CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
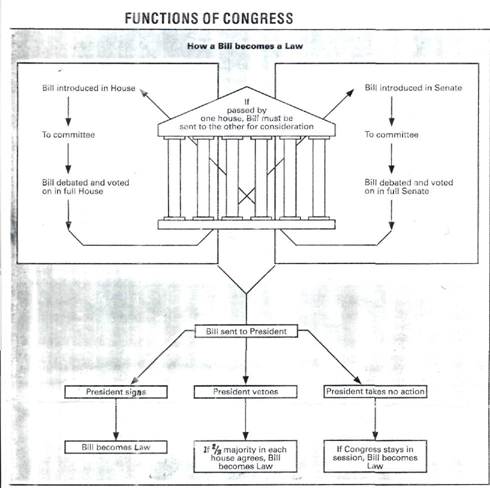
How Laws Are MadeLet's pretend the voters from Senator Jones' state (constituents) want a law requiring seatbelts on school buses. He and his staff write a bill, which is a draft (early version) of the proposed law. The bill is then passed out to each Senator. A Standing Committee (a small, permanent group made up of legislators who studies and reports on bills) reviews 1. Sends the bill back with no changes. If the committee sends it back with no changes, then the bill goes on the Senate's calendar to be voted on. When that day comes, the bill is voted on and over half of the senators (51 of 100) must vote yes to pass it.
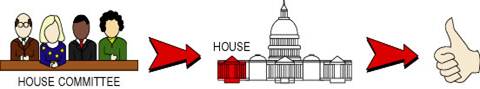
If the bill is passed by the Senate, it then moves to the other branch of Congress, the House of Representatives. The bill goes to a House committee, which studies the bill, and then is voted on by the representatives. Just as in the Senate, over half of the representatives (218 of 435) must vote yes to pass the bill.
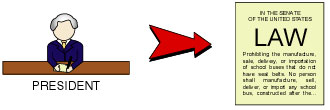
If the bill is passed in both the Senate and House, the bill goes to the President of the United States. If the president signs the bill, it then becomes a law. It may also become law if the president does not sign it for 10 days. If the president rejects (vetoes) the bill, it can still become a law if two-thirds of the Senate and two-thirds of the House then vote in favor of the bill.
A bill may begin in either the Senate or the House of Representatives. So, Representative Smith could introduce a bill of her own just like Senator Jones. This bill would take the same steps only it would begin in the House of Representatives instead of the Senate.
OTHER POWERS OF CONGRESS Congress decides upon taxes and how money is spent. In addition, it regulates commerce among the states and with foreign countries. It also sets rules for the naturalization of foreign citizens. Test Quiz
SUMMERY
1. The Constitution calls for Congress to be a bicameral body. It also details the qualifications, representation, election, and terms of members of each house. 2. The Senate is made up of 100 members, two from each state. Terms are six years long, with one third of the members being elected every two years. 3. The House of Representatives has 435 members, apportioned among the states according to population. Representatives serve two-year terms and, like Senators, are elected directly by the American people. 4. The most important powers of Congress are its legislative powers. 5. A bill must be introduced by a member of Congress. It then goes to a committee for study, hearings, changes, and recommendations. Once passed by one house, it goes through the same process in the other house. After passage in both houses, a bill may be signed into law or vetoed by the President. A vetoed bill still can become law if approved by two thirds of both houses.
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1041
|
 the bill and does one of three things:
the bill and does one of three things: