
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
SOME FACTS ABOUT CHEMISTRY
The science of chemistry deals with substances. Chemistry is the investigation and discussion of the properties of substances.
Common examples of substances are: water, sugar, salt, copper, iron and many others.
Chemists study substances in order to learn as much as they can about their properties and about the reactions that change them into other substances. This knowledge is very important as it can make the world a better place to live in, it ñan make people happier, it can raise their standard of living.
Chemists discovered many laws, investigated many important phenomena in life. They produced many artificial substances which have valuable properties.
Chemistry has two main aspects: descriptive chemistry, the discovery of chemical facts, and theoretical chemistry, the formulation of theories.
The broad field of chemistry may also be divided in other ways. An important division of chemistry is that into the branches of organic chemistry and inorganic chemistry.
Organic chemistry is the chemistry of the compounds of carbon that occur in plants and animals.
Inorganic chemistry is the chemistry of the compounds of elements other than carbon. Both of these branches of chemistry is in part descriptive and in part theoretical.
Analytical chemistry deals with the methods of separation. Synthetic chemistry deals with the methods by which complex bodies can be built from simpler substances. Physical chemistry deals with changes of state and with the motions of molecules. But at present time the scientists don’t maintain this definition.
The discovery of X-rays, an electron, and radioactivity marked a new era in all sciences and in chemistry. It was a very important discovery in science. It plays an important part in the development of geology and physiology, in technology and engineering.
Chemistry deals with medicine and agriculture as they are all concerned with the properties and changes of chemical substances.
Words to be remembered:
investigation separation
in order to motion
phenomena to be concerned with
artificial carbon compounds
division
¹3
SOME FACTS ABOUT ATOMS (I)
An atom may be spoken of as the smallest particle of any substance. If atoms cannot be seen it does not necessarily mean that they do not exist. It indicates that any particle, if present, must be extremely small. There are methods by means of which the sizes of atoms and their arrangement in molecules can be determined. One of these methods uses X-ray diffraction.
The results of a number of investigations show that when atoms are in contact with other atoms in molecules, their radius is as much as 0,1· 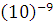 m(0,1nm).
m(0,1nm).
Some idea of how small atoms are can be obtained by imagining one million copper atoms / radius = 0,13· 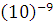 m (0,13 nm). If these copper atoms are stacked one on the top of the other, the pile will be as high as the full stop at the end of this sentence.
m (0,13 nm). If these copper atoms are stacked one on the top of the other, the pile will be as high as the full stop at the end of this sentence.
In the course of many investigations, chemists came to a conclusion that the atoms of different elements are all made essentially of three simple types of units, which were referred to as protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The following diagram shows us the constituents of the atoms. Atoms contain the following structural units:
Electrons Protons Neutrons
Charge –1, Charge +1, Zero charge,
very small relative relative mass 1 relative mass 1
mass
Notes on the text:
a full stop - òî÷êà in the course of
Words to be remembered:
particle by means of
necessary arrangement
to mean conclusion
to indicate constituent
extremely charge
¹4
SOME FACTS ABOUT ATOMS (II)
The position and numbers of these structural units in an atom is shown below:
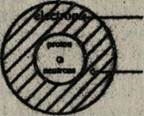 Electrons fill the space around nucleus. Number of electrons = Atomic number. Very small nucleus. Number of protons = Atomic number. Number of protons + Number of neutrons = Relative atomic mass.
Electrons fill the space around nucleus. Number of electrons = Atomic number. Very small nucleus. Number of protons = Atomic number. Number of protons + Number of neutrons = Relative atomic mass.
The numbers of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom of an element can be calculated if the atomic number and relative atomic mass of the element are known:
Number of electrons + Number of protons = Atomic number of element.
Number of protons + Number of neutrons =Relative atomic mass of element.
It was also found that many elements and compounds are composed of small numbers of atoms which are held together in a regular arrangement. These groups of atoms are referred to as molecules. The gas hydrogen, for example, is composed of pairs of hydrogen atoms and each pair is called a molecule and its formula is H2.
Another example is the compound carbon dioxide which is composed of molecules, the formula is CO2.
Words to be remembered:
space to be composed of
nucleus hydrogen
relative carbon dioxide
calculate
Note on the text:
regular arrangement
¹5
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 4252
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| CHEMISTRY | | | THE MEASUREMENTS IN CHEMISTRY |