CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
PERFECT TENSES PASSIVE
Read the text Man Must Build
Early builders were at first concerned almost entirely with constructing shelters against rain, cold, wild beasts, and human foes. Later, as their civilizations developed, they built temples, council chambers1, bazaars, and palaces. They took a special delight in erecting pyramids, towers, obelisks, coliseums, and the like. The story of modern structures is the story of the break from the materials of the past. Great and noble structures were built in brick, timber, and particularly in stone, but now steel and concrete have largely replaced them. With these newer materials we can build to greater heights, span wider gaps, and carry heavier loadings than ever before. In many countries today, mountainous masses of steel and concrete are reaching to the skies on a scale undreamed of in earlier times. Engineers have been able to do this because the rise of the science of structures and the advent of steel and concrete have enabled them to conceive and build their buildings and their structures as frameworks. Before this, the walls of buildings were "bearing" walls: they carried the dead weight and the live load of the structure. The modern large building, however, is essentially a framework or skeleton of steel or concrete that supports the roof and floors. The outside walls are enclosing or "curtain" walls, and often their weight at each floor is also taken by the framework. So the "sidewalk superintendent,'' gaping curiously at the busy scene on a building site, may see the walls rising simultaneously from the ground and midway between roof and ground. Since the walls do not earn' the structure, they are sometimes made of glass or plastic. When the lift-slab method was first devised, some people described it as a way of constructing a building from the top downward. The description, however fanciful, draws attention to the novelty of the system. The method does, nevertheless, give an excellent illustration of the framework principle employed in most modern buildings. One begins by constructing the various floors and the roof on top of one another, and around the columns, at ground level. These are then lifted by powerful hydraulic jacks to their correct positions in the structure, and permanently connected to the columns. In the case of a nine-storey building, the columns may be erected in three stages, and the tops of each stage temporarily braced together by the ascending roof. As the roof and higher floors move upward, they leave behind lower floors which, secured to the columns, serve to brace them permanently together. In this type of structure, therefore, the floors and the roof serve the added purpose of forming part .of the framework. When roof and floors are all finally in place and connected to the columns, the protective walls can be built up from ground level. In large buildings, the civil engineer's main task is the design of frameworks and foundations.
Left, model by Mies van der Rohe for a glass skyscraper, 1920. Right, Tokyo hotel designed by Frank Lloyd Wright; it rents on a concrete raft (diagram).
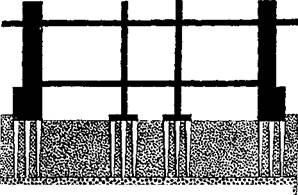
Where a building is supported by its walls, the weight is spread out over a large area. This gives relatively low pressures on the ground and makes foundation work easy. But in a modern building framework, the load is carried by a small number of columns, which leads to highly concentrated ground pressure. Hence the foundations must be strong, particularly if the ground is weak. If the ground is reasonably firm, it is often enough to place the columns on spread footings. These are blocks of concrete of such area as to spread the load to within the carrying strength of the ground. On soft ground, a building is sometimes put on a concrete raft, which is a footing covering the whole ground plan area. A building on its raft is virtually floating on the ground beneath. A method often used is to drive a number of piles under each column foundation. The piles are made long enough to rest on the hard ground below the soft surface. The building is then literally on stilts. Another method is to carry the columns on fairly large diameter cylinders sunk deeply into the ground.
Below, the Empire State Building lowers above :he skyscrapers of New York.
II. Answer the following questions. 1) What factors have led to the revolution in the "history of modern structures"? 2) Why is the «framework principle» used widely in modern constructions? 3) How does the "lift- slab" method work? 4) Why is it necessary for civil engineers to pay special attention to the design of frameworks and foundations? 5) What types of foundations are mentioned in the text?
III. Describe the types of foundation works given in the text. Determine what conditions must be considered to choose the right type of foundation works.
IV. Are these statements true or false? Correct the wrong statements. 1. The outside walls of new buildings are "bearing walls". 2. The weight of the outside walls is taken by the foundations. 3. "The lift -slab" method consists in the construction of the frame and floors on the top level. 4. The structure of the ground under the construction should be thoroughly examined. 5. It is enough to place the columns on spread footings if the ground is firm.
V. Complete the sentences using an appropriate link.
VI. Match the word from column A to its synonym in column B. A B 1. to substitute a) to place 2. to carry the load b) to replace 3. to invent c) to support 4. to settle d) to devise 5. to uphold e) to bear
Fill in the gaps with the words from column A. 1. New materials _______ the old ones and with these materials we can build to greater heights and ______ the greater_______. 2. When the lift-slab method was first _______, some people described it as a way of constructing a building from the top downward. 3. The protective walls can be built up from ground level, when roof and floors, are finally 4. As a mass construction is _____________by its walls, the weight is spread out over a large area.
VII. Translate into English the following word combinations. Use them in the statements of your own.
VIII. A) Fill in the gaps with appropriate words.
A study of some of New York's______________would convince you that in modern buildings the walls no longer act as ______________. To overcome ______________ from subway trains passing near the ______________, the ___________ are taken down below the______________and anchored in the solid rock____________ Manhattan. The walls are______________on the frame, but they do not touch the______________where the vibration______________. The Waldport Astoria Hotel is a good example of it.
B) Put the word given in brackets into the necessary word form. The Pirelli skyscraper in Milan is of most modern concrete design. A tall shaft, 32 storage (height) is cigar (shape). Four mass columns (extension) across the structure and present the (solve) to the difficult wind (resist) problems. Special account was taken of the severe (torsion) strains to which such a delicately proportioned building is subject. In order to check the (calculate) a 1/15th scale model was tested. And now the finished structure stands, giving (express) to the words of a (fame) French architect who spoke of the (accumulate) of very beautiful things in which economic law reigns (supremacy) and (exact) is joined to (imagine). That is beauty.
IX. Read the texts again and think of the main problems of these constructions and the engineering solutions to these problems.
X. Study some properties of steel and concrete.
XI. There are 3 types of building constructions read the decide which paragraph discusses.
a) a mass construction b) a frame construction c) a planar construction Building materials are used in two basic ways. In the first way they are used to support the loads on a building and in the second way they are used to divide the space in a building. Building components are made from building materials and the form of a component is related to the way in which it is used. We can see how this works by considering three different types îf construction: 1. In one kind of construction, blocks of materials such as brick, stone, or concrete are put together to form solid walls. These materials are heavy, however, they can support the structural loads because they have the property of high compressive strength. Walls made up of blocks both support the building and divide the space in the building.
lanar construction Mass construction 2. In another type of construction, sheet materials are used to form walls which act as both space-dividers and structural support. Timber, concrete and some plastics can be made into large rigid sheets and fixed together to form a building. These buildings are lighter and faster to construct than buildings made up of blocks. 3. Rod materials, on the other hand, can be used for structural support but not for dividing spaces. Timber, steel and concrete can be formed into rods and used as columns. Rod materials with high tensile and compressive strength can be fixed together to form framed structures. The spaces between the rods can be filled with light sheet materials which act as space dividers but do not support structural loads.
XII. Say whether these statements are true or false. Correct the false statements.
1. Rod materials can be used for both dividing space and supporting the building. 2. Concrete is used as a block material, a sheet material and a rod material. 3. Steel is used for frame constructions because it has a property of high tensile strength and low compressive strength. 4. The sheet materials, which act as space dividers in a frame building are light because they do not support structural loads. 5. Mass construction buildings are light whereas planar constructions are heavy.
PERFECT TENSES PASSIVE Table 2
Exercise 11. Define the Perfect Passive in the following sentences. Translate them into Russian. 1. By the end of the week the obtained results of the investigation will have been presented at the conference. 2. About half a million organic compounds have been described in the chemical literature. 3. This solution has been infused for a very long time. 4. Medicinal properties have been ascribed to iron since time immemorial. 5. By the time the instructor entered the biochemical laboratory, all necessary specimens had already been prepared by the laboratory assistant. 6. The solutions for laboratory diagnostics have not been delivered yet to the Institute. 7. A new book on organic chemistry has been published recently. 8. This report will have been finished by next month. Exercise 12. Practise the Present Perfect Tense Active and Passive voice in short dialogues as in the model.
1. To put the thermometer into the armpit; 2. To take a cough mixture; 3. To rinse his mouth with a mouth wash; 4. To apply compresses; 5. To make a hot foot bath.
1. to repeat these experiments. 2. to check the data of the experiment. 3. to wash up dirty glassware in the lab. 4. to feed the laboratory animals. 5. to bring the slides. 6. to put down the results of the test. Exercise 13. Rewrite the sentences in the Perfect Passive. 1. Biochemistry and biophysics have achieved remarkable results in analyzing and synthesizing DNA and RNA. 2. Modern scientists have discovered 20 new elements. 3. The scientists have made little progress in fundamental theory. 4. By 1939 Otto Hahn, Fritz Strassmann, and Lise Meitner had established the occurrence of uranium fission. 5. The rapid growth in the understanding of chemical processes in general, organic and biochemical reactions, in particular, has brought a revolution in the pharmaceutical industry. 6. After we had heated the solution, we wrote down the result of the experiment. 7. Today chemists have not only synthesized many of the organic substances in nature, but have prepared substances that do not occur in nature, such as plastic, different types of rubber, medicines, etc. Exercise 14. Choose the correct form of the verb. 1. The first steps towards scientific explanation of the world have been taken/ were taken in ancient Greece. 2. More and more is continually being learned/ is learned about plants. 3. During the chemical reaction a number of bonds will be formed/ won’t be formed or broken. 4. Medicinal properties have been ascribed/ were ascribed to iron from time immemorial. 5. Extensive amounts of carbon are found/ are being found in the form of its compounds. 6. At present much research will be carried on/ is being carried on in various areas of plant physiology. 7. Chemical formulas and equations are written/ was written in terms of atoms and molecules. 8. Plants have been found/ are found throughout the world, on land, in water, and in the air. Exercise 15. Open the brackets and use the correct tense form of the verb in Present, Past, Future Perfect and Indefinite Passive Voice. 1. More than 300 flowering plants (to recognize) today. 2. The classification of chemical elements (to express) by Mendeleyev in the form of periodic table. 3. Specimens of plants that (to prepared) properly can remain in excellent condition for 300 or more years. 4. Gallium (to discover) in 1875 but its existence (to predict) already six years earlier by D. Mendeleyev. 5. The greenness of plants (to cause) by chlorophyll. 6. The symbols of the elements (to establish) by international agreement and (to use) nowadays throughout the world. 7. Vitamins (to extract) formerly from natural sources, but now the majority (to make) by synthetic methods. 8. Plants (to find) throughout the world, on land, in water, and in air. 9. Matter (to compose) of elements, of which there are 107 known – 17 (to produce artificially and 90 (to occur) naturally on our planet.
Compound prepositions
Exercise 16. Read the following sentences and indicate compound prepositions. Translate the sentences. 1. Many carbon compounds play a vital role due to their effect on the processes in the human body. 2. Antibodies can be classified according to their mode of action. 3. As to the starch it was then recognized that it gave glucose when heated with dilute sulphuric acid. 4. By means of the glycolytic series of reactions pyruric acid is formed in the cells of plants. 5. Depending on the basis of the functional group carbon compounds are divided into several classes. 6. The chemical properties of phenols differ from those of alcohols chiefly because of the acidic character of the phenols. 7. In spite of the importance of the contributions that had been made earlier, the greatest portion of credit for the development of the Periodic system must undoubtly go to the Russian scientist, D.I. Mendeleyev (1834-1907). 8. Regardless of their diverse molecular structures, all hydrocarbons have a number of properties in common.
homonyms (prepositions and conjunctions)
Exercise 17. Translate the following sentences, pointing out conjunctions of the subordinate sentences. 1. Cells must grow before they can divide. 2. As the leaf ages, hormonal changes take place and at least two layers of cells become differentiated. 2. For a long period man has known about the medicinal properties of plants. 3. Until man learned to develop nuclear energy, he depended entirely on sunlight for his energy needs. 4. After algae and other simple green plants appeared in the oceans about 3.5 billion years ago, the amount of oxygen started to increase as a result of photosynthesis. 5. Two dyes are used for the preparation of lipstick. 6. In the vitamin field the efforts of the chemists are especially large since they isolated and synthesized a number of new vitamins. 7. Plants are very important as they help to maintain the balance of the atmosphere. 8. Since 1930 all other vitamins have been isolated. 9. Before the era of electricity, acetylene gas was used as a component of illuminating gas, for it burns with a colourless flame.
Exercise 1. Practise the dialogues paying attention to the use of Present Perfect and Past Simple.
Ex.2.Finish the dialogues according to the Models. - Have you ever met anyone famous? - … … … … … … … … … … … - Have you ever travelled abroad? - … … … … … … … … … … - Have you shown him your collection of coins? - … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … - Have you ever stay at the Metropol Hotel? - … … … … … … … … … … … … … …
Task: Prepare some questions for a QUESTAINARE using Have you ever pattern to find out something interesting or unusual about another person. DIALOGUES Meeting people after a long time.. Read the dialogues in pairs. I. A. We haven’t seen you for ages. Have you been ill? B. Yes, I have. Actually I have been ill for a week. C. What was it? D. It was the grippe. E. Are you well now? F. To be honest with you, I’m just recovering, so I feel like a wet rag.
II. A. How nice to see you again. Where have you been? Home? B. No, I’ve been at my relations. C. Whereabouts? D. I went to the country to see my uncle.
III. A. Come in and sit down. We haven’t seen much of you lately. B. No, I’ve been away on holiday. C. Where exactly? D. In the Crimea. I’ve got a cousin there.
IV. A. It’s a long time since we met. Where have you been all this time? B. I have just returned from Spain. C. Was it a business trip? D. Oh, no I was on leave. E. Lucky you are. Did you have a good rest? F. Oh, It was fantastic!
V. A. Hello! It’s ages since I heard from you. B. I’ve been away for a while. It was a business trip. A week has passed since I came back. C. I’m glad you called me. I’ve got a lot of news to tell you about. D. You see, the days have been so crowded since my return that I had no chance to visit any of my friends.
VI. A. Hello, Nick. B. Hello, Peter. It’s nice to see you again. How are you? C. Fine, thank you. And you? Hope you are O.K. Haven’t seen you for ages. Where have you been? D. I have just arrived from Moscow. Have you ever been there? E. Yes, I have been there several times. It’s a very interesting place, isn’t it? I hope you have enjoyed it greatly. F. Oh, yes, I have had a very nice time G. Did you go there alone? H. No, together with Michael, an old friend of mine. You remember him, don’t you? I. Sure. Has he graduated from college? J. No, not yet. He is in the last year. What about you? I haven’t heard from you of late. How are you getting on? K. Thank you, quite all right. Come and see me some day, will you? L. I’ll be delighted. So long. M. See you soon. Bye. Date: 2014-12-22; view: 2965
|