
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Phosphorus
The electronic formula of phosphorus is 1s22s22p63s23p33d0. 3s23p33d0 is the configuration of external electronic shell of phosphorus atom. In contrast to Nitrogen atom the phosphorus atom has unoccupied d-orbitals, thus gives the possibility to pass into excited state at "pair break" of 3s-electrons. According to current concept the following oxidation numbers are typical for phosphorus atom: 3-, 0, 3+, 5+:
Ground (nonexcited) state (3-, 0, 3+ oxidation number, for example, in PH3, P, P2O3 compounds):
| 3s | 3p | 3d | ||||||||
| ↑↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | |||||||
The excited state (5+ oxidation number, for example, in P2O5 compound):
| 3s | 3p | 3d | ||||||||
| ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | |||||
The most typical phosphorus compounds are given in Table 18.
Table 18. Compounds of Phosphorus
| Oxidation numbers | 3- | 1+ | 3+ | 5+ | |
| Compound | PH3 | P (P2, P4, Pn) | H3PO2 | P2O3, H3PO3 | P2O5, H3PO4, HPO3, H4P2O7 |
| Chemical properties | Reducing agent only | Oxidizing and reducing agents | Hypophosphorous acid, strong reducing agent | Phosphorus acid, reducing agent | Phosphoric anhydride and phosphoric acids, oxidizing agent only |
Phosphorus is produced from natural Phosphates of P2O5 vapors reduction by coal, which is isolated from melt (at 15000Ñ) according to the reaction:
Ca3(PO4)2 + 3SiO2 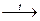 3CaSiO3 + P2O5;
3CaSiO3 + P2O5;
P2O5 + 5C 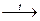 5CO + 2P
5CO + 2P
P5+ + 5 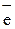 ® P0 ® P0
| 2 (reduction); |
C0 - 2 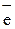 ® C2+ ® C2+
| 5 (oxidation). |
Phosphorus behaves as the typical non-metal. It reacts with Oxygen, formed acid oxides:
4P + 3O2 = 2P2O3;
4P + 5O2 = 2P2O5.
Phosphorus oxides (V), phosphoric acid, Phosphates
P2O5 (P4O10) is very hygroscopic white powder and the most effective agent for drying. Interacting with water it forms phosphoric (monophosphoric) acid:
P4O10 + 6H2O  4H3PO4.
4H3PO4.
Acid properties of P2O5 are shown in its interaction with hydroxides and basic oxides:
6KOH + P2O5 = 2K3PO4 + 3H2O;
3CaO + P2O5 = Ca3(PO4)2.
Orthophosphoric acid H3PO4 is threebasic acid:
  H-O H-O
| |
  H-O H-O
| P = O |
| H-O |
At heating monophosphoric acid dehydration and formation of cyclic or linear polyphosphoric acids take place and among them diphosphoric and metaphosphoric acids are of great value:
2H3PO4 = H2O + H4P2O7 (diphosphoric acid);
H4P2O7 = H2O + 2HPO3 (metaphosphoric acid).
In fact, metaphosphoric acid is inorganic polymer of cyclic structure mostly with three and four chain rings: (HPO3)3 and (HPO3)4. Diphosphoric acid and other condensed phosphoric acids with the same structure are inorganic polymers:
| O | O | |
| ││ | ││ | |
| H - O - | P - O - | P -O - H |
| │ | │ | |
| O-H | O-H |
In Phosphate fertilizer production the extraction phosphoric acid is received by sulfuric acid action to Ca3(PO4)2, which is the part of natural phosphorites and apatites:
Ca3(PO4)2 + 3H2SO4 = 3CaSO4 + 2H3PO4.
Phosphoric acid forms mono- , di- and triple-substituted salts. For example, NaH2PO4 - Sodium dihydroPhosphate, Na2HPO4 - Sodium hydroPhosphate, Na3PO4 - Sodium Phosphate.
The ability of phosphoric acid to react with metals, basic oxides, hydroxides and weak acid salts are used in industry for production of mineral fertilizers:
CaHPO4 ∙ 2H2O (precipitate);
Ca3(PO4)2 + 4H3PO4 = 3Ca(H2PO4)2;
in fact Ca(H2PO4)2∙H2O - triple superphosphate is produced.
Ca3(PO4)2 + 2H2SO4 = Ca(H2PO4)2 + 2CaSO4 - is the receipt of simple superPhosphate. The real composition of simple superphosphate is Ca(H2PO4)2∙H2O + 2[CaSO4∙2H2O].
PRACTICE PROBLEMS
1. In which compounds and at which oxidation numbers can Nitrogen and phosphorus show only reducing or only oxidizing properties in the reactions and why?
2. Draw structural-graphic formulas of N2O3, N2O5, P4O10, HNO2, HNO3, H3PO4, H3PO3.
3. Estimate Nitrogen and Phosphorus oxidation numbers in the compounds:
NH3∙H2O, PH4I, Ca(H2PO4)2, NH4H2PO4, Fe(NO3)3, Na4P2O7, NH2OH, NH4Cl.
4. Draw the reaction equations according to transformation series:
N2 → NH3 → NO → NO2 → HNO3 → NH4NO3;
Ca3(PO4)2 → P → P2O5 → H3PO4 → Ca(H2PO4)2 → CaHPO4;
Ca3(PO4)2 → H3PO4 → NH4H2PO4 → (NH4)2HPO4.
5. Draw the diagrams of electron redistribution and put the coefficients in the equations of the following reactions:
NaNO2 + FeCl2 + HCl → FeCl3 + NO + NaCl + H2O;
NO2 + H2O + O2 →
NH4NO3 → N2O + H2O →
P + HNO3 + H2O →
LABORATORY TRAINING
Experiment 1. Study the ammonia solution properties
A) Put 5-6 drops of Iron Chloride (III) into test-tube, add 4-5 drops of ammonia solution. Describe the color of precipitation and write the reaction.
B) Put 5-6 drops of ammonia Chloride into test-tube, add 5-7 drops of alkali solution (KOH or NaOH) and heat the mixture in water bath. Identify the isolated gas taking into account the odor and color change of pink litmus paper wetted by water, putting it into the vapor under test-tube. Draw the reaction.
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1200
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Nitrogen | | | Experiment 2. Oxidation and reducing power of nitrous acid and Nitrites |