CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Dynamic RAMs
As we wish to maximize the number of cells in a memory, every effort must be made to implement them as simply as possible. They normally consist of just a few transistors [3.1]; in the case of static CMOS RAMs, a 6-transistor cell is normally used. In the simplest case, even the flip-flop is omitted and replaced by a MOSFET whose gate-source capacitance is used to store 1 bit as a charge.
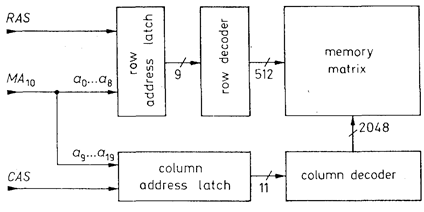
Fig. 3.34 - Address decoding in a dynamic 1 Mbit memory.
RAS: Row Address Strobe (simultaneously Chip Enable) CAS: Column Address Strobe
This makes a single-transistor cell possible. However, as the charge is only Stained for a short time, the capacitor must be recharged at regular intervals (every 2 to 8 ms approx). This operation is known as refresh, the memories are ailed dynamic RAMs. This disadvantage is offset by several advantages. Dynamic memories can provide about four times more storage capacity on the same printed-circuit ward area, with the same current drain and at the same cost. To save on pins, with dynamic memories the address is entered in two stages and buffered in the IC. The block diagram of a 1 Mbit RAM is shown in Fig. 3.34. In the first step, address bits a0 to a8 are stored in the row-address latch with the RAS signal, and simultaneously bit a9 in the column-address latch. In the second step, address bits a10 to a19 are loaded into the column-address latch with the CAS signal. This makes it possible to accommodate a 1 Mbit memory in an 18-pin package. Figure 3.35 lists commonly used IC types.
Fig. 3.35 - Examples of dynamic RAMs.
1 Other manufacturers: Fujitsu, Hitachi, NEC, Oki, Texas Instr. 2 Pseudo-static since it has an integrated refresh controller 3 Hybrid circuit (module) Date: 2015-01-12; view: 920
|