey and the Palace of Westminster.
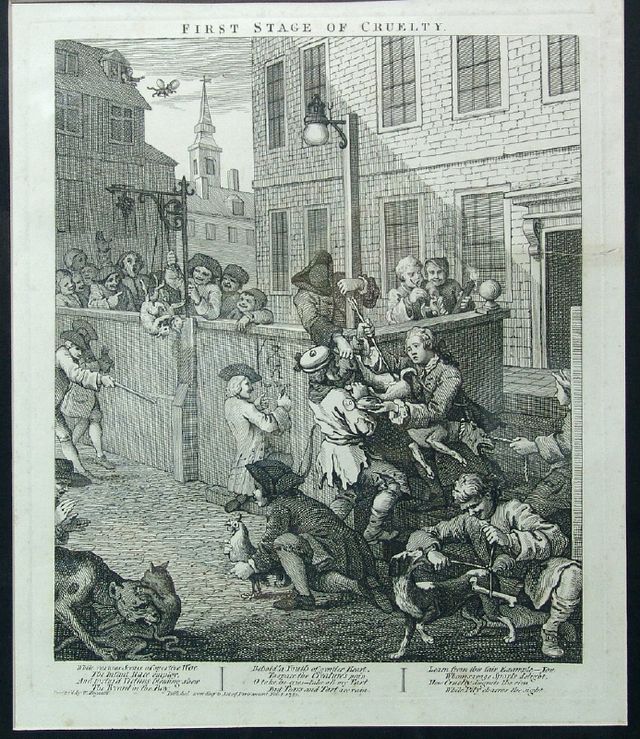 The Protestant Reformations of England and Scotland were especially destructive of existing religious art, and the production of new work virtually ceased. The Artists of the Tudor Court were mostly imported from Europe, setting a pattern that would continue until the 18th century.
The Protestant Reformations of England and Scotland were especially destructive of existing religious art, and the production of new work virtually ceased. The Artists of the Tudor Court were mostly imported from Europe, setting a pattern that would continue until the 18th century.
From the creation of the United Kingdom, the English school of painting is mainly notable for portraits and landscapes. Among the artists of this period are Sir Joshua Reynolds (1723–1792), George Stubbs (1724–1806), and Thomas Gainsborough (1727–1788). William Hogarth painted far more down-to-earth portraits and satires, and was the first great English printmaker.
 If Hogarth was the artist of the towns, Gainsborough, contemporary of Reynolds, was the painter of the countryside, frequently the background to his portraits. In a similar tradition was Stubbs, as famous for his portraits of horses as of people.
If Hogarth was the artist of the towns, Gainsborough, contemporary of Reynolds, was the painter of the countryside, frequently the background to his portraits. In a similar tradition was Stubbs, as famous for his portraits of horses as of people.
The late 18th century and the early 19th century was perhaps the most radical period in British art, producing William Blake (1757–1827), John Constable (1776–1837) and William Turner (1775–1851), three of the most influential British artists, each of whom have dedicated spaces allocated for their work at the Tate Britain. 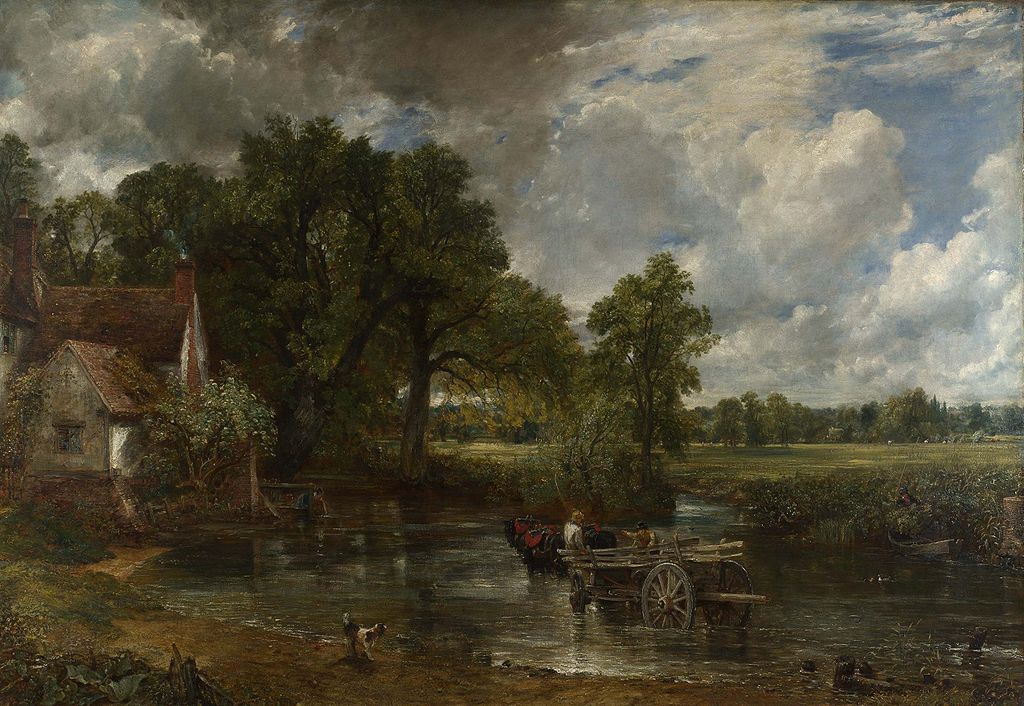
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (PRB) achieved considerable influence after its foundation in 1848 with paintings that concentrated on religious, literary, and genre subjects executed in a colourful and minutely detailed style. PRB artists included John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti and subsequently Edward Burne-Jones. Also associated with it was the designer William Morris, whose efforts to make beautiful objects affordable (or even free) for everyone led to his wallpaper and tile designs to some extent defining the Victorian aesthetic and instigating the Arts and Crafts movement. 
Both William Burges and Augustus Pugin were architects committed to the Gothic Revival, who expanded into designing furniture, metalwork, tiles and objects in other media. There was an enormous boom in re-Gothicising the fittings of medieval churches, and fitting out new ones in the style, especially with stained glass, an industry revived from effective extinction.
The modern period in British art may be said to date from the year 1910, when the first Post-Impressionist Exhibition was held in London.
British attitudes to modern art were "polarized" at the end of the 19th century. Modernist movements were both cherished and vilified by artists and critics; Impressionism was initially regarded by "many conservative critics" as a "subversive foreign influence", but became "fully assimilated" into British art during the early-20th century.
Visual artists from the United Kingdom in the 20th century include Lucian Freud, Francis Bacon, David Hockney, Bridget Riley, and the pop artists Richard Hamilton and Peter Blake. Also prominent amongst twentieth-century artists was Henry Moore, regarded as the voice of British sculpture, and of British modernism in general. In 1958 artisplt Gerald Holtom designed the protest logo for the British CND, which later became a universal peace symbol used in many different versions worldwide. As a reaction to abstract expressionism, pop art emerged originally in England at the end of the 1950s. 
 British graphic designer Storm Thorgerson co-founded the English graphic art group Hipgnosis, who have designed many iconic single and album covers for rock bands. His works were notable for their surreal elements, with perhaps the most famous being the cover for Pink Floyd's The Dark Side of the Moon. The subversive political artwork of Banksy (pseudonym of the renowned English graffiti artist whose identity is concealed) can be found on streets, walls and buildings all over the world, and has also featured in TV shows.
British graphic designer Storm Thorgerson co-founded the English graphic art group Hipgnosis, who have designed many iconic single and album covers for rock bands. His works were notable for their surreal elements, with perhaps the most famous being the cover for Pink Floyd's The Dark Side of the Moon. The subversive political artwork of Banksy (pseudonym of the renowned English graffiti artist whose identity is concealed) can be found on streets, walls and buildings all over the world, and has also featured in TV shows.
Date: 2015-01-29; view: 1710
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Anti-virus software and other preventive measures | | |