
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
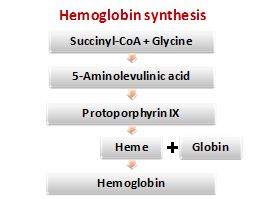
The hemoglobin biosynthesis
Synthesis of pyrrole complex in the body occurs from the low molecular weight precursors de novo. The sources of iron are food and iron which is liberated by the destruction of red blood cells.
Heme synthesis
Stage I. Formation of 5-aminolevulinate from glycine and succinyl-CoA. 5-aminolevulinate synthetase is a regulatory allosteric enzyme of tetrapyrroles synthesis. Its coenzyme is pyridoxal phosphate. Synthesis is induced by steroids and inhibited by heme (feedback inhibition).
Stage II. Synthesis of porphobilinogen. The enzyme porphobilinogen syntase is inhibited by end products of synthesis and heavy metal ions.
Stage III. Formation of tetrapyrrole complex (protoporphyrin IX) from four molecules of porphobilinogen. It is a multi-stage process.
Stage IV. Protoporphyrin IX attaches iron by the participation of ferrohelatase (hemesynthetase), and heme is formed. Ferritin is the source of iron. Vitamin B12 and copper ions are involved in heme synthesis.
The protein part of hemoglobin is synthesized in the same manner as all other proteins. The synthesis of polypeptide chains of hemoglobin occurs only in the presence of heme.
2.7. Nucleoproteins metabolism
The breakdown of the nucleic acids. Under the influence of the stomach enzymes and hydrochloric acid nucleoproteins of meal break down into polypeptides and NA. The breakdown of NA occurs in the small intestine by a hydrolytic action of pancreatic juice nucleases. They belong to the phosphodiesterase subclass. There are endonucleaseand exonuclease, ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease. The products of hydrolysis are mononucleotides and oligonucleotides. Nucleases cleave NA in the tissues too.
The breakdown of nucleoside phosphates. The first stage is splitting of phosphoric acid residue. The second stage is the transfer of the ribose residue from nucleoside to phosphoric acid. This reaction is accelerated by ribosyl transferase.
F-U-A ® F + Y-A; Y-A + F ® F-F + A
The breakdown of the purine bases begins with deamination of those bases that have amino groups. Specific amino hydrolases catalyse this process.
adenine® hypoxanthine; guanine ®xanthine
Hypoxanthine and xanthine are oxidized to uric acid by the enzyme xanthine oxidase.

The uric acid formation occurs mainly in the liver. This is the main product of the purine nucleotides catabolism in humans. It is formed 0.5-1 g per day in the body and excreted through the kidneys. Chronic increase in the concentration of uric acid (hyperuricemia) often leads to the development of gout. Gouty arthritis is associated with the deposition of sodium urate crystals in the joints. Hyperuricemia is usually hereditary desease (primary gout). Secondary gout is observed in cancers, psoriasis, and starvation.
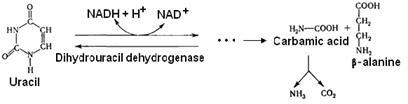
The breakdown of pyrimidine bases also begins with the deamination. Deaminated pyrimidine bases are reduced. Carbamic acid and b-alanine are the end products of U and C breakdown. b-aminobutiric acid is formed from the b-alanine.



Date: 2016-04-22; view: 1091
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| The degradation of hemoglobin in the tissues | | | Biosynthesis of purine bases A, T |