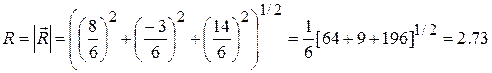CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Type C. On Work-energy theorem14. A bullet of mass 20 g strikes a target with a velocity of 150 m/s and brought to rest after piercing 10 cm into it. Calculate the average force of resistance offered by target. 22,500 N
15.A bullet of mass 25 g was moving at the rate of 500 m/s After passing through a solid substance, it continued Ii move at the rate of 100 m/s. How much work had to do in passing through the substance? 3000 J
Two bodies of masses 2 g and 10 g have position vectors Sol. Here, and
The distance of the centre of mass from the origin is given by
In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 A. Find the approximate location of the CM. of the molecule, given that chlorine atom is 35.5 times as massive as hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleolus. [Ans. 1.235 A (from hydrogen atom)] Q. 1.01. Where does the centre of mass of a two particle system lie, if one particle is more massive than the other? Ans. Near to the massive of the two particles. Q. 1.02. Is centre of mass a reality ? Ans. No. It is only a mathematical concept. Q. 1.03. Where does the centre of mass of a rectangle lie ? Ans. At the point of intersection of the diagonals of the rectangle. Q. 1.04. What is the location of centre of mass of a triangular lamina? Ans. At the centroid of the triangle i.e. at the point, where the medians of the triangle meet. Q. 1.05. Should the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body ? Ans. Not necessarily. For example, the centre of mass of a ring lies at the centre of the ring i.e. at a point, where actually there is no mass. What will be nature of motion of centre of è of an isolated system ? Ans. The centre of mass of an isolated system external force acting on the system) will either be at rest or it must be moving with a constant velocity.
4. Define centre of mass for a system of n-particles. Prove that it moves with constant velocity, provided the system is not acted upon by any external force. 1. What do you mean by centre of mass of a system ? Obtain expression defining the centre of mass of a system of two particles. Prove that the centre of mass of a system moves with constant velocity in the absence of external force on the system.
5. Discuss the motion of centre of mass in the following systems :
(a)Earth-moon system revolving around the sun. (b)The Indian club thrown by a player towards the other.
11. The distance between the centres of the carbon and 2. The identical spheres À, Â and C, each of radius R are placed touching each other on a horizontal table. Where is the centre of mass of the system located relative to the [Ans i(AB + AC)l
4. Two mass of 0-8 kg and 1-2 kg are lying in XY plane at the locations, whose coordinates are (1, -2) and (-3, 4)
respectively. Find the coordinates of the centre of mass of 5. Three point masses of 0-5 kg, 1-5 kg and 25 kg are located in XY-plane at points (2, -3), (3,5) and (-4, -6) respectively. What are the coordinates of the centre of mass of the system. [Ans. (1, -2)] 6. Two masses m-, and m2 constrained to move in a horizontal plane collide. Given that òã = 85 g, m2 = 200 g and initially ù = 6-48 cm s_1 and tu = — 6-78 cm s_1, find the velocity of the centre of mass. [Ans. - 2-83 cm s_1l 7. Two point masses of 2 kg and 3 kg are moving along the same line with speeds 3 m s'1 and 5 m s_1 respectively. Find the speed of the centre of mass of the system, if both the masses are moving in (a) the same direction and (b) in opposite directions. [Ans. (ÿ) 4-2 m s_1 (b) - 1-8 m s-1l
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 889
|
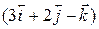 and
and 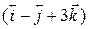 respectively. Find the position vector and distance of CM. from the origin.
respectively. Find the position vector and distance of CM. from the origin. g ;
g ;  g,
g, 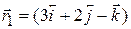
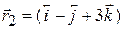 .The position vector of the centre of mass is given by
.The position vector of the centre of mass is given by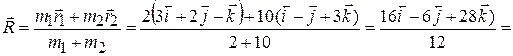
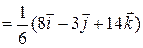 .
.