
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Storage and transport of ammonia
1. Aspartic and glutamicprovide immediate binding of NH3 when it is formed in cells. Enzymes asparagine synthetase and glutamine synthetase belong to ligases class. ATP using is necessary.

The synthesis of glutamine is particularly active in muscle, brain and liver. Some part of ammonia binds to a-ketoglutaric acid.

Ammonia is removed from the brain predominantly as glutamine. Glutamine and asparagine are excreted in the urine in small quantities. Their function is storage and transport of ammonia in a nontoxic form.Alanine also performs transport function.
Amidation of aspartic and glutamic acids can also occur in the case when they are part of the protein molecule. This provides an immediate binding of ammonia wherever it occurs as a result of metabolism.
2. Urea is the main end product of protein metabolism in many animals. Urea nitrogen is about 90% of the total output of nitrogen. Urea is synthesized in liver. This process includes several stages, which form urea cycle (ornitine, or Krebs – Henselein cycle).
1. Formation of carbamoyl phosphate from NH3, CO2 and ATP is done under the action of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Carbamoyl phosphate is the energy rich compound. It is metabolically active form of ammonia:
NH3+ CO2 + 2 ÀÒP + Í2ήH2N-ÑÎ-ÎÐÎ3Í2 + 2ÀDP + Í3ÐÎ4
In humans, two ways of carbamoyl phosphate synthesis have been discovered:
a) the reaction which is catalyzed by the enzyme ammonia dependent carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. It was opened in mitochondria of liver cells and is primarily used for the synthesis of arginine and urea;
b) the reaction which is catalyzed by glutamine dependent carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. The donor of amino group is glutamine. It was opened in the cytosol and primarily is used for the synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides.
2. The condensation of ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate. The enzyme is ornithine transcarbamoilase. Citrulline is formed. The 1st and 2nd reactions occur in mitochondria.

3. Citrulline passes into the cytosol and reacts with aspartic acid. Argininosuccinate is formed. The enzyme is argininosuccinate synthase.

4. Argininosuccinate cleaves to give arginine andfumarate. The enzyme is argininosuccinase. Fumarate provides a connecting link with Krebs cycle, gluconeogenesis and other processes.

5. Hydrolysis of arginine and urea formation. The enzyme is arginase.

One nitrogen atom in urea is from ammonia and the second is from aspartate.
The resulting ornithine is involved in the urea cycle. Fumarate is converted to aspartate:
fumarate® pyruvate ® aspartate
3 moles of ATP are consumed to 1 mole of urea synthesized.
The overall equation of urea synthesis:
CO2 + NH3 + 3 ATP + 2 H2O + Aspartate ® Urea + 2 ADP + + AMP + Fumarate + 2 Pi + PPi
All enzymes of urea cycle are present only in hepatocytes. Urea is transported in blood to kidney and excreted.
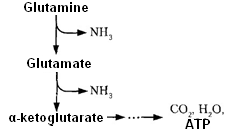 3. A certain amount of ammonia is excreted in the urine as ammonium salts. The ammonia formation occurs in glutamine. Ammonia accepts a proton to form ammonium ion. Cell membrane is impermeable for it. Ammonium ion formation and excretion by kidneys are the mechanism of proton excretion. Ammonia excretion in the urine is about 0.5 grams per day in norm. It increases with acidosis (up to 20 times). In alkalosis excretion of ammonia is absent.
3. A certain amount of ammonia is excreted in the urine as ammonium salts. The ammonia formation occurs in glutamine. Ammonia accepts a proton to form ammonium ion. Cell membrane is impermeable for it. Ammonium ion formation and excretion by kidneys are the mechanism of proton excretion. Ammonia excretion in the urine is about 0.5 grams per day in norm. It increases with acidosis (up to 20 times). In alkalosis excretion of ammonia is absent.
4. Nitrogen is also excreted in the form of creatinine, which is formed from creatine and creatine phosphate.
5. Some part of ammonia is used for amino acids biosynthesis by reductive amination of a-keto acids. This is the main way of amino acids neogenesis in the human body. This reaction is reverse to oxidative deamination of amino acids. Reductive amination of any keto acids is possible. But a-ketoglutaric acid and pyruvic acid are aminated the most actively:
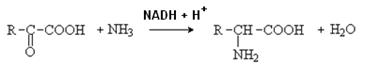
Other amino acids are formed by transamination reactions of aspartic and glutamic acids and alanine with the corresponding keto acids. Therefore, alanine, aspartic and glutamic acids are called the primary amino acids, and all others are secondary.
Date: 2016-04-22; view: 1098
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Reactions of the carboxyl group | | | Metabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine. |