
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Mask-type LIC of the ROM
Two-port memories
Two-port memories are special RAMs which allow two independent processes to access common data. This enables data to be exchanged between the two processes [3.4, 3.5]. To be able to do this, the 2-port memory must have two separate sets of address, data and control lines, as shown in Fig. 3.3. Implementation of this principle is subject to limitations, since it is basically impossible to write into the same memory cell simultaneously from both ports.

Fig. 3.3 - External connections of a 2-port memory.
The "Read-While-Write" memories overcome this problem by only reading from one of the two ports and only writing at the other. Figure 3.4 shows that memories of this type have two separate address decoders which allow simultaneous writing to one address while reading from another.
If reading and writing are to take place at both ports of a two-port memory an access conflict can generally only be avoided by preventing simultaneous memory access. To do this, the address, data and control lines can be made available via multiplexers to the port accessed as shown in Fig. 3.5. In many cases, the two processes accessing the memory are synchronized to prevent simultaneous access. If this is not possible, a priority decoder (arbiter) can be used which, in the event of access overlap, temporarily stops one of the two processes by a wait signal. Some integrated 2-port memories are listed in Fig. 3.6. Their capacities, however, are limited. In order to implement large two-port memories, it is advisable to use normal RAMs in conjunction with a dual-port RAM controller. In this case the Valvo 74LS764 offers particular advantages, since it supports the operation of dynamic RAMs as two-port memories.
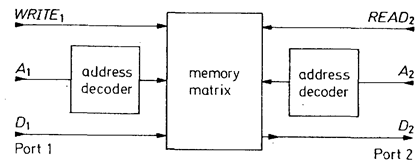
Fig. 3.4 - Structure of a Read-While-Write memory with separate address inputs.
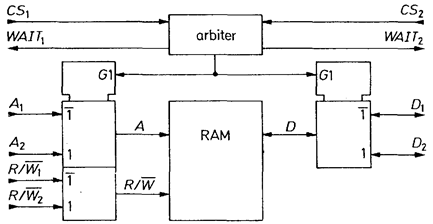
Fig. 3.5 - Two-port memory with standard RAMs.
| Capacity | Organization | Type | Manufacturer | Operating power, typical | Access time, max | Pins |
| 8 kbit | 1k x 8 | IDT7130 | Id, Cy, Am | 325 mW | 35ns | |
| 16 kbit | 2k x 8 | 1DT7132 | Id, Cy, Vt | 325 mW | 35ns | |
| 32 kbit | 4k x 8 | IDT7134 | Id | 500 mW | 35ns | |
| 32 kbit | 2k x 16 | IDT7133 | Id | 375 mW | 45ns | |
| 64 kbit | 8k x 8 | IDT7005 | Id | 750 mW | 35ns | |
| 64 kbit | 4k x 16 | IDT7024 | Id | 750 mW | 30ns | |
| 128 kbit | 16k x 8 | IDT7006 | Id | 750 mW | 35ns | |
| 128 kbit | 8k x 16 | IDT7025 | Id | 750 mW | 30ns |
Manufacturers: Am = AMD, Cy = Cypress, Id = IDT, Vt = VTI
Fig. 3.6 - Examples of two-port memories (CMOS).
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1583
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Memory Devices | | | RAMs as shift registers |