
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Concentration of solutionsThe concentration of solution is the measurement of the amount of solute in a given amount of solvent or solution. Some medications are solutions of drugs - one-teaspoonful dose at correct concentration might cure the condition; the same dose in the wrong concentration might kill the patient. Sometimes solutions are referred as “concentrated” or “diluted”. These are relative terms. “Diluted” means that there is relatively small amount of solute in solvent. “Concentrated”, on the other hand, means that these terms are unrelated to the degree in which the solution is saturated. Saturated solution of substance that is not very soluble might be very diluted. Percent by Mass (mass concentration, percent concentration) Percent by Mass (P) of a solute in solution is the number of grams of solute dissolved in 100 g of solution. For example, the percent by mass of a solution made from 10 g of Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) dissolved in 90 g of water is found as follows: P = = Note that the mass of solution is the sum of the masses of the solute and solvent. Percent concentration is common for solutions used for practical purposes - household or industrial cleaning, killing pests in the garden, medical applications. Percent-by-mass concentration is based only on the mass of solute and is unrelated to its chemical formula of molar mass. P = Date: 2015-01-12; view: 755
|
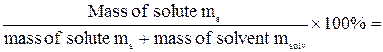
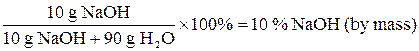 .
.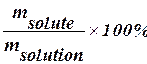 (6)
(6)