CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
General Medical CouncilA relation between finite sets can be represented using a zero-one matrix. Suppose that R is a relation from In other words, the zero-one matrix representing R has a 1 as its (i, j) entry when ai is related to bj, and a 0 in this position if ai is not related to bj. Example. Suppose that A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {1, 2}. Let R be the relation from A to B containing (a, b) if Solution: Since Example. Let Solution: Since R consists of those ordered pairs
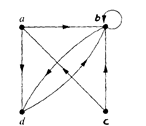
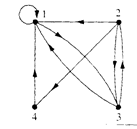
Representing relations using digraphs A directed graph, or digraph, consists of a set V of vertices (or nodes) together with a set E of ordered pairs of elements of V called edges (or arcs). The vertex a is called the initial vertex of the edge (a, b), and the vertex b is called the terminal vertex of this edge. An edge of the form (a, a) is represented using an arc from the vertex a back to itself. Such an edge is called a loop. Example. The directed graph with vertices a, b, c and d, and edges (a, b), (a, d), (b, b), (b, d), (c, a), (c, b) and (d, b) is displayed in Figure: Example. The directed graph of the relation R = {(1, 1),(1, 3), (2, 1),(2, 3),(2, 4), (3, 1), (3, 2),(4, 1)} on the set {1, 2, 3, 4} is shown in Figure: Example. What are the ordered pairs in the relation R represented by the directed graph shown in Figure below?
Solution: The ordered pair (x, y) in the relation are R = {(1, 3),(1, 4), (2, 1),(2, 2),(2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 3), (4, 1), (4, 3)}. Each of these pairs corresponds to an edge of the directed graph, with (2, 2) and (3, 3), corresponding to loops.
Glossary composite Цкомпозици€;power Цстепень;directed graph Цориентированный граф vertex Цвершина;edge Цребро;loop Ццикл
General Medical Council
The GMC registers doctors to practise medicine in the UK. Our purpose is to protect, promote and maintain the health and safety of the public by ensuring proper standards in the practice of medicine.
Doctors must be registered with a licence to practise with the General Medical Council (GMC) to practise medicine in the UK.
We are required to maintain the GP Register by law. Since 1 April 2006 all doctors working in general practice in the health service in the UK, other than doctors in training such as GP registrars, are now required to be on the GP Register. This requirement extends to locums.
The GMC regulates all stages of doctors' training and professional development in the UK. We promote high standards and ensure that medical education and training reflects the needs of patients, the service, students and trainees. Date: 2015-01-02; view: 1005
|
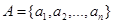 to
to 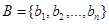 . The relation R can be represented by the matrix
. The relation R can be represented by the matrix 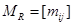 , where
, where 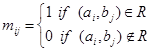 .
. and a > b. What is the matrix representing R if
and a > b. What is the matrix representing R if 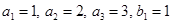 and
and  ?
?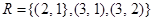 , the matrix for R is
, the matrix for R is  .
.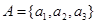 and
and  . Which ordered pairs are in the relation R represented by the matrix
. Which ordered pairs are in the relation R represented by the matrix 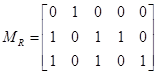 ?
? with
with  , it follows that R = {(a1, b2), (a2, b1),(a2, b3), (a2, b4), (a3, b1), (a3, b3), (a3, b5)}.
, it follows that R = {(a1, b2), (a2, b1),(a2, b3), (a2, b4), (a3, b1), (a3, b3), (a3, b5)}.