
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Check up for Comprehension
I. Answer the following questions.
1. Is the binary code a recent invention?
2. Were the early calculators based on a decimal or a binary system?
3. The mechanical calculator invented by Pascal could perform practically all mathematical calculations, couldn't it?
4. In what way did the mechanical computer differ from calculators?
5. What are the principles of work of the electronic computer?
6. How does a vacuum tube work?
7. Why was it impossible to make computers smaller and more reliable until 1948?
8. What was the invention of the microprocessor preceded by?
9. How is the latest generation computer different from the first one?
II. Read the text again, divide it into logical parts and find a suitable title for each part from the list below.
Mechanical computers
Diodes, transistors and microchips
Binary code
Calculators
Generations of computers
Electronic computers
II. Look through the text once again and choose the best answers to complete the following statements.
1. The improved mechanical calculator could do
a) addition and subtraction;
b) multiplication and division;
c) all four mathematical functions.
2. The first general-purpose computer was
a) Colossus;
b) ENIAC;
c) Analytical Engine.
3. The first-generation computers used
a) semiconductor diodes;
b) vacuum tubes;
c) microchips.
4. The third-generation computers could do
a) 1,000 calculations a second;
b) 100,000 calculations a second;
c) 1,000,000 calculations a second.
5. Modern computers are to be given instructions on
a) punched cards;
b) magnetic tapes;
c) input devices directly.
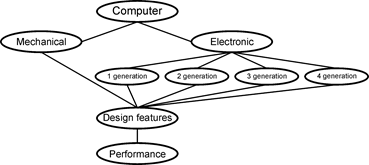
III. Summarise the main stages of computer development using the diagram below.
IV. Match the characteristics of each generation of computers given on the right-hand side with the sequence on the left:
| A. First generation | a. Used transistors. Data stored internally on magnetic disks. |
| B. Second generation | b. Used integrated circuits, electronic solid-state memory. External memory stored on magnetic disks. |
| C. Third generation | c. Vacuum-tube based machines. Magnetic drums used for internal storage and magnetic tape for external storage. |
| D. Fourth generation | d. Used microchips. Have greatly reduced size. Perform operations very fast. |
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1343
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Future Time Clauses | | | COMPUTERS AND IT TECHNOLOGIES |